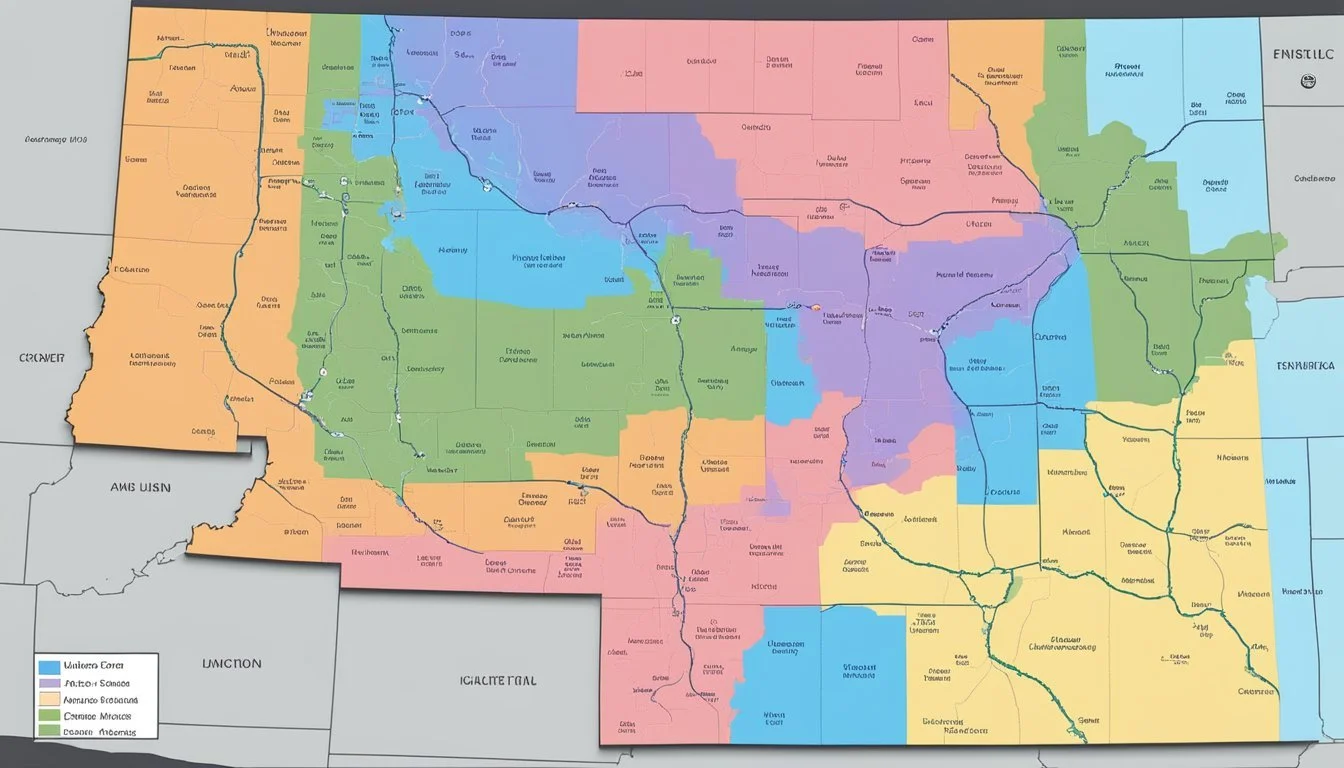
USDA Hardiness Zones in Utah
Navigating the State’s Gardening Climate
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is an essential tool for gardeners and horticulturists in Utah, providing a clear guide to the region's diverse climate conditions. It divides North America into areas based on the average annual extreme minimum temperatures. For Utah, this means a range of zones that accommodate a variety of perennial plants, each suited to the local temperature extremes. Accurate knowledge of these zones helps ensure successful gardening by aligning plant selection with the environmental tolerances of different areas within the state.
Within Utah, the hardiness zones vary significantly due to the state’s unique topography which includes mountains, valleys, and desert regions. This variety results in hardiness zones ranging from 4b, with extreme minimum temperatures as low as -25°F, to 7b, where temperatures seldom drop below 5°F. Understanding these zones enables growers to determine which plants are most likely to thrive in their specific location.
Updated periodically, the most recent hardiness zone map reflects current climate trends and offers more precise guidance than ever before. The latest version of the map for Utah, released in 2023, integrates extensive temperature data and the latest in geographic information system (GIS) technology. The Utah USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map has become a critical reference for those looking to cultivate a successful and resilient garden in Utah’s varied climates.
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is an essential tool for gardeners and horticulturists to determine the most suitable plants for their location based on climatic conditions.
The Basics of Hardiness Zones
Hardiness zones, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA), provide a standard for gardeners to compare their garden climate with the growing requirements of plants. They denote areas based on the average extreme minimum temperature recorded for that region, using a scale that breaks the country into 10-degree Fahrenheit zones.
Interpreting the USDA Zone Map
When viewing the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, one will see these zones are further subdivided into 5-degree F half zones to provide a more precise guide. A person residing in Utah can look at the map to understand which zone covers their exact location and thereby get insights into the average annual extreme minimum winter temperature they can expect.
Significance of Hardiness Zones in Gardening
Hardiness zones are invaluable for ensuring successful plant growth and yield in a garden. By selecting plants that are appropriate for their zone, gardeners increase the chances of plant survival and health. Through the USDA's zone information, it's easier to predict which plants will thrive at a specific location and which might struggle due to temperature extremes.
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, produced by the Agricultural Research Service (ARS), is a critical tool enabling gardeners and researchers to identify suitable plants based on climate data, specifically average annual extreme minimum temperatures.
Interactive Map Features
The interactive GIS-based map presents detailed views of different hardiness zones, including half zones, which reflect more precise climate demarcations. With a broadband internet connection, users can explore a highly responsive and interactive experience, allowing for efficient navigation and examination of specific areas of interest.
How to Use the Interactive Map
To utilize the interactive capabilities effectively, users can input their ZIP code in the search box provided on the website. Instantly, they will be directed to the corresponding hardiness zone, enabling them to assess the compatibility of perennial plants with their locale's climate conditions.
Benefits of GIS-Based Mapping
GIS-based mapping on the USDA's website enhances the user experience by offering real-time data visualization and in-depth analysis capabilities. Users are empowered to make informed decisions that are critical for agricultural planning and selecting the right plants for their region's specific climate zone.
Utah's Varied Climates and Zones
Utah's diverse topography results in a range of USDA Hardiness Zones, profoundly affecting local gardening strategies. The state's extreme winter temperatures and specific climate conditions require gardeners to understand their local zones for successful plant cultivation.
Zone Distribution in Utah
In Utah, the USDA Hardiness Zones span from a chilly 4a in the northern regions to a warmer 9a in the southwestern parts of the state. These zones indicate the average extreme minimum temperature a region experiences. For instance, Utah's colder climates, such as Woodruff, fall into Zone 4b with temperatures reaching -25°F to -20°F, while St. George in the southwest experiences milder winters, placing it in Zone 9a.
Northern Utah: Generally exhibits colder hardiness zones (4a to 6b).
Central Utah: A mix of mid-range zones (5b to 7a).
Southern Utah: Hosts some of the warmest zones in the state (7b to 9a).
Gardeners must pay close attention to these fahrenheit zones when selecting plants for their landscape.
Climate Impact on Gardening
The climate in Utah, notably its extreme winter temperatures, dictates the survival and success of perennial plants. Cities like Woodland Hills embrace zone 6a, where temperatures can fall between -10°F to -5°F, impacting what flora can thrive. Understanding the details of weather data for these zones is pivotal for every gardener’s planning.
Snow and Frost Dates: Higher zones tend to have a shorter growing season due to later spring frosts and earlier fall frosts.
Garden Planning: Detailed climate information supports strategic choices around plants that are robust enough for the specific extreme minimum temperature.
By considering local weather data and USDA Hardiness Zones, Utah's gardeners can enhance their landscape with plants suited to their environment's unique demands.
Gardening in Utah's Climate
Gardening in Utah demands an understanding of the local USDA Hardiness Zones and the average annual extreme minimum winter temperatures that determine the survival of plants. Gardeners and growers must carefully select perennial plants that are appropriate for their specific zone to ensure successful cultivation.
Selecting Appropriate Plants for Utah Zones
When selecting plants for a garden in Utah, one must consider the diversity of hardiness zones across the state. The Utah Interactive USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map provides a guide for gardeners to determine which perennial plants have the best chance of survival. For example, Garden City falls within Zone 5a, which sustains temperatures as low as -20°F to -15°F. The choice of plants must reflect the region's capacity for extreme cold, focusing on species known to flourish within these thermal boundaries.
Managing Microclimates
Within any given zone, Utah gardeners may encounter microclimates—small areas where the temperature or soil conditions might differ from the surrounding area. For gardeners in urban areas like Salt Lake City, where colder temperatures might be offset by the heat from buildings or pavement, it is important to consider these variations. Creating windbreaks or employing strategic plant placement can mitigate harsh conditions, providing a more hospitable microclimate that expands the variety of plants that can be cultivated. The awareness and management of such microclimates allow growers to push the boundaries of their hardiness zones effectively.
Resources and Updates
To select the right plants for landscaping and agriculture in Utah, one must consult the latest USDA hardiness zone information. These updates assist in understanding the regional climate constraints and making informed choices about plant viability.
Accessing the Latest Zone Information
The most recent USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map serves as a crucial resource for gardeners and growers. It provides details about the local climate and which plants are expected to thrive in specific areas of Utah. The map displays average annual extreme minimum winter temperatures in 10-degree Fahrenheit zones with 5-degree Fahrenheit half zones. To access this vital information, visit the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map.
Utilizing the USDA ARS Website
For those involved in national updates regarding agricultural research, the USDA Agricultural Research Service (ARS) website is an indispensable tool. It provides updated hardiness zones, reflecting the latest climatic data. This serves not only the gardening community but also bolsters agricultural research efforts crucial to the nation's food supply. Explore the most recent hardiness zone developments on the USDA ARS website, a platform managed by the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Frequently Asked Questions
The USDA plant hardiness zones in Utah range widely due to its varied topography, affecting gardening and crop selection. These FAQs address common concerns regarding hardiness zones, planting times, and suitable plants for Utah's diverse climate.
What are the most common USDA hardiness zones found in Utah?
Utah's landscape hosts a range of hardiness zones from a frosty 4a to a balmy 9a, with significant variation from the northern to the southern parts of the state.
How can I determine the USDA hardiness zone for my specific location in Utah?
To find the hardiness zone for a specific location in Utah, one can use the 2023 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, an authoritative resource for gardeners to identify the most appropriate plants for their area based on the average annual extreme minimum winter temperatures.
Which plants are suitable to grow in Utah's zone 6a?
In Utah's zone 6a, gardeners can successfully grow a variety of plants, including Russian sage, peonies, daylilies, and certain types of fruit trees like apples and cherries that are hardy to this zone's conditions.
Which cities in Utah fall under the hardiness zone 5b?
Cities like Woodruff in Utah fall under the hardiness zone 5b, characterized by minimum temperatures ranging from -25°F to -20°F.
How do seasonal variations in Utah affect plant hardiness and growing seasons?
Seasonal variations in Utah, which can include wide temperature fluctuations and different moisture levels, affect plant hardiness by determining the length of the growing season and the types of plants that can survive and thrive in a given area.
When is the ideal time to plant in Salt Lake City considering its USDA hardiness zone?
Given Salt Lake City's classification within USDA hardiness zone 7a, the ideal planting time for many plants is after the average last frost date, typically occurring in early to mid-spring.