3 Proven Strategies to Overcome IBS
Effective Techniques for Symptom Relief
This article is part of our series on Natural Health
Discover > Natural Health > 3 Proven Strategies to Overcome IBS
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder that affects millions of people worldwide. The symptoms can range from mild to severe abdominal symptoms, including belly pain, bloating, diarrhea, constipation and adverse events that can occur daily. While there is no known cure for IBS, various strategies have been proven to help manage and alleviate its symptoms, allowing individuals to lead more comfortable and fulfilling lives.
In this article, we will discuss three evidence-based approaches that have shown effectiveness in overcoming challenges on a daily basis posed by IBS. Irritable Bowel Syndrome symptoms can be debilitating and overwhelming, but with the right strategies in place, individuals can work toward meaningful symptom relief and improved quality of life. These strategies consist of dietary modifications, stress management techniques, and targeted medical therapies. By implementing these methods, individuals suffering from IBS may experience notable improvements in their overall quality of life and gastrointestinal health.
While the exact causes of IBS are not fully understood, there are several treatment options available to manage the symptoms associated with the condition. These include fiber supplements, gut-directed hypnotherapy, clinical trials, psychological therapies, and alternative therapy. In addition, a gluten-free diet, muscle contractions, a healthcare provider, visceral hypersensitivity, and other techniques have shown promising health benefits in managing IBS symptoms.
Understanding IBS
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder affecting around 10-15% of the population worldwide. It is a chronic condition characterized by a group of symptoms that occur simultaneously, including abdominal pain, bloating, and changes in bowel movements.
Dietary modifications, stress management techniques, and targeted medical therapies are proven approaches to help manage IBS effectively on a daily basis. Moreover, considering the impact of peppermint oil (how long does peppermint oil last?) and understanding one's medical history is integral to addressing individual needs and mitigating potential side effects.
Though IBS is not considered a life-threatening disorder, it can significantly impact an individual's quality of life. Diagnosis of IBS is primarily based on a patient's description of their symptoms, and in many cases, a definitive cause is not identified. It is important to note that IBS is not the same as Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), which is a more severe condition involving inflammation in the digestive tract.
Several factors can contribute to the development of IBS, such as genetics, gut sensitivity, and an imbalance in the gut microbiome. Additionally, psychological factors, like stress and anxiety, can exacerbate the symptoms. IBS can present differently in each individual, with some experiencing predominantly constipation (IBS-C), diarrhea (IBS-D), or a mix of both (IBS-M).
Individuals grappling with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) often contend with a myriad of challenges, including chronic pain, digestive symptoms, and fluctuations in bowel function. For those exploring potential relief strategies, it's crucial to consider the impact of peppermint oil. Studies have delved into the potential benefits of peppermint oil in alleviating IBS symptoms, specifically its impact on smooth muscles and gastrointestinal symptoms. However, it's imperative to approach these options cautiously, especially for those with severe symptoms, as certain individuals may find their symptoms worsen.
Moreover, understanding one's medical history is paramount in navigating the complex landscape of IBS management. Factors such as celiac disease and inflammatory mechanisms can significantly influence the choice of interventions. While an elimination diet may be a safe option for some, it's essential to consult with healthcare providers to ensure that the chosen approach aligns with individual health needs and mitigates potential side effects, such as dry mouth or blurred vision. By comprehensively addressing these aspects, individuals can make informed decisions in tailoring a holistic approach to managing their Irritable Bowel Syndrome symptoms.
Recognizing IBS Symptoms
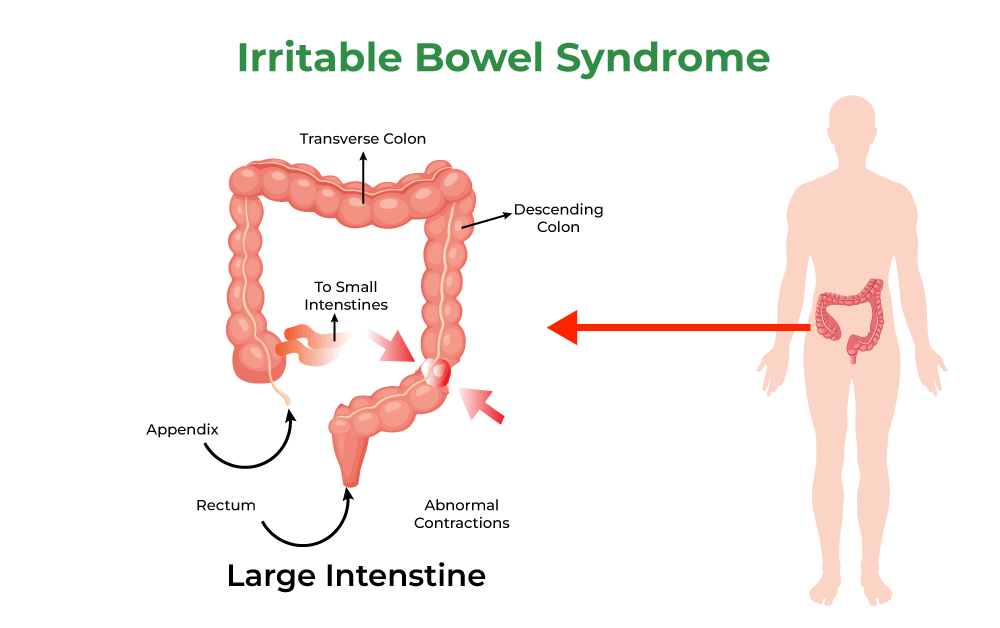
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common, chronic disorder that affects the large intestine, leading to uncomfortable symptoms. To overcome IBS, it is crucial to recognize its symptoms as they manifest differently in each individual. Some of the most common symptoms of IBS are as follows:
Gas: Excessive gas production can cause discomfort and embarrassment. It is a common symptom of IBS and can lead to bloating or painful abdominal cramps.
Bloating: Individuals with IBS often report a feeling of fullness and swelling in their abdomen. This bloating can be caused by gas or irregular bowel movements and can contribute to abdominal pain.
Abdominal Pain and Discomfort: IBS can cause persistent abdominal pain that is often described as cramping, aching, or sharp. The pain may be relieved after a bowel movement but can recur during periods of high stress or after certain meals.
Diarrhea: Individuals with IBS may experience frequent, loose bowel movements. This symptom can vary in intensity, ranging from mild to severe bouts of diarrhea. It can also alternate with periods of constipation.
Constipation: Those with IBS may find it difficult to have regular bowel movements. Constipation can lead to straining, hard stools, and feelings of incomplete evacuation.
These symptoms can vary greatly among individuals with IBS and may change over time. Although it is a challenging syndrome to manage, understanding the symptoms and being able to recognize them is the first step toward finding effective strategies for overcoming IBS.
Potential IBS Triggers
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common disorder that affects the large intestine, causing abdominal pain, bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation. IBS can be managed by identifying and avoiding triggers. Here, we discuss various IBS triggers and how to manage them effectively.
Dietary Triggers
Diet plays a significant role in managing IBS symptoms. Some common dietary triggers include:
FODMAPs: Fermentable oligo-, di-, and mono-saccharides and polyols are carbohydrates that are poorly absorbed in the small intestine. Examples include wheat, barley (how long does barley last?), beans, lactose, fructose, and certain fruits and vegetables.
High-fiber foods: Although fiber is essential for a healthy diet, some IBS sufferers may experience discomfort from fibrous foods like whole grains and nuts (how long do nuts last?).
Processed foods: Foods high in sugar, fat, and artificial additives can exacerbate IBS symptoms.
Alcohol and carbonated drinks: These beverages can cause bloating and discomfort.
To help manage symptoms, individuals with IBS can try:
Implementing a low-FODMAP diet
Choosing soluble fiber (e.g., oats (how long do oats last?), psyllium) over insoluble fiber (e.g., whole grains, nuts)
Consuming small, regular meals instead of large ones
Limiting alcohol and carbonated beverage consumption
Lifestyle Triggers
Lifestyle factors may also contribute to IBS flare-ups. Some examples are:
Stress: High stress levels exacerbate IBS symptoms. Incorporating stress management techniques, such as meditation, yoga, and exercise, may help reduce symptoms.
Sleep: Poor sleep quality can negatively impact gastrointestinal health. It's essential to establish a healthy sleep routine to manage IBS.
Lack of exercise: Exercise can help reduce stress, improve digestion, and relieve constipation.
Medical Triggers
Some medical conditions and treatments can trigger IBS symptoms:
Conditions: Hormonal changes, such as menstruation or menopause, may cause IBS flare-ups. Other gastrointestinal issues, such as gastroenteritis or bacterial overgrowth, can also contribute to IBS symptoms.
Medications: Antibiotics, certain pain relievers, and antidepressants can cause changes in bowel habits and exacerbate IBS symptoms.
It's crucial to consult with a gastroenterologist or physician for proper diagnosis and management of medical triggers.
Other Triggers
There may be other factors influencing IBS symptoms, such as mental health and environmental elements. For instance, individuals with depression or anxiety may experience more frequent or severe IBS flare-ups.
Additionally, traveling to new places or experiencing a significant change in daily routine can also trigger symptoms. It's essential to recognize potential triggers and develop coping strategies to maintain a good quality of life despite the presence of IBS.
Medical Treatments for IBS
Medication Options
Gastroenterologists often prescribe various medications to help alleviate IBS symptoms. Some common options include laxatives to relieve constipation, antispasmodic medications to reduce abdominal pain, and drugs to prevent diarrhea. For patients with IBS and accompanying anxiety or depression, doctors may also prescribe antidepressant medications such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs). It's crucial to follow your doctor's advice and discuss any side effects or concerns.
Therapeutic Treatments
Besides medications, several therapeutic approaches can be beneficial for IBS patients. Behavioral therapies, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), psychotherapy, and hypnotherapy, have shown promise in managing IBS symptoms. With the guidance of a qualified therapist, these treatments aim to identify and address triggers, modify negative thinking patterns, and build effective coping strategies for managing stress and anxiety related to IBS.
Dietary Treatments
Dietary changes play a significant role in managing IBS symptoms. A dietitian can help create a tailored diet plan taking into account individual triggers and food sensitivities. Key dietary strategies include incorporating soluble fiber, reducing insoluble fiber, and avoiding potential trigger foods such as FODMAPs (fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols). Additionally, introducing probiotics and supplements like bifidobacterium can support gut health and alleviate symptoms.
Natural Treatments
Natural treatments focus on a holistic approach to managing IBS, often incorporating lifestyle changes to support overall well-being. Regular exercise, meditation, and yoga can help reduce stress levels, improve gut function, and alleviate IBS symptoms. Drinking adequate amounts of water and maintaining a healthy sleep schedule are also important factors in managing IBS.
Living with IBS
Living with Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) can be a challenge, but incorporating key strategies into daily life can help individuals maintain a good quality of life. When managing IBS, it is essential to have a strong support system, adapt coping mechanisms, and make necessary dietary modifications to keep symptoms under control.
One of the most important factors in managing IBS is establishing a strong support system. Friends, family, or even support groups can provide an understanding environment to share experiences and advice during difficult times. A reliable network can make a significant difference in helping individuals cope with both the emotional and physical aspects of IBS.
Coping with IBS requires developing strategies to manage flare-ups and avoid triggers. Stress management is crucial, as stress can worsen symptoms and trigger IBS flare-ups. Techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, and mindfulness can help reduce stress levels and promote relaxation. In addition, maintaining a regular exercise routine and getting adequate sleep can improve overall health and reduce the frequency and intensity of IBS episodes.
Dietary modifications play a critical role in controlling IBS symptoms. Keeping a food diary can help identify trigger foods and patterns in diet-related flare-ups. Some common IBS-trigger foods include:
High-fat foods
Dairy products
Alcohol and caffeine
Spicy foods
Gas-producing foods, such as beans and cruciferous vegetables
A well-balanced diet with adequate fiber intake is essential for managing IBS. In some cases, a low-FODMAP (Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols) diet may be beneficial to reduce symptoms. It is important to work with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to develop a personalized meal plan that addresses individual needs and preferences.
Living with IBS can be a significant adjustment, but adopting a combination of support, coping strategies, and dietary modifications can help individuals manage their symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
Meal Planning for IBS
Making dietary changes is often an essential component of managing Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). Consulting with a dietitian can help to develop an individualized meal plan to address your specific needs. Here are some key considerations for meal planning for IBS:
It is crucial to incorporate a well-balanced diet containing all essential nutrients, including fiber, fruit, vegetables, and protein. Be cautious with your fiber intake, as both soluble and insoluble fibers can impact IBS symptoms differently. Gradually increase your fiber consumption, opting for sources like fruit and vegetables over beans and nuts, which can sometimes worsen symptoms.
Monitor your consumption of common IBS triggers such as lactose and fructose, found in dairy products and certain fruits, respectively. Intolerances of these sugars can exacerbate IBS symptoms, so they may need to be limited or eliminated from your diet.
Incorporating protein sources like lean meats, poultry, and fish into your meal plan can benefit your overall health and provide essential nutrients. For plant-based protein, opt for alternatives like tofu (how long does tofu last?) or tempeh (how long does tempeh last?), which may be easier to digest than beans and nuts.
Make an effort to choose whole grains over processed foods, as they provide a better source of nutrients and are less likely to trigger symptoms. When selecting bread, pasta (how long does pasta last?), or rice, opt for whole-grain versions that are free from added sugars or other triggering ingredients.
Avoiding specific triggers is vital for managing IBS; processed foods, sugar, and alcohol have all been shown to aggravate symptoms. By limiting or eliminating these from your diet, you can achieve better digestive health and alleviate IBS symptoms.
Meal planning for IBS involves focusing on balanced, whole foods while being cautious of potential trigger foods. Working with a dietitian to develop a personalized plan can provide the best results and help you maintain a healthy and comfortable lifestyle.
Your Role in Managing IBS
It is essential to understand that overcoming Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) requires a proactive approach. As an individual dealing with IBS, you play a crucial role in finding effective strategies to manage the symptoms. Addressing various lifestyle factors can significantly contribute to an improvement in your quality of life even with IBS.
Stress management is an important aspect of managing IBS, as stress can aggravate the symptoms. Incorporating relaxation techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or even taking up a hobby, can help alleviate stress and keep IBS symptoms in check.
Maintaining an active lifestyle and including exercise in your routine can also help manage IBS symptoms. Regular, low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or yoga can improve digestion and reduce stress, thereby contributing to symptom relief.
Dietary modification is often an effective strategy for managing IBS symptoms. Identifying and removing trigger foods from your diet, such as caffeine, alcohol, or fatty foods, can help prevent symptom flare-ups. Consuming fiber-rich foods, drinking plenty of water, and eating smaller, more frequent meals can also aid in digestion and provide relief.
Seeking support from others, whether it be friends, family, or support groups, can make a significant difference in how you cope with IBS. Sharing your experiences and learning from others who have similar challenges can lead to the discovery of new strategies for dealing with IBS and alleviate feelings of isolation.
Acquiring coping skills to handle the challenges IBS presents is essential for effectively managing symptoms. Developing coping strategies such as regular exercise, relaxation techniques, or engaging in enjoyable activities can greatly improve your ability to handle the physical and emotional aspects of living with IBS.
In summary, managing IBS requires a comprehensive approach that includes stress management, exercise, dietary modifications, relaxation strategies, seeking support, and acquiring coping skills. By actively engaging in these strategies, you can take control of your symptoms and improve your overall well-being.