USDA Hardiness Zones in Nevada
A Guide to Optimizing Your Garden
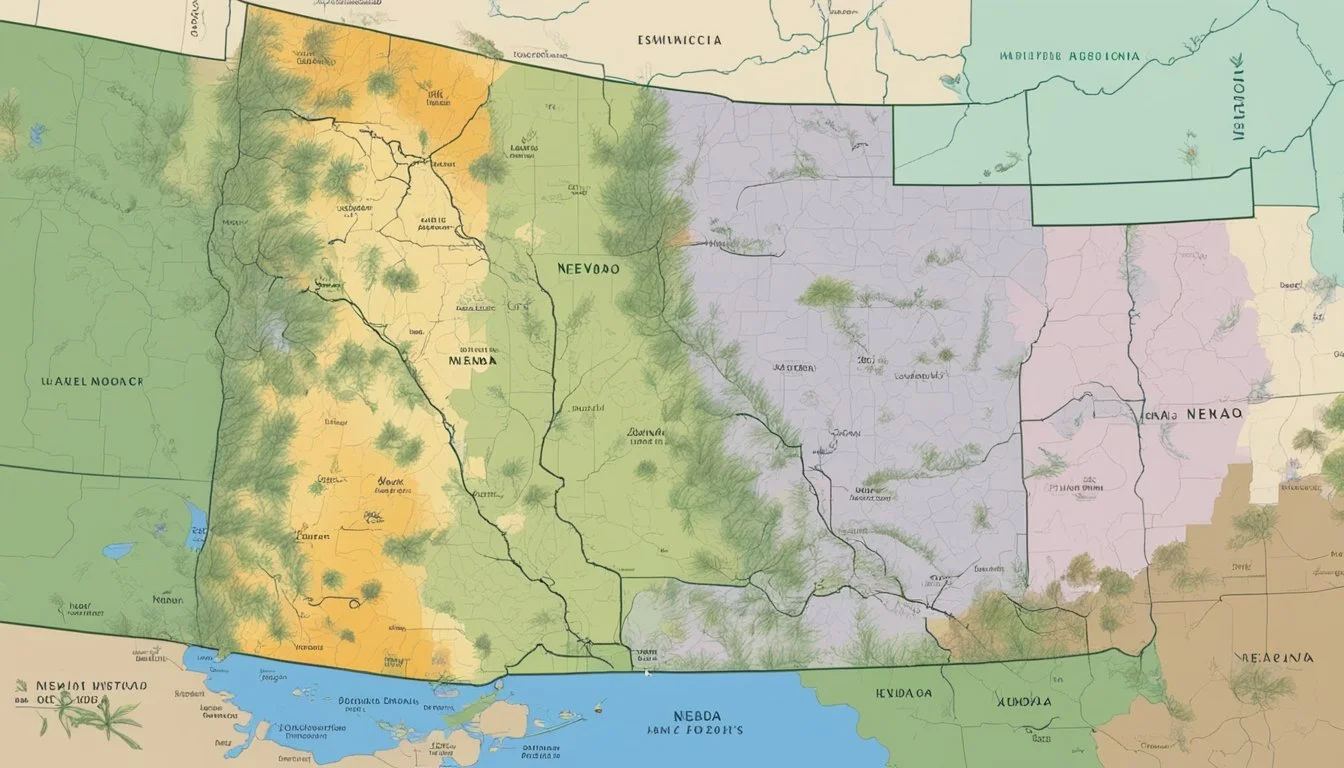
Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is crucial for gardeners and agricultural professionals in Nevada. This mapping system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), provides vital information about the suitability of specific plant species based on the regional climate, particularly the average annual extreme minimum winter temperature. Gardeners in Nevada can refer to this map to make informed decisions about which plants are likely to thrive in their local climate.
The map divides the state into zones represented by 10-degree Fahrenheit increments, further refined by 5-degree Fahrenheit half zones. These designations assist in identifying which perennial plants have the best chance of enduring the winter in a given location. Nevada's diverse topography and climatic conditions mean that it has several different planting zones, ranging from cooler mountainous regions to the warmer desert areas.
Updated periodically, the USDA zone map reflects the most recent climatological data, making it an essential resource for staying current with planting trends. The latest version, released by the USDA, takes into account a vast number of weather station data points to offer a more accurate guide for Nevada's gardeners. By understanding and utilizing the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, those who are invested in the state's horticulture can enhance the success of their planting endeavors.
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones
The USDA Hardiness Zones classify regions based on their lowest average annual temperature, crucial for successful plant cultivation.
Defining Hardiness Zones
Hardiness zones indicate the climate conditions where specific plants can grow, denoting areas based on their expected minimum winter temperatures. They guide gardeners and growers in deciding which plants may thrive in their geographic location.
The Role of USDA in Hardiness Designations
The USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) is instrumental in developing and updating the Plant Hardiness Zone Map. By providing this resource, the USDA helps cultivators understand which plants are most likely to survive and produce in their regions, based on temperature and light conditions.
Interpreting the Plant Hardiness Zone Map
When looking at the Plant Hardiness Zone Map, one should focus on the color-coded zones indicating minimum temperature ranges that plants are expected to withstand. This map is a vital tool for making informed choices about which plants are appropriate for a certain area's climate and soil conditions, thus maximizing agricultural and gardening success.
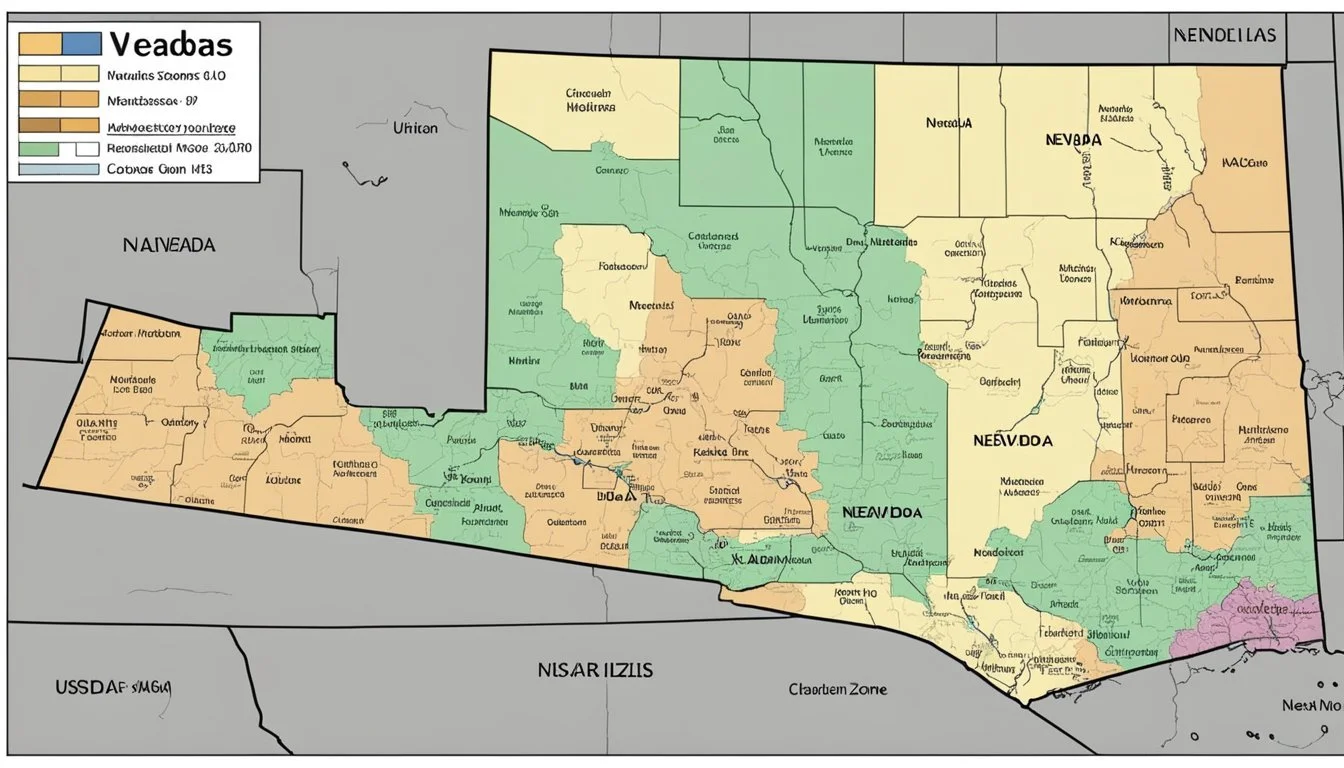
Hardiness Zones of Nevada
The USDA Hardiness Zones in Nevada range from 4a to 10a, which indicate the variety of climates suitable for plant growth across the state. This variation is largely due to the state's diverse elevations and geography.
Geographical Overview of Nevada's Zones
Nevada encompasses a wide range of USDA Hardiness Zones. Northern Nevada cities like Ely and Elko fall into zones 5a to 6b. These zones suggest that the region experiences winter lows that can reach -20°F to -5°F. Conversely, the southern portions of Nevada, specifically areas closer to Las Vegas, fall within zones 8b to 10a, where the minimum temperatures range from 15°F to 40°F.
Variations across Elevations
Elevation has a profound impact on Nevada's hardiness zones. As elevation increases, temperatures typically become cooler, impacting which plants can thrive. For instance, at higher elevations, such as the mountains around Ely, which can be over 6,500 feet above sea level, zone numbers are lower (4a to 5b). On the other hand, lower elevation areas like Elko, at approximately 5,060 feet, experience slightly warmer zones (5b to 6a).
Zone-Specific Information for Nevada Cities
The USDA Hardiness Zone Map provides essential information for gardeners and farmers in Nevada, delineating the regions where specific plants are most likely to thrive. The map takes into account the average extreme minimum winter temperatures, facilitating informed decisions about planting and growing.
Northern Nevada: Ely to Jarbidge
Ely: Positioned in USDA Hardiness Zone 6b, Ely experiences winter temperatures that can dip as low as -5°F to 0°F. Residents can cultivate plants that tolerate these colder conditions.
Commonly grown plants in Ely: includes species such as Russian Sage and certain varieties of hardy sedums and conifers.
Jarbidge: This remote northern locality is also classified within Zone 6b. Comparable to Ely, Jarbidge gardeners must select plants that can survive in the chilly winters.
Suitable plants for Jarbidge: Covering a similar selection as Ely, with the addition of aspens and cold-hardy perennials being ideal choices.
Southern Nevada: Las Vegas to Searchlight
Las Vegas: The heart of Southern Nevada falls into a warmer Hardiness Zone 9a, with minimum temperatures ranging from 20°F to 25°F. This allows for a wider variety of plants that can endure the milder winters.
Popular Las Vegas plantings: encompasses a range of palm trees, evergreen shrubs like oleander, and vibrant annuals.
Searchlight: Located in Zone 8b, Searchlight sees winter lows from 15°F to 20°F, demanding a slightly different plant palette from the warmer Las Vegas area.
Favored options for Searchlight gardens: may include native wildflowers, Joshua trees, and heat-tolerant ornamental grasses.
For detailed information on which specific plant varieties will perform best in each of these Nevada cities, consult the Nevada Interactive USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map and the latest version of the 2023 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map.
Seasonal Considerations in Nevada
Understanding Nevada's varying climate is crucial for successful gardening. This section outlines what gardeners need to consider regarding winter temperatures and how to navigate the half-zone specifications in planting strategies.
Winter Temperature Patterns
In Nevada, winter temperatures can significantly influence plant survival and growth. Regions within the state experience a range of average extreme minimum temperatures during winter. For instance, Zone 4b experiences temperatures reaching between -25°F and -20°F, while in Zone 6a, temperatures hover around -10°F to -5°F. These figures are critical for selecting appropriate plants that can withstand Nevada's cold periods.
Anticipating Half Zones
The USDA also recognizes subcategories known as half zones, which represent 5-degree F increments within the broader 10-degree zones. For gardeners, this means considering not just the primary zone but also the half zones, which offer a more detailed understanding of the microclimates within their gardens. For example, Zone 5b is characterized by winter lows between -15°F and -10°F, which can impact planting times and plant hardiness.
Nevada's half zones allow for tailored gardening strategies, ensuring plant selections are suited to the precise conditions experienced in specific areas, leading to more robust and resilient gardens.
Gardening Applications
When gardening in Nevada, understanding USDA Hardiness Zones is crucial for the selection of perennial plants and leveraging advanced tools such as weather stations and GIS data to inform gardening practices.
Selecting Perennial Plants
Gardeners look to the USDA Nevada Planting Zone Map to determine which perennial plants will thrive in their specific region. These zones are defined by the average extreme minimum winter temperature, a critical factor for perennial survival.
Zone 4b: Here, gardeners might choose plants that endure temperatures down to -25°F.
Zone 5a: Options expand slightly with plants capable of withstanding lows of -20°F.
Zone 6b: In this warmer zone, a more diverse range of perennials can be cultivated due to milder winter conditions.
Utilizing Weather Stations and GIS Data
Incorporating data from weather stations provides gardeners with real-time insights into current climate conditions. This information complements the USDA Hardiness Zones by offering a more dynamic picture of the environment.
Weather stations: They provide updates on temperature fluctuations, enabling gardeners to take preventive actions to protect their plants.
GIS Data: It plays an influential role by offering a spatial analysis of gardening conditions, allowing for accurate and efficient planning of plant placement based on microclimates within a larger zone.
By utilizing these cutting-edge resources, Nevada's gardeners can make informed decisions, enhancing the success rate of their perennial gardens.
Updating and Interpreting Hardiness Zone Data
Understanding changes and applying local insights are key to effectively using the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone data. This ensures gardeners and farmers choose the best plants for their areas.
Recent Updates to the Plant Hardiness Zone Map
The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) periodically updates the Plant Hardiness Zone Map to reflect the changing climate patterns and provide the most current information to gardeners, growers, and researchers. The most recent revision, published by the USDA's Agricultural Research Service (ARS), introduced a fine-tuned map with 10-degree Fahrenheit zones and 5-degree Fahrenheit half zones, providing a nuanced view of localized climate zones. This update leverages advanced Geographic Information System (GIS) technology for greater detail and precision in zone demarcation.
Incorporating Local Experience
While the USDA map is an invaluable tool, it does not account for all local variances such as microclimates, urban heat islands, or soil conditions. Gardeners are encouraged to integrate local experience and observations with the USDA data. They might notice that despite the zone indications, certain plants may perform better or worse than expected due to specific regional characteristics. This local knowledge helps refine plant selection and cultivates a more resilient garden or crop setup.
By considering both the detailed data from the USDA's ARS and their own experiential knowledge, individuals in Nevada can make well-informed decisions about their planting strategies.
Practical Tips for Using USDA Hardiness Zones
When gardening in Nevada, utilizing the USDA Hardiness Zone Map ensures the selection of appropriate plants. This tool helps in recognizing the most favorable areas for plant survival and growth based on temperature extremes.
Analyzing Hardiness Zones by Zip Code
Gardeners can determine the specific hardiness zone for their area in Nevada by entering their zip code into the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. This step is essential for cities like Caliente or Pahrump, where microclimates may vary greatly even within small geographic areas. By understanding the precise zone of a location, one can make informed decisions about which plants are suitable to thrive in their garden.
Evaluating Hardiness for North Nevada Regions
For regions in North Nevada, such as around Fallon, it's imperative to consider your hardiness zone when selecting perennial plants. Due to the colder climate in Northern Nevada compared to the south, plants that can withstand lower temperatures are necessary. The USDA map is segmented into 10-degree F zones and, for more detailed planning, 5-degree F half-zones, which are crucial for assessing the viability of plant species in the varied climates found throughout the state. This ensures that gardeners can choose plants that are proven to withstand the northern Nevada winter temperatures.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones is crucial for Nevada gardeners to ensure the successful growth and cultivation of plants. This section addresses common queries about planting zones within the state.
What are the various USDA Hardiness Zones found in Nevada?
Nevada showcases a diversity of climates within its borders, reflected in its USDA Hardiness Zones ranging from 4b, where the temperatures can drop to -25°F, through to zone 9a, with minimum temperatures of 20°F to 25°F.
How can I determine the specific planting zone for my zip code in Nevada?
To find the planting zone for a specific zip code in Nevada, one can use the interactive tool provided on the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map website, which offers precise data based on climatic conditions.
In which USDA Hardiness Zone does Las Vegas, Nevada fall?
Las Vegas, Nevada is situated in USDA Hardiness Zone 9a, characterized by mild winters and an average minimum temperature ranging between 20°F and 25°F.
Which USDA zone covers Reno, Nevada for gardening and planting?
Reno, Nevada is located in USDA Hardiness Zone 7a, which indicates the region experiences winter lows of 0°F to 5°F, suitable for a variety of cold-hardy plants.
Can I obtain a USDA Hardiness Zone map that is specific to Nevada?
Gardeners can access a Nevada-specific USDA Hardiness Zone map through online resources such as Plantmaps that provide detailed zone information tailored to the state.
What are the climate considerations for gardening in Henderson, Nevada's Hardiness Zone?
In Henderson, Nevada, gardeners must consider its classification as USDA Hardiness Zone 9a. This suggests a warm climate with relatively mild winters, guiding plant selection and gardening practices in the area.