The Ultimate Guide to Building a Safe and Effective Cattle Chute for Homesteaders
Essential Tips and Strategies
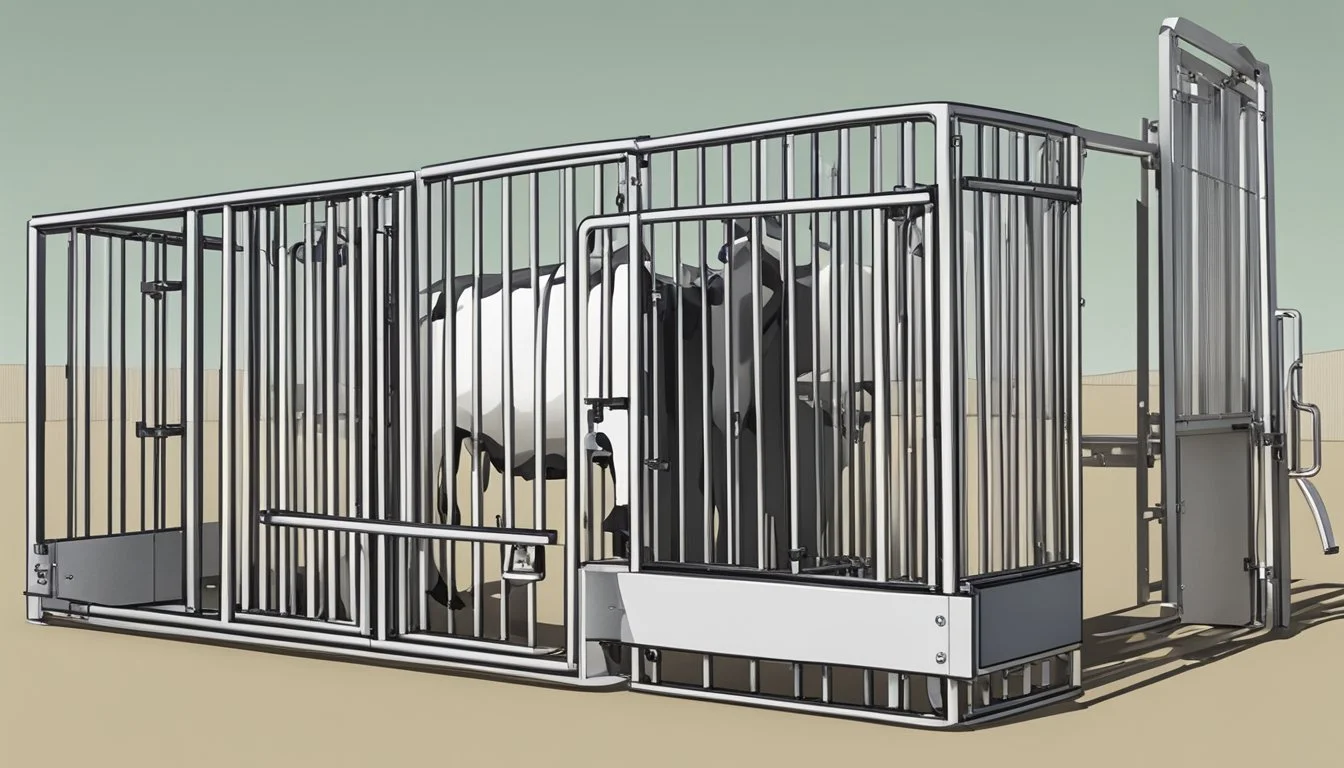
Building a cattle chute on a homestead requires meticulous planning and a thorough understanding of both the handler's and the cattle's needs. An effectively designed cattle chute contributes to the safety and efficiency of livestock management by ensuring smooth cattle handling and minimizing stress and injury to both the cattle and the handlers. It is an essential component of modern husbandry that serves multiple purposes, from routine vaccinations to more complex veterinary procedures.
A cattle chute must be built with robust materials to withstand the strength and size of cattle, and it should be designed to restrict the movement of the animal, providing a secure environment for both livestock and handlers. The chute should be adjustable to accommodate different sizes of cattle, ensuring that from the largest bull to the smallest calf, all can pass safely and comfortably. It's about creating a balance between animal welfare and the practical demands of ranch work.
Incorporating features such as non-slip flooring, smooth internal surfaces, and rounded corners can significantly reduce the risk of injury to animals. By meticulously designing the layout and dimensions of the chute to prevent cattle from turning around or escaping, and providing easy access for handlers, routine livestock tasks can be performed with greater efficiency and less stress. With animal behavior in mind, the chute should promote a natural flow, moving cattle calmly and in the desired direction.
Understanding Cattle Chutes
In the realm of modern farming, a well-constructed cattle chute is essential for the efficient handling of cattle, serving as a cornerstone of safe and productive livestock management.
Historical Context
Cattle chutes have evolved from rudimentary wooden structures to advanced systems built with durability and safety in mind. Historically, ranchers utilized cattle chutes primarily for restraining animals during branding or treatment. However, with the progression of time and the introduction of animal welfare considerations, the design emphasized reduced stress and injury to both livestock and handlers.
Different Types of Cattle Chutes
Cattle chutes come in various configurations, each designed to meet particular needs and operation scales. The two main categories are:
Manual Chutes:
Emphasize simplicity and reliance on manual force.
Often constructed from steel, providing durability.
Cost-effective but may require more labor.
Hydraulic Chutes:
Operate using hydraulic mechanisms for improved efficiency.
Offer greater control and can be less stressful for the cattle.
Typically a more significant investment but can enhance operational speed.
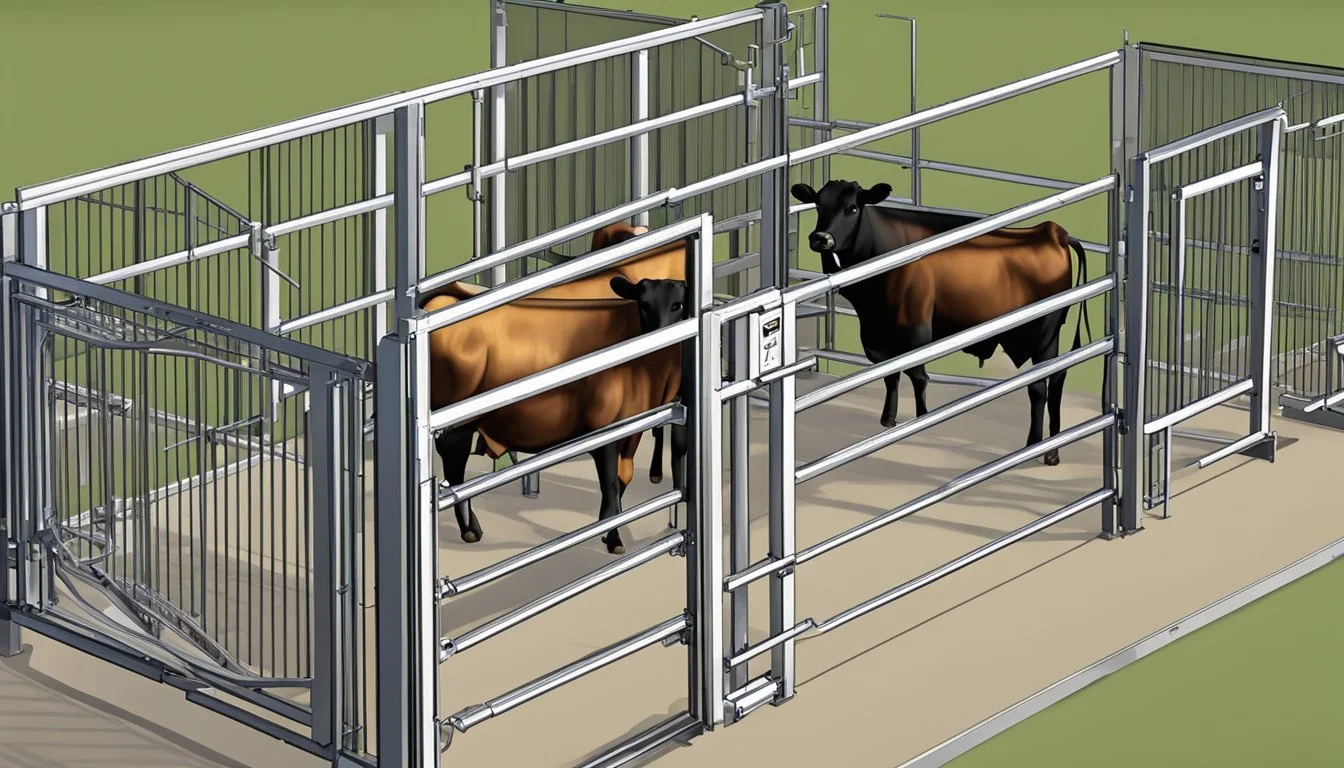
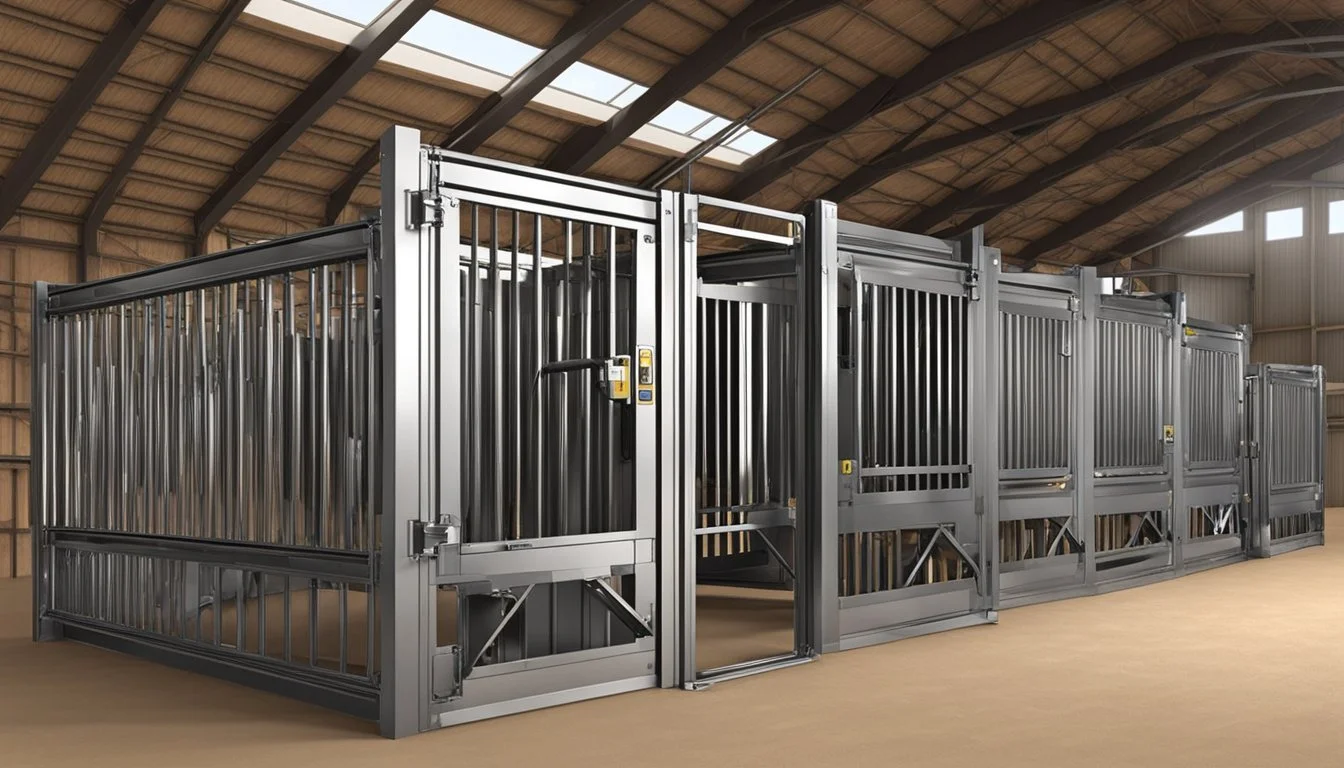
In both types, the squeeze chute design is prevalent, featuring sides that can be adjusted to securely hold the animal in place. Materials like steel ensure longevity, and the modern design promotes flexibility in handling various cattle sizes. Hydraulic chutes, though requiring energy sources such as electricity or hydraulics, present an option that reduces the physical labor and potential for strain on both the animal and handler, aligning with the necessities of contemporary ranch operations.
Design Principles for Effective Cattle Chutes
When constructing a cattle chute, the primary goals are to ensure animal welfare and operational efficiency. Smart design principles focus on these aspects, including safety features and materials that promote the longevity and reliability of the chute.
Key Components and Their Functions
Cattle Pens: Serve as the initial holding area and must allow for easy movement into the chute while minimizing stress.
Crowding Pen: It acts as a funnel, encouraging livestock to enter the working chute in a calm and orderly fashion.
Working Chute: A straight or slightly curved path that leads cattle to the squeeze chute while promoting steady, stress-free movement.
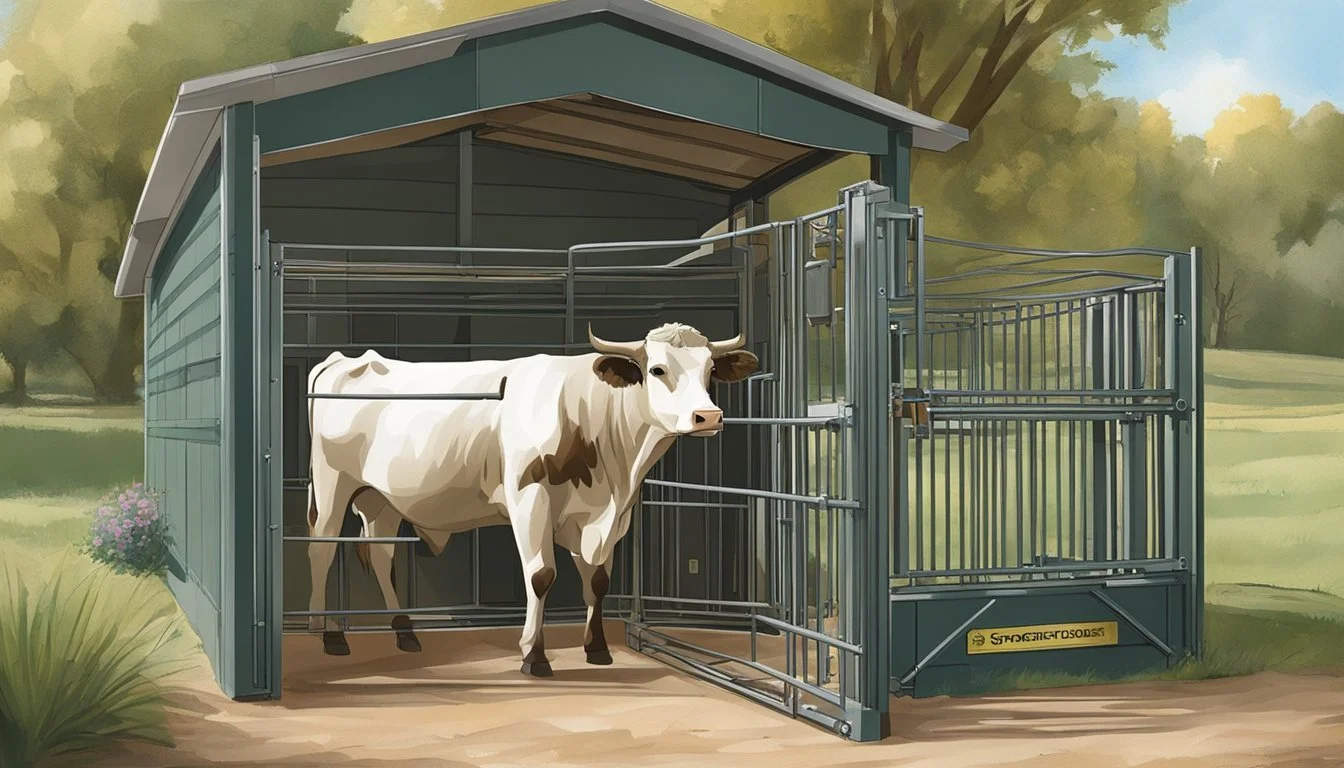
Squeeze Chute and Headgate: Secure cattle for various operations, providing restraint while ensuring the safety of both livestock and handlers.
Loading Chute: It is designed to facilitate the safe transfer of cattle to and from transport vehicles.
Each component plays a critical role in the overall effectiveness of the cattle chute system. The design must incorporate smooth edges to prevent injury and should reduce noise to a minimum to avoid startling the animals.
Material Selection for Durability and Reliability
Steel: Heavy-duty steel is the preferred material due to its durability and strength, ensuring the chute withstands the demands of frequent use.
Flooring: Should provide ample traction to prevent slips; rough-finished concrete is commonly used for its ease of cleaning and good grip properties.
The construction materials of a cattle chute must balance the need for durability with the consideration of animal welfare. Rust-resistant coatings can extend the life of metal components, while the strategic placement of padding can protect livestock from harm.
The Importance of Animal Welfare
In the context of cattle chutes, animal welfare is paramount for both ethical reasons and operational efficacy. Prioritizing the well-being of cattle through reduced stress and comprehensive safety features not only aligns with humane practices but also enhances the overall productivity and longevity of livestock.
Stress Reduction Techniques
Implementing stress reduction techniques in cattle chute design is vital. Techniques include:
Quiet operation: Noise minimization prevents startle and stress in livestock. This can be achieved through the use of rubber bumpers and silencers on metal parts.
Non-slip flooring: It provides secure footing, reducing the likelihood of panic-induced thrashing which can lead to injuries and heightened stress levels.
Safety Features That Protect Livestock
Safety features are integral to a cattle chute's design, directly influencing animal welfare. Key features include:
Head gates: These must be adjustable and smooth-operating to accommodate different sizes while preventing injury during movement.
Side panels: Panels should have the flexibility to allow for different cattle sizes and should be designed to eliminate sharp edges that could harm the animals.
Through careful consideration of these elements, homesteaders can ensure that their cattle handling practices promote animal welfare and operational success.
Sizing and Customization
In building a cattle chute, homesteaders must consider the individual needs of their operation to ensure a secure and effective handling system. The chute should be adaptable, with adjustable features to accommodate various sizes of cattle.
Adapting Chutes to Specific Needs
A cattle chute that meets specific needs is paramount for a homesteader's safety and operational efficiency. A squeeze chute, which is the core component where the cattle are held during processing, should be configurable to handle cattle of different sizes. Therefore, the homesteader must look for features such as adjustable sides. These can be moved in or out to securely hold the cattle without causing undue stress or possibility of injury.
When analyzing cattle handling equipment, homesteaders should evaluate the following:
Size Considerations
To 600 lb. cattle: Require chutes with smaller dimensions
600-1200 lb. cattle: Need chutes with medium dimensions
Over 1200 lb. cattle: Require larger chute sizes
Key Customizable Features
Entry and Exit Points: The entrance gate should open widely and smoothly to encourage cattle to enter, while the exit should allow for quick and stress-free release.
Adjustable Sides: These are critical to accommodate various cattle sizes and ensure they are appropriately restrained.
Customization for Safety
Chutes should include features that prevent slipping, such as a rough finish on the floor for traction.
Proper design can significantly reduce the risk of injury to both the livestock and the handler.
Innovations in Cattle Chute Systems
The evolution of cattle chute systems focuses on safety and efficiency. These improvements primarily address the ease of operation and adaptability, enhancing overall livestock management.
Automated Features for Enhanced Efficiency
Modern cattle chutes integrate automated features to reduce labor and streamline cattle handling. Technological advancements such as hydraulic chutes enable handlers to operate gates and squeeze mechanisms with precision, often via remote control, improving the speed and safety of the process. For instance:
Automation: The inclusion of sensors and automatic locking systems.
Hydraulic Systems: Utilized for smooth and quiet operation, minimizing stress on the cattle.
Portability and Versatility in Chute Design
The design of cattle chutes now emphasizes portability and versatility, ensuring they can be easily moved and adjusted to fit different scenarios. Materials like aluminum have been introduced to reduce weight without compromising strength.
Portability: Chutes are designed to be moved easily, often including wheels or designed for quick attachment to vehicles.
Aluminum Construction: This offers a lightweight yet durable solution, increasing the ease of repositioning the chute when necessary.
Developing a cattle chute with these innovative features increases the flexibility and efficiency of livestock management practices, catering to the dynamic needs of modern homesteaders.
Installation and Setup
The pivotal aspects of installation and setup involve meticulous site preparation and ensuring safe transport and assembly of the cattle chute. These stages lay the groundwork for durable construction and the smooth functioning of the chute.
Site Preparation and Transport
Prior to delivery, one must select an optimal location, taking into consideration the accessibility for livestock and handlers, as well as the ease of connecting to other handling facilities. The site should be level and well-drained to prevent water accumulation. For transport, ensure the route accommodates the chute’s dimensions and maintain open communication with the delivery team about site specifics to facilitate a smooth offloading process.
Site Checklist:
Accessibility for animals and handlers
Connection to handling facilities
Level and well-drained ground
Transport Considerations:
Confirm route for delivery
Communicate site details with transporters
Prepare for offloading chute components
Assembling the Chute Safely
When assembling the cattle chute, safety is paramount, both for the handlers and the animals. Manufacturers usually provide a detailed manual — adhering to these instructions is crucial. Enlist capable assistants and use the proper tools to ensure a secure assembly. Inspect all components for any damage that could have occurred during transport before assembly begins.
Assembly Instructions:
Follow manufacturer’s manual rigorously
Gather capable assistants for assembly
Use appropriate tools for construction
Inspect all pieces prior to assembly
The successful setup hinges on rigor and attention to detail, ensuring that the cattle chute will function effectively and stand the test of time.
Operation and Handling Procedures
When operating cattle chutes, it is crucial for handlers to employ proper handling techniques and understand the use of restraint and squeeze mechanisms to ensure both animal welfare and handler safety.
Proper Handling Techniques
Handlers must respect the natural behavior of cattle, moving alongside the animals calmly and without unexpected noise. Approaching from the side, they should maintain a low-energy demeanor and avoid direct eye contact to reduce the likelihood of startling the cattle. It's essential to work cattle in small groups, ideally less than ten, which allows for easier management and decreases stress on the animals. Additionally, handlers should use a single-file chute designed to minimize the chances of clogging, facilitating smooth and continuous movement. Encouraging cattle movement using non-electric driving aids is a recommended technique to maintain a steady flow without causing panic.
Use of Restraint and Squeeze Mechanisms
Restraint devices such as the squeeze chute must be utilized with care to protect the animal's welfare. The utilization of a squeeze chute involves adjusting the restraint to fit the size of the cattle, never over-tightening as it might cause injury or distress. Implementing safety features like non-slip flooring and rounded corners can help prevent injury. The squeeze mechanism should be operated smoothly to firmly but gently restrain the animal for procedures like vaccination or examination. Prompt release after the operation prevents prolonged stress. Handlers must continuously monitor the animals for signs of distress and be prepared to adjust techniques accordingly.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Maintaining a cattle chute is crucial for its longevity and the safety of both cattle and handlers. A well-kept chute ensures efficient operation and reduces the risk of injury and equipment failure.
Regular Cleaning and Inspection
Regular cleaning of a cattle chute is essential to prevent build-up of manure, mud, and debris, which can corrode metal components and create unsanitary conditions. After each use, one should remove any organic materials and rinse the chute thoroughly. At a minimum, a monthly inspection routine is advised to check for any signs of wear and tear, ensuring all moving parts, such as gates and locking mechanisms, operate smoothly.
Key Areas for Inspection Include:
Surfaces: Check for corrosion or damage.
Moving Parts: Ensure hinges and latches function properly.
Locks: Verify that they are secure and working.
Bolts and Connectors: Tighten any that have loosened.
Flooring: Look for signs of wear that could cause slipping.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Effective customer service mechanisms should be in place for homesteaders to resolve any issues swiftly. Regular maintenance often involves troubleshooting common problems such as jammed gates or unresponsive locking mechanisms.
Simple Troubleshooting Steps:
Stuck Components: Apply lubricant to hinges and latches.
Unresponsive Locks: Inspect for obstructions; clean and lubricate if necessary.
Wear and Tear: Replace any worn-out parts promptly to avoid further damage.
Through consistent cleaning, thorough inspections, and quick responses to common issues, a cattle chute can remain a reliable asset for safe and effective cattle handling.
Maximizing Efficiency and Profitability
In the context of building a cattle chute for homesteaders, maximizing efficiency and profitability involves a careful assessment of the operation's performance and a strategic approach to enhancing productivity. It is important that handlers are able to work swiftly without compromising the safety or quality of the process.
Evaluating Performance and Enhancing Productivity
Evaluating Performance: Performance must be measured to identify areas for improvement. This can involve reviewing the speed at which cattle move through the chute and the number of animals processed per hour. Handlers should note the flow of cattle and bottlenecks that may arise. This can be done by:
Timing Operations: Record the time it takes for cattle to pass through different sections of the chute.
Incident Tracking: Keep logs of any safety incidents or moments when cattle become agitated, as this can indicate design flaws.
Enhancing Productivity: Once performance has been evaluated, steps can be taken to enhance productivity. This may include refresher training for handlers to ensure they are using the most efficient methods and making necessary adjustments to the chute design for smoother operation. Consider these actions:
Optimize Workflow: Arrange handlers and equipment strategically to allow for an uninterrupted flow of operations.
Quality Assurance: Regularly inspect the chute for wear and tear, and maintain all components to ensure peak performance.
By focusing on these crucial aspects, homesteaders can ensure their cattle chute operation runs effectively, resulting in increased profitability and a sustainable business model.
Compliance and Best Practices
When constructing a cattle chute for a homesteading environment, homesteaders must adhere strictly to industry standards and strive for continuous improvement to ensure both animal welfare and operational efficacy.
Following Industry Standards
In ranching, it's crucial that cattle chutes meet the industry standards set forth by agricultural and animal welfare organizations. These standards serve as the foundation for constructing chutes that are safe for both livestock and handlers. Homesteaders should consult with veterinarians and other animal health experts to ensure that their chute design accommodates stress-free and injury-free movement of cattle. Key components of these standards may include:
Dimensions: Specific size recommendations to accommodate various breeds.
Materials: Usage of durable materials that ensure the longevity and safety of the chute.
Restraint: Features that effectively restrain the animal while providing comfort and minimizing stress.
Homesteaders should access resources from industry leaders and validate their designs against current standards to uphold animal welfare and functionality.
Advocating for Continuous Improvement
The commitment to continuous improvement is essential in developing and maintaining an effective cattle chute. Homesteaders should:
Monitor and record usage.
Regularly inspect their chute for wear and potential hazards.
Seek feedback from users, including ranch hands and veterinarians.
By integrating these practices, they can proactively identify and implement enhancements to the chute system. This might involve innovations in material use, adjustments in design to improve accessibility for veterinary care, or altering restraint methods to better align with updated animal welfare guidelines. The goal is to keep evolving with the industry and setting a higher standard for ranching operations.