Tidewater Off Grid Living
Sustainable Solutions for Independence
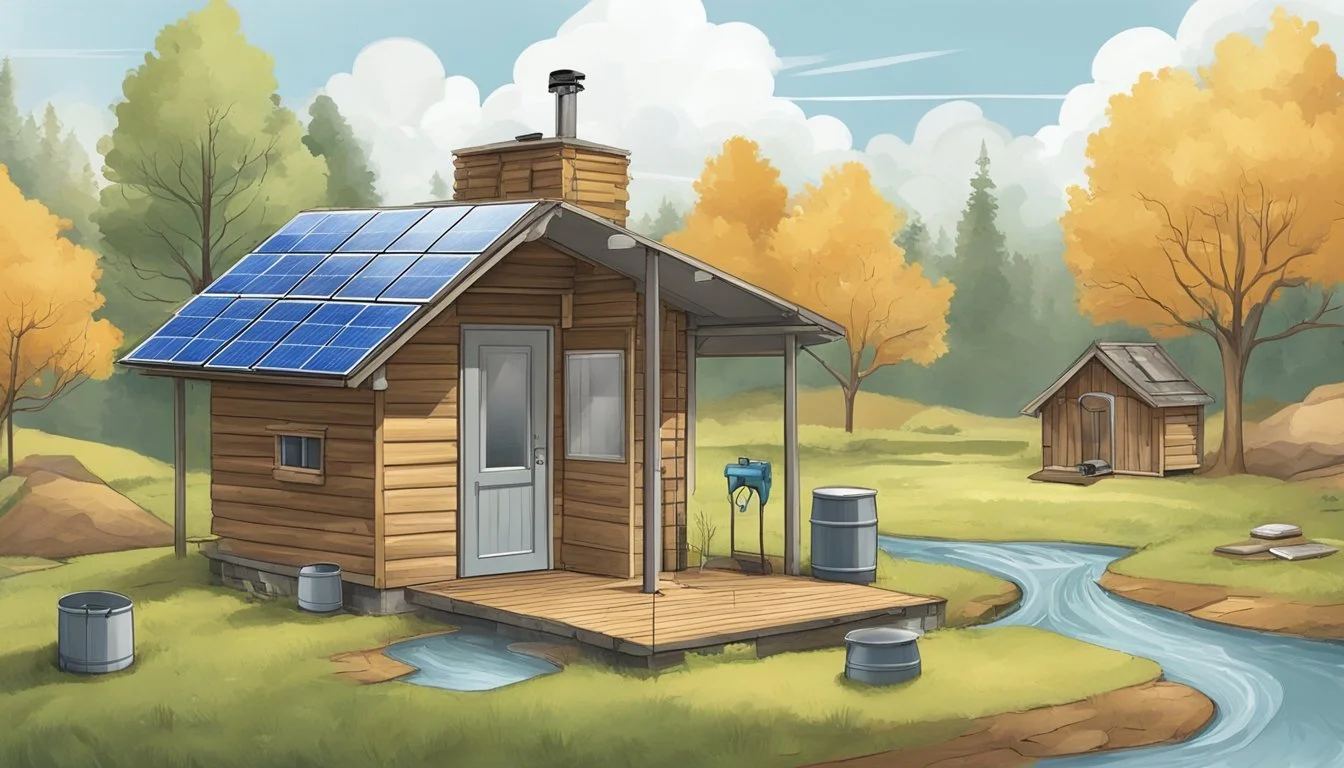
Tidewater off-grid living represents a unique blend of sustainability and self-reliance in a coastal environment. This lifestyle not only allows individuals to live independently from traditional utility systems but also to embrace a more eco-friendly way of life. The tidal waterways provide natural resources that, when combined with innovative renewable energy and water systems, create a reliable setup for off-grid households.
Ensuring a reliable water supply is crucial for any off-grid living setup, particularly in tidewater regions. Gravity-fed water systems, manual well pumps, and cisterns are some of the proven methods used to secure a sustainable water source. These systems allow for water to be stored and transported efficiently, keeping the needs of a household met even in remote locations.
The journey to self-sufficiency leads many to explore solar and wind power as primary energy sources. The consistent winds and ample sunlight found in tidewater areas make them ideal for harnessing renewable energy. With careful planning and system setup, tidewater off-grid living can offer a fulfilling, self-reliant lifestyle that aligns closely with environmental conservation goals.
Understanding Off-Grid Water Systems
Off-grid water systems focus on tapping natural water sources, implementing effective collection methods, and ensuring sustainable storage to maintain a consistent water supply.
Sources of Water
Off-grid water systems require identifying dependable water sources. Natural sources like lakes, rivers, streams, and springs are common.
For those without access to such sources, rainwater harvesting is a crucial alternative. Groundwater from an aquifer can be extracted via wells, ensuring a consistent supply. Natural springs provide another reliable option, delivering fresh water directly from the ground.
These sources must be assessed for quality and reliability to meet household needs.
Water Collection Methods
Once a water source is identified, effective collection methods must be implemented. Rainwater harvesting involves a catchment system using roofs and gutters to channel water into storage.
For groundwater, manual or electric pumps are essential to draw water from wells.
Rivers and streams can be accessed using gravity-fed systems that transport water to where it's needed.
Collection methods must ensure minimal contamination and efficient capture, even in varying weather conditions.
Water Storage Solutions
Storing collected water in appropriate containers ensures a steady supply. Cisterns and water tanks are the primary storage options, coming in different sizes and materials.
Below-ground cisterns are ideal for preventing freezing in colder climates.
Above-ground tanks are easier to access and maintain but may require insulation.
Choosing the right storage solution depends on climate, capacity needs, and space availability. Proper maintenance is crucial to keep the water safe for use.
Water Filtration and Purification
Ensuring access to clean and safe drinking water is crucial for off-grid living. Effective water filtration and purification methods are essential for removing contaminants and harmful bacteria. Key techniques include filtration systems and purification methods.
Filtration Systems
Filtration systems play a vital role in off-grid water treatment by physically removing debris, sediments, and other contaminants. Sediment filters are commonly used to remove large particles such as dirt and sand. These are essential for the first stage of water filtration.
Activated carbon filters are effective at removing organic compounds, chlorine, and some heavy metals. The carbon’s porous structure allows it to absorb impurities, improving water taste and smell. Gravity-fed filters like the Platypus GravityWorks 4L are practical for off-grid use.
Ceramic filters use small pore sizes to block bacteria and protozoa. These filters are durable and can be cleaned and reused, making them a sustainable option. Regardless of the type used, it's important to maintain and service filters regularly to ensure optimal performance.
Purification Techniques
Purification techniques go beyond physical filtration to eliminate harmful microorganisms and chemicals from water. Boiling is one of the simplest and most effective methods. Heating water to a rolling boil for at least one minute can kill most bacteria, viruses, and parasites.
Chemical disinfection involves using substances like chlorine or iodine. These chemicals can effectively kill microorganisms but might leave an aftertaste. It’s crucial to follow manufacturer guidelines to achieve the desired disinfection levels.
Solar disinfection (SODIS) uses sunlight to purify water. Plastic bottles filled with water are exposed to direct sunlight for six hours, where UV radiation and heat work together to kill pathogens. This method is inexpensive and environmentally friendly.
Removing Contaminants
Removing contaminants is essential for safe drinking water. Iron removal is often necessary in off-grid settings where groundwater may contain high iron levels. Specialized iron filters or oxidation methods can be effective.
To remove harmful bacteria and protozoa, integrating a combination of filters such as microfiltration and ultraviolet (UV) treatment can be effective. Distillation is another method that can remove a broad spectrum of contaminants by heating water to produce steam, then condensing it back into liquid, leaving impurities behind.
Overall, combining filtration, purification techniques, and consistent water testing ensures access to clean drinking water in off-grid living.
Water Pumping and Distribution
Water pumping and distribution are crucial for Tidewater off-grid living. This section explores various types of pumps, effective distribution systems, and methods of harnessing natural pressure for sustainable water management.
Pump Types and Uses
Different types of water pumps serve unique purposes in off-grid living. Manual well pumps like the Simmons No. 2 Pitcher Pump offer a reliable backup when power is unavailable. These pumps are hand-operated, requiring manual effort to draw water from wells.
Powered pumps include solar, wind, and fuel-powered options. The Shurflo 2088 and Little Giant pumps are notable choices. Solar water pumps are eco-friendly and efficient for sunny areas, while wind-powered pumps suit regions with consistent wind. Fuel-powered pumps, though reliable, may increase dependency on fuel supply.
Distribution Systems
Efficient distribution systems ensure water is delivered where needed. Plumbing networks connect the pump to various outlets, including kitchens, bathrooms, and gardens. Using pressure tanks, these systems maintain consistent water pressure, reducing pump cycling and extending pump life.
Gravity-fed systems leverage natural elevation differences to move water with minimal energy use. These systems work well in areas with varied topography, using gravity to bring water to lower-lying areas. Comprehensive planning and installation of these systems are vital for maximizing efficiency and reliability.
Harnessing Natural Pressure
Harnessing natural pressure is an efficient way to distribute water without continual pump operation. Gravity-fed systems, as previously mentioned, utilize the height difference between the water source and the usage point.
Rainwater harvesting systems often combine with gravity-fed distribution, collecting and storing rainwater in elevated tanks. From these tanks, water flows downward naturally, supplying homes and gardens. Incorporating both gravity and pressurized systems can optimize water usage and reduce the need for electronic pumps, providing a sustainable solution for off-grid living.
Power Sources for Off-Grid Water Systems
Choosing an appropriate power source is critical for off-grid water systems. Each option has its unique advantages based on availability, sustainability, and cost.
Solar Power Solutions
Solar energy is widely used for off-grid water systems due to its availability and sustainability. Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity, which can power water pumps and filtration systems.
Storage batteries are essential for maintaining power supply during cloudy days or nighttime. Solar-powered pumps are ideal for drawing water from wells or moving water to storage tanks. Solar installations may require initial investment for panels, batteries, and installation.
Periodic maintenance of solar panels to remove dust and debris ensures maximum efficiency. Solar-powered systems are particularly beneficial in areas with abundant sunlight, providing a reliable and sustainable solution for off-grid water needs.
Other Renewable Options
Wind and hydro power are other renewable options for powering off-grid water systems. Wind turbines can generate electricity in windy areas, providing a constant energy source. This is effective in regions with consistent wind patterns.
Hydropower utilizes flowing water to generate energy. A small-scale hydroelectric system can be set up if there is a reliable water source with sufficient flow. Both wind and hydro systems can power electric pumps, offering consistent water supply.
Maintaining wind turbines and hydro systems requires regular checks and maintenance. These options can be more complex to set up compared to solar but are viable alternatives depending on regional conditions.
Rainwater Collection and Utilization
For effective tidewater off-grid living, setting up a rainwater collection system and employing strategies to maximize rainwater usage are essential. These systems provide a sustainable water source, reduce dependence on external supplies, and support self-sufficiency.
Designing a Rainwater Collection System
A rainwater collection system begins with choosing a suitable catchment area. Typically, rooftops serve as effective catchment surfaces due to their large area and natural incline. Flat and pitched roofs both work, but the surface must be clean and free of debris.
Gutters and downspouts should be properly installed to direct rainwater from the roof into storage tanks. Selecting high-quality materials like aluminum or vinyl, which withstand the elements and have high capacity, ensures durability.
Storage tanks are crucial. These tanks should be placed strategically to utilize gravity for water flow and to facilitate easy access. Materials like polyethylene or concrete are commonly used for their strength and longevity.
Maximizing Rainwater Usage
To make the most of harvested rainwater, it’s important to adopt techniques that ensure its efficient use. Filtration systems should be in place to remove contaminants, enhancing water quality for domestic use. Common filtration methods include sediment filters and UV purifiers.
Rainwater usage can extend to various household applications such as flushing toilets, laundry, gardening, and even potable water if properly treated. Incorporating greywater systems allows reclaimed water to be reused, further conserving resources.
Effective distribution requires pumps and gravity-fed systems. Pumps can aid in moving water to higher elevations, while gravity systems help deliver water from tanks to usage points without additional energy costs.
By investing time in planning and installing appropriate systems, off-grid families can ensure a reliable and sustainable water supply, embracing eco-friendly and cost-effective living practices.
The Economics of Off-Grid Water Systems
Off-grid water systems can offer substantial financial benefits and independence from municipal water supplies, but they come with significant initial and ongoing costs. It's essential to evaluate both the benefits and the expenses of setup, maintenance, and regulatory compliance.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Setting up an off-grid water system involves various costs, including purchasing and installing equipment such as storage tanks, filters, and pumps. For instance, rainwater harvesting systems require storage tanks which can be installed on rooftops for efficient water collection.
Funding a private well system might entail drilling, which is expensive but can provide a reliable water source.
The initial investment can be considerable, but the long-term savings on water bills and the independence from municipal supplies can make these systems cost-effective.
When budgeting, it's crucial to consider the costs of energy sources like solar panels or wind turbines used to power the water system. These can increase the upfront costs but lead to reduced operational costs over time.
Maintenance and Upkeep
Maintaining an off-grid water system includes regular checks and servicing to ensure efficiency and safety. Common tasks include cleaning filters, inspecting tanks for leaks, and checking pump functionality.
Below-ground cisterns, popular in cold climates, need to be inspected regularly to avoid issues caused by freezing temperatures.
Tools and equipment for DIY maintenance might be necessary, but hiring professionals for complex tasks can ensure proper upkeep, adding to the overall expense.
Energy sources like solar panels and wind turbines also need maintenance, though they generally require less frequent servicing than fuel-powered systems. Despite being a recurring cost, proper maintenance is vital to extend the lifespan of the system and maintain water quality.
Regulatory Considerations
Installing an off-grid water system requires navigating local regulations and permits. This can include applying for drilling permits for wells or ensuring rainwater harvesting systems comply with local laws.
Regulations may impact the types of systems that can be used and the standards they must meet, affecting both cost and design.
Seeking professional advice to comply with these requirements can add to initial costs but is crucial for legal and operational success. Neglecting this aspect can result in penalties and the need for costly modifications.
Living Off-Grid: Practicalities and Lifestyle
Off-grid living requires careful planning and self-reliance in areas like water management, home construction, and homesteading to build a sustainable life.
Daily Living without a Municipal Water System
Living off the grid demands a reliable water source. Without a municipal water system, residents need to collect, store, and purify water themselves.
A common solution is to use natural sources such as lakes, rivers, or rainwater. For instance, installing rainwater harvesting systems on roofs can provide a substantial supply of water.
Purification methods, including UV filters, boiling, and bio-sand filters, ensure water is safe for drinking. Another essential system is greywater recycling, which treats and reuses water from sinks and showers for irrigation.
Building and Designing Off-Grid Homes
Constructing an off-grid home involves integrating systems that support self-sufficiency.
Materials like reclaimed wood or straw bales contribute to sustainable construction. Designing a cabin or home with passive solar heating can reduce energy needs significantly.
Energy independence often relies on solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage systems. Insulation and efficient design minimize energy consumption. For waste management, composting toilets are essential in reducing water use and providing compost for gardening.
Creating an Off-Grid Homestead
An off-grid homestead is more than just a home; it's a way to produce food and live sustainably.
Growing vegetables, raising livestock, and maintaining a food forest can provide year-round sustenance. Essential equipment includes tools for gardening, canning, and food preservation.
Homesteaders often use permaculture principles to create a sustainable ecosystem. Composting organic waste enriches soil quality, and polyculture practices improve resilience. The independence gained from producing one's own food fosters a sense of security and self-sufficiency.
Living off the grid can be enriching and fulfilling, but it requires commitment and proper planning to ensure a sustainable and comfortable lifestyle.
Case Studies and Examples
Exploring real-life instances and technological progress helps understand the practical applications and benefits of off-grid living.
Individuals and Communities
Melinda and Ezra Auerbach are prominent figures in off-grid living. Since the 1970s, they have continuously improved their lifestyle on Lasqueti Island, BC, Canada.
Transitioning from kerosene lamps to advanced battery systems, their home now supports modern amenities, such as dishwashers and Wi-Fi, while remaining independent from traditional utilities.
Lasqueti Island Community exemplifies a larger-scale off-grid lifestyle. This community thrives on renewable energy sources, like solar and wind power, and has developed self-sufficient water and waste management systems.
Residents collaborate, sharing resources and knowledge to maintain a sustainable and independent mode of living.
Innovations and Advancements
Battery Technology has seen significant advancements, exemplified by the Auerbachs' switch to a 390 A/h (18kWh) Discover AES Battery Bank, which provides a more efficient power storage solution than earlier lead-acid models.
Improved energy storage capabilities are critical for the reliability and sustainability of off-grid homes.
Solar Power Systems are now more efficient and affordable. Innovations include high-efficiency solar panels and sophisticated inverters that maximize energy capture and conversion.
These advancements make off-grid installations more feasible and beneficial, supporting a wide range of home energy needs.
Water Purification Technologies have also advanced, allowing off-grid communities to access clean water from natural sources. Systems like ultraviolet purifiers and advanced filtration units ensure safe and reliable water supply for off-grid homes.
These technologies collectively enhance the quality of life and reduce dependency on municipal services.
Conclusion: The Future of Tidewater Off Grid Living
The future of Tidewater off-grid living appears increasingly promising. This lifestyle is not only environmentally friendly but also sustainable. By embracing innovative technology, residents can reduce their carbon footprint.
Technological advancements in solar panels, wind turbines, and battery storage systems are making off-grid living more viable. These technologies ensure a consistent and reliable power supply. Tidewater communities are now capable of generating and storing their own energy efficiently.
Residents are also investing in sustainable water solutions. Rainwater catchment and well systems provide reliable water sources. These methods are both cost-effective and environmentally beneficial.
The Tidewater region’s unique climate and geography offer ideal conditions for off-grid living. Renewable resources like solar and wind are abundant here.
Community support and collaboration play a crucial role. Shared knowledge and resources enhance self-sufficiency among residents. New innovators and traditional perspectives come together to create robust solutions.
Housing designs in the Tidewater area cater to off-grid needs. Eco-friendly materials and efficient designs minimize environmental impact. These homes offer comfort while adhering to sustainable practices.
Economic factors are also favorable. Reducing dependence on public utilities lowers living costs over time. Initial investments in technology and infrastructure are offset by long-term savings.
The commitment to off-grid living extends beyond individual households. Local governments and organizations support these initiatives, encouraging a broader adoption of sustainable practices.
In Tidewater, off-grid living reflects a forward-thinking approach. It balances modern conveniences with environmental stewardship. This harmonious blend promises a bright and sustainable future for the Tidewater region.
As technological and environmental innovations progress, the off-grid lifestyle will likely continue to grow. This evolution makes Tidewater a model for other regions pursuing sustainability.