Top Foods Rich in Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) for Heart Health
Boost Your Health with These Nutrient-Rich Choices
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a naturally occurring antioxidant found in the body's cells, responsible for energy production and cellular health. As an essential compound, maintaining adequate levels of CoQ10 through diet can support various bodily functions and overall well-being.
Incorporating foods high in CoQ10 into one's diet can help boost energy levels and promote heart health. These foods range from certain meats to vegetables and nuts, offering a variety of options to meet different dietary preferences. Understanding the sources of CoQ10 can empower individuals to make informed nutritional choices.
1) Beef Heart
Beef heart is a rich source of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). This nutrient is essential for energy production and acts as a powerful antioxidant within the body.
Beef heart contains more than 50 milligrams of CoQ10 per kilogram. Among organ meats, it ranks as one of the highest providers of this compound.
In addition to CoQ10, beef heart is packed with other nutrients. These include protein, zinc, iron, vitamin B12, and selenium.
Consuming beef heart can contribute to better heart health due to its nutrient density. The high levels of CoQ10 may assist in boosting cellular energy and protecting cells from oxidative damage.
2) Pork Liver
Pork liver stands out as a rich source of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), a compound crucial for energy production at the cellular level.
Among animal-based foods, pork liver is notable for its high CoQ10 concentration, offering more than 50 milligrams per kilogram. This makes it an excellent choice for those looking to boost their CoQ10 intake.
Apart from its CoQ10 content, pork liver is packed with essential nutrients. It provides a significant amount of protein, vitamin B12, iron, selenium, and zinc, supporting various bodily functions. Including pork liver in the diet, therefore, offers both CoQ10 benefits and a nutrient-dense meal.
3) Chicken Thighs
Chicken thighs are a notable source of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), a compound that plays a critical role in cellular energy production.
Compared to other cuts of chicken, thighs offer more CoQ10 due to their richer fat content.
This makes them an excellent choice for those looking to increase their intake of this essential nutrient through their diet.
In addition to CoQ10, chicken thighs provide a good amount of protein, which is vital for muscle repair and growth.
They also contain various vitamins and minerals, including iron and zinc, which contribute to overall health.
Cooking techniques can affect the CoQ10 content, so it is advisable to opt for methods that preserve nutrients, such as baking or grilling.
Chicken thighs are versatile and can be used in a wide array of dishes, from savory stews to light salads.
Their flavor and texture make them a popular choice in many cuisines around the world.
4) Mackerel
Mackerel is a nutrient-rich fish that is exceptionally high in Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). This oily fish is not only a great source of this important antioxidant but also provides a substantial amount of omega-3 fatty acids.
A typical serving of mackerel (about 3.5 ounces or 100 grams) contains approximately 2.6 milligrams of CoQ10. This makes it one of the best dietary sources for individuals looking to boost their CoQ10 intake through natural foods.
In addition to CoQ10, mackerel offers significant health benefits owing to its high protein content and essential nutrients such as vitamin B12, selenium, and niacin. These nutrients support overall cardiovascular health, energy production, and cognitive function.
Eating mackerel regularly can help in maintaining optimal levels of CoQ10, especially important for those whose production of this enzyme decreases with age. Incorporating mackerel into a balanced diet can be both a delicious and effective way to harness the benefits of CoQ10.
For those who enjoy seafood, including mackerel is a practical and enjoyable way to ensure they are not missing out on these valuable health benefits. It’s versatile and can be prepared in various ways such as grilling, smoking, or baking, making it an easy addition to any meal plan.
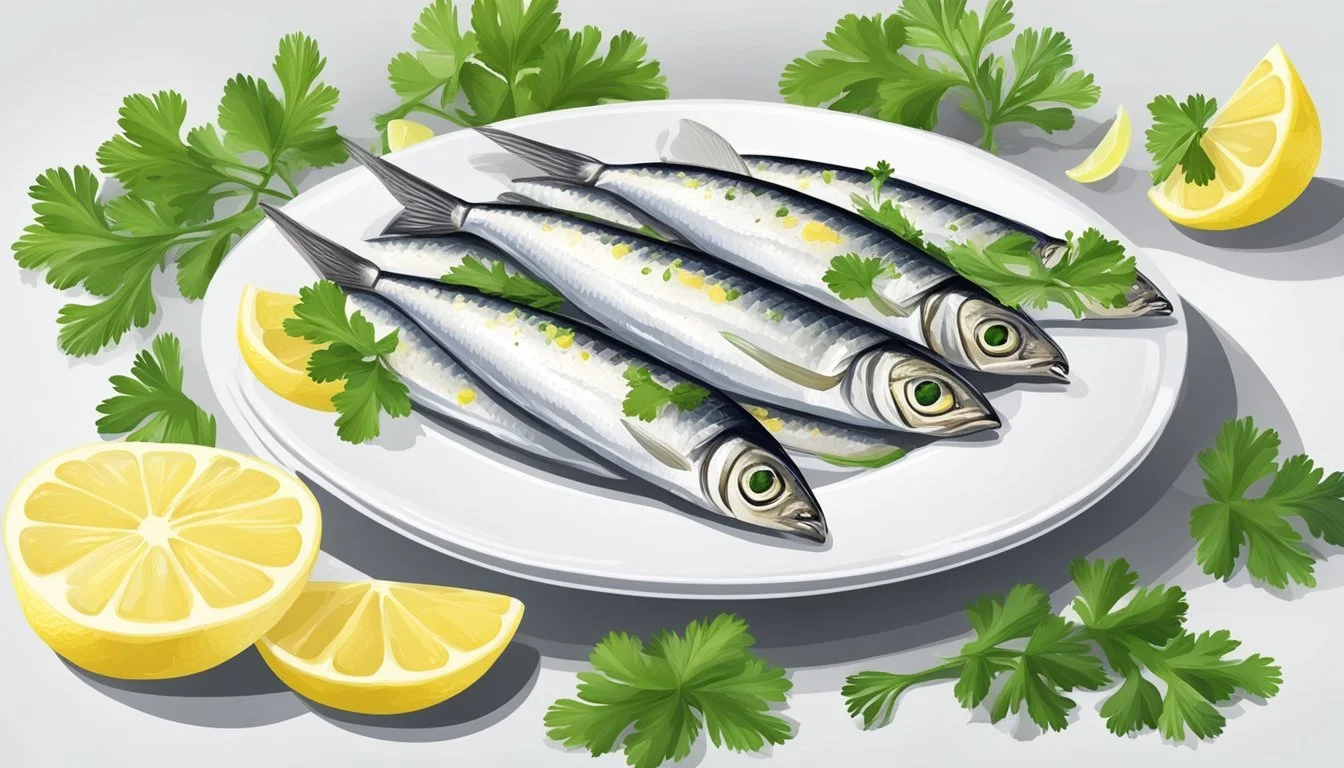
5) Sardines
Sardines are a rich source of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). Containing up to 64.3 milligrams per kilogram, these small fish rank high among natural sources of this vital antioxidant.
In addition to CoQ10, sardines provide essential omega-3 fatty acids. These fats support cardiovascular health and reduce inflammation.
Sardines are versatile and can be eaten fresh, canned, or smoked. This fish is also packed with vitamin B12, which supports nerve function and red blood cell production.
For those seeking to increase their CoQ10 intake through diet, incorporating sardines can be an effective and nutritious choice.
6) Trout
Trout is a notable source of Coenzyme Q10, commonly referred to as CoQ10. This nutrient plays a vital role in producing energy within cells and acts as an antioxidant.
In 100 grams of rainbow trout, there is approximately 0.85 milligrams of CoQ10. Including trout in your diet can contribute to your daily CoQ10 intake while also providing valuable protein and omega-3 fatty acids.
To gain significant CoQ10 benefits, you would need to consume larger quantities of trout. However, even smaller portions can integrate CoQ10 into your meals. Trout can be grilled, baked, or poached, making it a versatile addition to various dishes.
Including trout in your diet offers a healthful way to boost your CoQ10 levels alongside other essential nutrients.
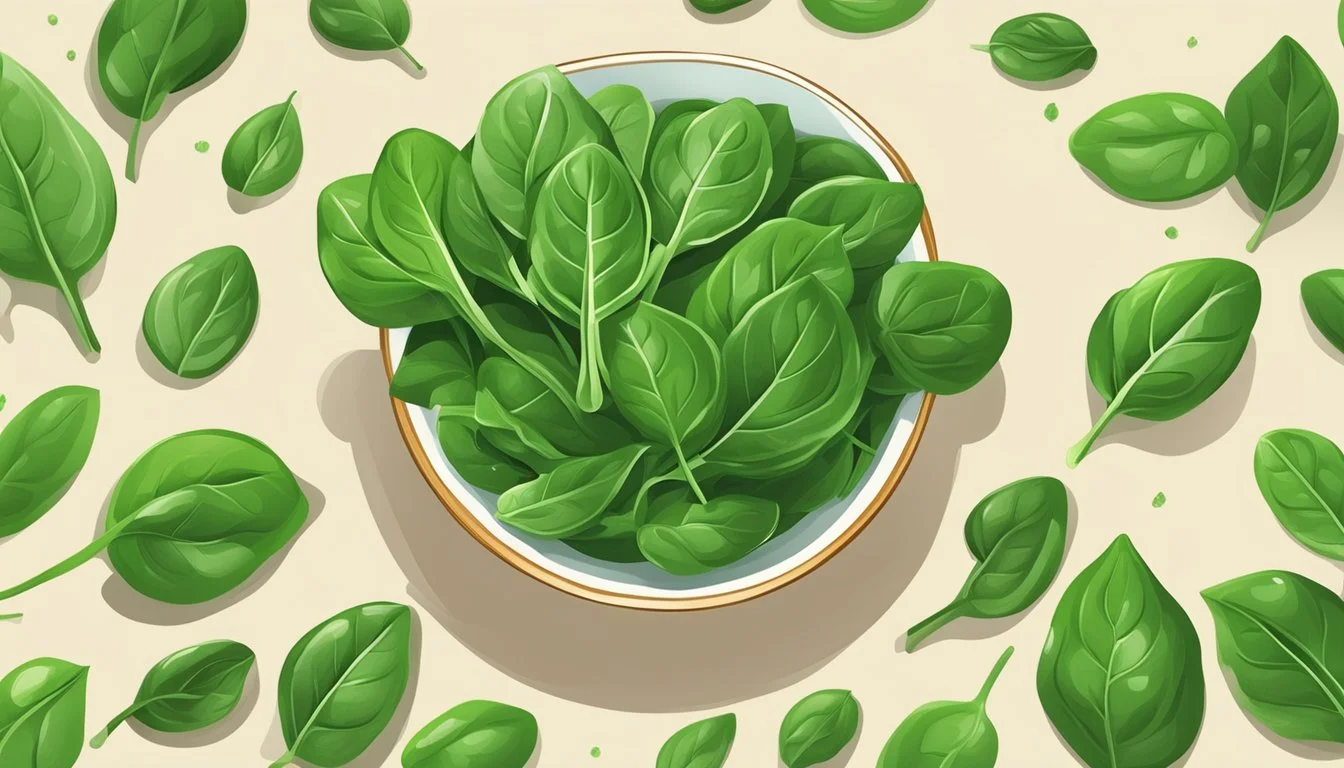
7) Spinach
Spinach stands out as one of the richest vegetable sources of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). This leafy green contains significant levels of CoQ10, making it an excellent dietary choice for those looking to boost their intake naturally.
Fresh, raw, and unprocessed spinach provides the most benefit. Cooking methods can affect CoQ10 levels, so it's best to consume spinach in salads or smoothies.
In addition to CoQ10, spinach is packed with essential nutrients like iron, vitamin K, and antioxidants. This combination makes it not only beneficial for CoQ10 but also for overall health and well-being.
Spinach's versatility in cooking allows it to be included in various meals, enhancing both nutrition and flavor. Whether in stews, soups, or as a side dish, spinach remains a top choice for increasing CoQ10 intake.
8) Broccoli
Broccoli is a nutritious vegetable that contains a modest amount of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). While not the highest source, it still contributes to daily intake. This cruciferous vegetable is highly regarded for its numerous health benefits.
Broccoli is rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. Including it in a balanced diet can support overall wellness. Among its benefits, the presence of CoQ10 helps in energy production within cells.
One can easily incorporate broccoli into meals. It can be steamed, sautéed, or added to salads and soups. Such versatility makes it a valuable addition to a diet aimed at boosting CoQ10 levels naturally.
9) Cauliflower
Cauliflower is a versatile vegetable that contains a substantial amount of CoQ10. While not as high in CoQ10 as organ meats or nuts, it still provides a notable boost. This cruciferous vegetable can be easily incorporated into various dishes, making it a practical source of this essential antioxidant.
Including cauliflower in your diet offers additional nutritional benefits. It is rich in vitamins C and K, and also provides a good amount of fiber. These nutrients contribute to overall health and well-being, making cauliflower a valuable addition to any meal.
Cauliflower is also adaptable in culinary uses. It can be eaten raw, steamed, roasted, or even riced to serve as a low-carb substitute for grains. By incorporating cauliflower into your meals, you can enjoy a tasty way to increase your CoQ10 intake.
10) Peanuts
Peanuts are a notable source of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). Roasted peanuts contain approximately 0.8 mg of CoQ10 per 1-ounce serving. This makes peanuts one of the higher CoQ10 sources among nuts.
Peanuts also provide a wealth of other nutrients. They are rich in protein, healthy fats, and essential vitamins such as niacin and folate. These nutrients contribute to overall health and well-being.
In addition to being nutritious, peanuts are versatile. They can be enjoyed on their own, added to dishes, or turned into peanut butter. This makes them an easy and delicious way to increase CoQ10 intake.
Peanuts are a convenient snack option. They have a long shelf life and are widely available, making it easy to include them in daily diets.
For those looking to boost CoQ10 levels, incorporating peanuts is a practical choice. They offer a tasty, nutrient-packed way to support the body's natural CoQ10 production.
Health Benefits of Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 offers several critical benefits, especially concerning heart health and cellular energy production.
Cardiovascular Health
Coenzyme Q10 is essential for maintaining heart health. It acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from damage. This compound helps improve blood vessel function by enhancing the dilation of blood vessels, which can reduce high blood pressure.
It also plays a role in preventing the oxidation of LDL cholesterol, a factor in the development of atherosclerosis. Some studies suggest that CoQ10 supplementation may improve symptoms in individuals with heart failure and reduce the risk of further cardiac events.
Moreover, CoQ10 has been linked to better outcomes in conditions like angina and congestive heart failure by increasing energy production within heart muscle cells.
Energy Production
Coenzyme Q10 is vital for cellular energy production. It is predominantly found in the mitochondria, the powerhouse of cells, where it assists in the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is the primary energy carrier in all living organisms, making CoQ10 crucial for energy-intensive organs like the heart and brain.
A deficiency in CoQ10 can lead to reduced energy levels and overall fatigue. Supplementing with CoQ10 has been shown to enhance exercise performance and reduce feelings of tiredness among individuals with certain medical conditions and healthy people alike.
By supporting mitochondrial function, CoQ10 helps maintain energy levels and overall cellular health, aiding in both day-to-day activities and athletic performance.
Understanding Coenzyme Q10
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is a vital compound found in every cell of the body, playing a crucial role in producing energy and protecting cells from damage. It is naturally found in certain foods and is sometimes taken as a supplement for its health benefits.
What is Coenzyme Q10?
CoQ10, also known as ubiquinol, is a fat-soluble antioxidant produced by the body. It is present in all tissues and organs, particularly in the heart, liver, kidneys, and pancreas.
The body’s ability to produce CoQ10 decreases with age, making dietary intake important. It aids in cell growth and maintenance and can be found in various foods such as meat, fish, nuts, and seeds.
How Coenzyme Q10 Works
CoQ10 is essential for the production of ATP, the primary energy carrier in cells. It assists in the mitochondrial electron transport chain, which is critical for energy generation.
Additionally, CoQ10 acts as an antioxidant, neutralizing free radicals and protecting cells from oxidative damage. This function helps support heart health and can improve conditions like heart failure and fertility issues. Its dual role in energy production and antioxidant protection makes CoQ10 significant for overall cellular health.
Dietary Considerations
Understanding the bioavailability of Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) and the role of supplements can help optimize dietary intake for health benefits. Consuming specific foods with CoQ10 and considering supplementation are important aspects.
Bioavailability of Coenzyme Q10
CoQ10’s bioavailability—or how well it is absorbed and used by the body—varies significantly among different food sources. Foods high in fats, such as organ meats, fatty fish, and oils, generally offer better absorption. This is because CoQ10 is fat-soluble, meaning it dissolves better and is more readily absorbed with dietary fats.
Cooked meats, particularly organ meats like liver and heart, show higher levels of CoQ10 due to the concentration in mitochondria of cells.
Meanwhile, the body absorbs CoQ10 from both food and supplements differently. For instance, supplements often come in oil-based capsules to enhance bioavailability. Other factors affecting absorption include the individual's health, age, and concurrent intake of other fats or foods.
Supplementing Coenzyme Q10
For individuals unable to get enough CoQ10 from their diet or those with increased requirements, such as older adults or individuals with certain chronic conditions, supplementation is an option. CoQ10 supplements usually come in two forms: ubiquinone and ubiquinol, with ubiquinol being the more absorbable form.
Supplements can vary in dosage, typically ranging from 30 mg to 200 mg per day based on the needs. Healthcare providers often recommend these supplements in divided doses throughout the day for optimal absorption.
It is essential to follow recommended dosages and consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice, especially since high doses might not be necessary or beneficial for everyone. This ensures that individuals are getting the most benefit without adverse effects.