Beet Stem Kvass
Unveiling the Health Benefits of this Probiotic Drink
Beet stem kvass is a fermented beverage that capitalizes on the natural probiotic qualities of beets and their stems, a part often discarded in culinary use. As a drink deeply rooted in Eastern European tradition, kvass is traditionally made from rye bread or beets and is revered for its potential health benefits. In the modern health-conscious landscape, beet kvass specifically has gained popularity for its probiotic properties, which are instrumental in promoting a healthy gut microbiome.
The process of creating beet kvass involves fermenting beet chunks or stems in a salty brine, which encourages the growth of beneficial bacteria. These bacteria, in turn, convert the natural sugars in the beets into lactic acid, a naturally occurring preservative that inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria. The result is a tangy, earthy beverage that provides a wealth of antioxidants and can be part of a well-rounded wellness routine.
While the origins are traditional, the process for making beet kvass is simple, making it accessible for individuals seeking to incorporate probiotic foods into their diet. The fermentation period varies depending on ambient temperature and desired tartness, but typically ranges from several days to over a week. With its deep red hue and complex flavor profile, beet kvass not only stands as a testament to the resourcefulness of traditional culinary methods but also as a contemporary staple for those seeking functional foods that offer benefits beyond basic nutrition.
History and Cultural Significance
The narrative of beet kvass is deeply rooted in the cultural practices of Eastern Europe, where it has been esteemed for both its probiotic qualities and its traditional preparation methods.
Origins of Kvass
Kvass originated in Russia over a thousand years ago and is considered a staple among traditional Eastern European beverages. Initially, kvass was made from stale rye bread, with its name derived from the Russian word for "leaven". The making of kvass was a resourceful way to utilize bread that would otherwise go to waste, fermenting it into a lightly carbonated and nourishing drink. As a humble yet vital part of the region's diet, it was enjoyed by people from all social strata, underscoring its cultural significance.
Beet Kvass in Different Cultures
While the traditional bread-based kvass is well-known, beet kvass spotlights Ukraine as a prominent culture in its modification and adoption. Ukrainian cuisine embraced beet kvass, a vibrant, lacto-fermented beverage incorporating the substantial nutritional profile of beets. Distinct from the bread-based original, beet kvass is appreciated for its digestive benefits and is often consumed together with meals to aid digestion. Its prevalence in Ukraine has imbued it with cultural importance as a symbol of home fermentation and the utilization of local produce.
Benefits of Beet Kvass
Beet kvass boasts a range of health benefits, specifically targeting gut health and digestion, liver detoxification, cardiovascular system, and immune support. The beverage is particularly valued for its high probiotic content and associated health properties.
Gut Health and Digestion
Beet kvass is a probiotic beverage, meaning it contains live microorganisms that can benefit the gut microbiota. This fermented drink not only promotes regularity but also alkalizes the blood, which can lead to improved digestion and gut health.
Probiotic Content: Helps to maintain a healthy balance of gut flora.
Digestive Health: May aid in digestion and promote intestinal health due to its anti-inflammatory properties.
Detoxification and Liver Health
The beverage has traditionally been used to cleanse the liver and has anti-inflammatory properties. Containing betalains, an antioxidant compound, beet kvass supports the liver's ability to process toxins.
Liver Function: The betalains in beet kvass can help stimulate liver function and detoxification.
Anti-Inflammatory: It is thought to reduce the inflammation that can lead to liver disease.
Cardiovascular Benefits
Beet kvass is believed to benefit the cardiovascular system. Its content of naturally occurring nitrates may help to dilate blood vessels, ultimately lowering blood pressure and improving blood flow.
Dilation of Blood Vessels: May lower blood pressure and improve circulation.
Cardiovascular Health: Regular consumption might be beneficial for maintaining cardiovascular health.
Immune System Support
Thanks to the probiotics in beet kvass, it can bolster the immune system. A strong immune system is key in fighting off pathogens and maintaining overall health.
Probiotic Support: Enhances the immune system through improved gut health.
Health Benefits: May reduce the frequency of sickness and promotes overall health.
By regularly incorporating beet kvass into one's diet, individuals may experience these diverse and beneficial health impacts.
Nutritional Profile of Beet Kvass
Beet kvass stands out as a fermented beverage rich in probiotics and nutrients with a specific composition that varies slightly with each batch due to the natural fermentation process.
Vitamins and Minerals
Beet kvass contains a range of vitamins and minerals critical for maintaining good health. Its nutrient profile includes B vitamins, particularly folate, which is essential for DNA synthesis and repair. Additionally, it provides vitamin C, which supports the immune system and acts as an antioxidant.
Vitamin C: Antioxidant properties, supports immune function
Folate: Vital for DNA synthesis, important for pregnant women
B Vitamins: Aid in energy metabolism within the body
The drink is also a source of several important minerals:
Iron: Essential for transporting oxygen in the blood
Calcium: Important for bone health
Magnesium: Involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body
Potassium: Helps to regulate fluid balance and blood pressure
Manganese: Supports bone health and promotes proper enzyme functioning
Caloric and Macronutrient Content
Beet kvass is typically low in calories, making it a suitable addition to the diet for those monitoring their caloric intake. Each serving contains a modest amount of macronutrients, with carbohydrates being the most prevalent due to the natural sugars in beets.
Calories: Low-calorie profile per serving
Protein: Generally low
Fat: Minimal to none
Fiber: Approximately 2 grams per 6-ounce serving; supports digestion
Carbohydrates: Around 6 grams per 6-ounce serving; includes sugars and contributes to the drink's energy content
It is the fermentation process that transforms the raw beets into kvass which fortifies the beverage not only with nutrients but also with probiotics that promote a healthy digestive system.
The Science of Fermentation
Fermentation is a transformative process where bacteria convert carbohydrates into alcohols or acids, which acts as a natural preservative and can enhance the nutritional value of food.
Lacto-Fermentation Process
In lacto-fermentation, Lactobacillus bacteria convert sugars present in the beet stems into lactic acid. Sea salt or a saltwater brine is added to create an anaerobic environment where these beneficial bacteria thrive while inhibitory to harmful bacteria. The whey, sometimes used as a starter culture, accelerates the fermentation, introducing additional beneficial bacteria and enzymes.
The steps are as follows:
Preparing beet stems and placing them in a jar.
Adding a saltwater brine or whey to submerge the beet stems.
Ensuring that the jar allows gases to escape, while keeping out contaminants.
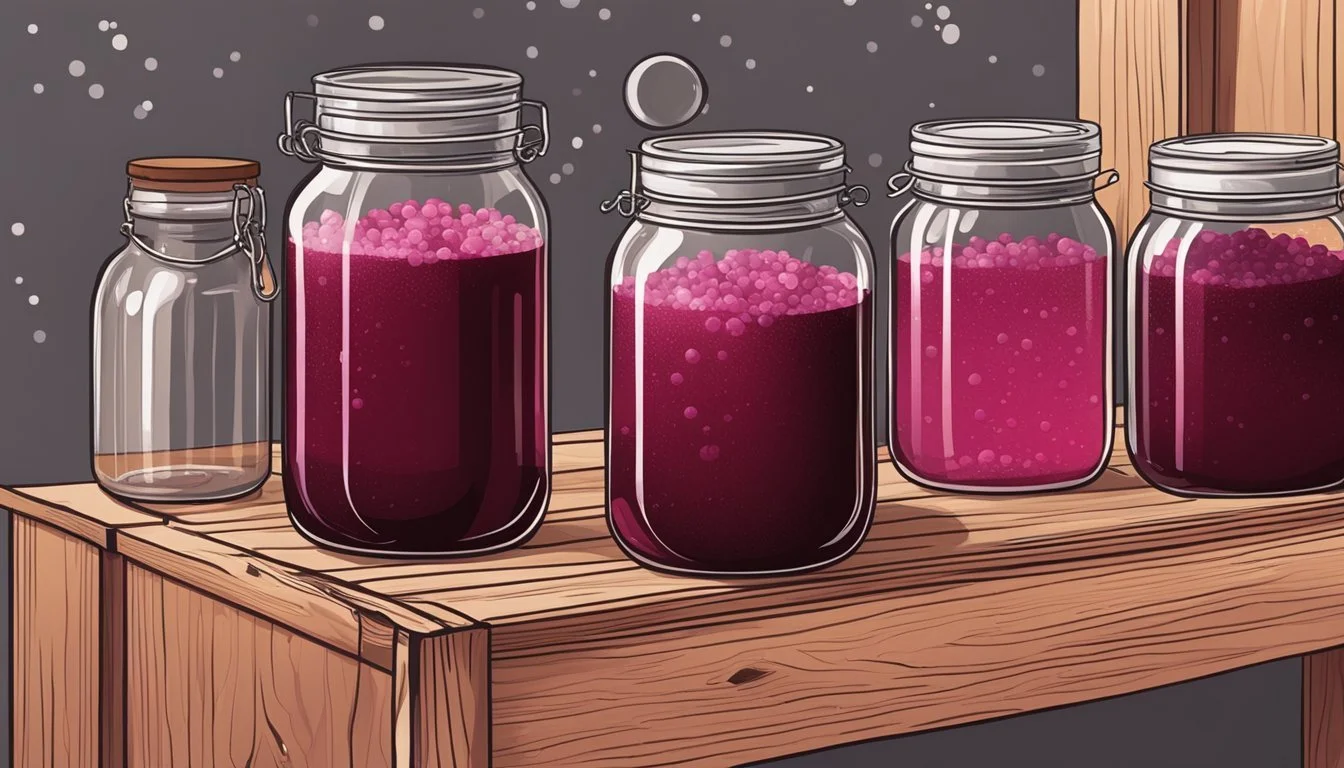
The jar is then left at room temperature, generally for a period of 2-7 days, during which the lacto-fermentation takes place.
Role of Probiotic Bacteria
The lactic acid produced during the fermentation process not only preserves the beet stems but also promotes the growth of probiotic bacteria. These bacteria are beneficial to the microbiome—the community of microorganisms living in the human gut—which is crucial for digestive health. The probiotic bacteria involved in lacto-fermented products like Beet Stem Kvass may aid in digestion, boost the immune system, and help synthesize essential vitamins.
Fermented beverages are important for their enzymes and probiotics, which contribute to gut health. Beet Stem Kvass showcases the live cultures that can enrich the consumers' gut flora, supporting the overall health of the microbiome.
Preparing and Making Beet Kvass
Beet Kvass is a traditional fermented drink known for its probiotic benefits. This section outlines the essential ingredients and equipment required, follows with a detailed recipe for making beet kvass, and concludes with valuable tips to ensure successful fermentation.
Ingredients and Equipment
Beet kvass requires simple, natural ingredients and basic kitchen equipment. Below is a comprehensive list to prepare this probiotic beverage:
Ingredients:
Beets: 2-3 medium-sized organic beets
Water: 4 cups of filtered or boiled water
Salt: 1 tablespoon, preferably sea salt without additives
Optional flavorings: Spices like ginger, or herbs (amounts can vary based on taste preferences)
Equipment:
Jar: 1-quart mason jar with a tight-fitting lid
Starter culture: Only if desired for an existing batch of kvass or whey (1/4 cup)
Knife and chopping board: For preparing beets
Measuring spoons: For salt and optional flavorings
Step-by-Step Beet Kvass Recipe
1. Prepare the Beets:
Wash the beets thoroughly.
Peel, if preferred, and cut the beets into 1/2-inch cubes. Do not grate to avoid rapid fermentation and alcohol production.
2. Assemble in Jar:
Place the beet cubes into the mason jar, filling it halfway.
Add optional flavorings like ginger or herbs at this stage.
3. Create Brine:
Dissolve the sea salt in the filtered water.
If using a starter culture, blend it with the water now.
4. Combine and Ferment:
Pour the salty water or brine over the beets ensuring they are completely submerged while leaving at least 1-inch of headspace.
Seal the jar with the lid, or cover with an airlock if available.
5. Ferment:
Allow the mixture to ferment at room temperature for 4-7 days, depending on the desired level of tartness and the room temperature.
6. Storage:
After fermentation, strain out the beet cubes.
Store the kvass in the refrigerator in a clean bottle or jar.
Tips for Successful Fermentation
Temperature Control: Keep the fermenting kvass at a consistent room temperature, away from direct sunlight.
Brine Check: Ensure beets are fully submerged in the brine to prevent mold growth; add more brine if necessary.
Taste Test: Taste the kvass after a few days to determine if the fermentation level is to your liking.
By carefully gathering and preparing the right ingredients, following the methodical steps of the recipe, and keeping in mind the key tips, anyone can create a flavorful and health-supportive beet kvass.
Serving and Storage
Proper serving and storage are crucial to maintaining the quality and health benefits of Beet Stem Kvass. This fermented drink is not only easy to make but also versatile, complementing various dishes with its unique flavor profile.
How to Serve Beet Kvass
Beet Kvass can be enjoyed in various ways due to its distinct salty-sweet taste and probiotic nature. Traditionally, it is served chilled, straight from the refrigerator to savor its refreshing qualities. For a culinary twist, one might incorporate it into salads or use it as a base for salad dressings, adding a nutty depth of flavor.
Straight: Pour chilled Beet Kvass into a glass and enjoy.
In Salads: Drizzle over fresh greens for a tangy zest.
As Dressing: Blend with olive oil, garlic, and herbs to create a probiotic-rich salad dressing.
Storage Best Practices
To preserve Beet Kvass effectively, storage conditions must be carefully managed. After fermentation, Beet Kvass should be transferred to the refrigerator to slow down any further fermentation processes. It is important to leave at least 1-inch of headspace in the container to prevent pressure build-up. The concoction typically remains potent and palatable for several weeks when stored properly.
Transfer: After fermentation, decant the Beet Kvass into clean jars.
Headspace: Ensure there is enough room at the top of the container.
Refrigerator: Store the jars in the refrigerator to sustain freshness.
Duration: Enjoy your Beet Kvass within a few weeks for best taste.
Variations and Flavorings
As a versatile beverage, Beet Kvass can be customized with a variety of flavorings and additions that enhance its naturally earthy, tangy profile. By integrating spices, herbs, and other condiments, one can tailor the drink to personal taste or use it creatively in culinary applications.
Common Additions and Substitutes
While the traditional recipe includes beets, water, and salt, many choose to include additional flavorings such as:
Garlic: Adds a robust depth of flavor.
Herbs: Dill, mint, or basil can introduce refreshing notes.
Spices: Mustard seeds or peppercorns offer warmth and complexity.
Sugar: Sometimes a small amount of sugar can balance the flavors, although the beets’ natural sugars are often sufficient.
Substitutes for some ingredients are sometimes necessary:
Instead of table salt, one might use sea salt or Himalayan salt for their mineral content.
For those seeking a beverage similar to kombucha or yogurt in terms of probiotics, beet kvass acts as an earthly alternative.
Creative Uses in Cooking
Incorporating beet kvass into dishes adds a probiotic boost along with its signature flavor. Here are some ways to use it:
Salad Dressing: Mix with olive oil and vinegar for a tangy dressing.
Soups: Use as a base for borscht or add into soups for a subtle acidity.
By exploring these variations, beet kvass can be more than a beverage—it becomes a multifaceted component that complements a range of dishes with its unique flavor and health benefits.
Health Considerations
When considering the health aspects of Beet Stem Kvass, it is essential to acknowledge the contents and their implications on one's dietary needs, specifically regarding salt, sugar, and potential allergens or interactions with medications.
Managing Salt and Sugar Intake
Beet Stem Kvass includes salt in its fermentation process, and while salt acts as a preservative and flavor enhancer, it is crucial for individuals to monitor their intake. Excessive salt consumption can lead to increased blood pressure and a risk of cardiovascular diseases. Kvass typically contains lower levels of sugar than other fermented beverages owing to the metabolic actions of beneficial bacteria, but it is still present. Consuming kvass in moderation helps manage sugar levels, aiding in maintaining a balanced diet especially for individuals with diabetes.
Nutrient Consideration Salt High intake may elevate blood pressure, monitor consumption Sugar Presence due to fermentation, consume in moderation
Potential Allergies and Interactions
Those with specific allergies should check the ingredients of Beet Stem Kvass to ensure there are no allergens. Kvass may interact with certain medications due to its nitrate content derived from beets which can affect the body's ability to process certain drugs. While nitrates occur naturally in several vegetables and may support anti-inflammatory processes, they should be consumed with caution if one has a medical condition that limits nitrate intake. Beet Stem Kvass, as a fermented product, also has anti-inflammatory properties and may reduce stress and inflammation, but its probiotic nature could potentially interact with one’s health conditions or medications, and a healthcare provider should be consulted.
Sustainability and Sourcing
When brewing beet stem kvass, a probiotic-rich beverage, the provenance and environmental considerations of the ingredients play a central role. Let's take a closer look at why selecting organic and local beets is crucial, along with the broader environmental implications of fermenting foods.
Choosing Organic and Local Beets
Organic beets are a cornerstone for making beet stem kvass. They ensure that the beverage is free from synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, which aligns with the health-conscious nature of probiotic foods. Sourcing beets from local farmers not only supports community agriculture, but it also reduces the carbon footprint associated with long-distance transportation. When possible, shoppers should opt for beets from their local farmers market, ensuring they are getting the freshest possible produce, often harvested with less environmental impact than their mass-produced counterparts.
Benefits of using organic beets include:
No synthetic chemicals
Often richer in beneficial nutrients
Advantages of local sourcing:
Supports local economies
Reduces transportation emissions
Environmental Impact of Fermented Foods
Fermented foods like beet stem kvass offer a more sustainable approach to food consumption. The fermentation process itself is low-energy, requiring no heat or electricity, and it can transform ingredients like vegetable trimmings, that might otherwise go to waste, into a valuable product. Kvass, traditionally made from stale bread or overripe fruits, symbolizes a sustainable model of utilizing all food resources efficiently. This is particularly relevant when using parts of vegetables that are typically discarded, such as beet stems.
Fermentation's environmental benefits:
Low energy requirements
Can upcycle would-be food waste
By prioritizing organic produce and mindful sourcing practices, the production of beet stem kvass can become a shining example of sustainable food culture.
Comparison to Other Fermented Beverages
Beet kvass, a Slavic traditional fermented drink, stands out for its unique preparation and health benefits. This comparison explores how beet kvass differs from kombucha, yogurt and kefir, and sauerkraut juice in several key aspects.
Beet Kvass vs Kombucha
Beet kvass and kombucha are both fermented drinks but they originate from different cultures and are made with different base ingredients. Kombucha is a fermented tea often infused with fruit or herbs, relying on a symbiotic culture of bacteria and yeast (SCOBY) for its fermentation process. It's known for its slightly acidic and carbonated profile. Beet kvass, on the other hand, is made from fermented beetroot and has a salty and earthy flavor profile. The fermentation process of beet kvass just requires salt and water and it often includes lactic acid bacteria. While both are probiotic-rich, kombucha typically contains a wider variety of bacterial strains due to the SCOBY.
Beet Kvass vs Yogurt and Kefir
Yogurt and kefir are both dairy-based fermented foods that are rich in probiotics, which aid in digestion and support gut health. Yogurt is made by fermenting milk with specific bacterial cultures, usually Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus. Its texture is creamy, and it comes in a variety of flavors. Kefir, similar to yogurt, utilizes a kefir grain containing a larger array of bacteria and yeast, resulting in a tangier and thinner product.
In contrast, beet kvass is a non-dairy beverage, suitable for vegan diets, and offers a source of probiotics mainly through lactic acid bacteria. While kefir and yogurt are often consumed for their calcium and protein content, beet kvass provides different nutritional benefits such as betalains, compounds that contribute to its deep red color and are known for their antioxidant properties.
Beet Kvass vs Sauerkraut Juice
Sauerkraut juice is the liquid that comes from the fermentation of cabbage to make sauerkraut. It shares a similar tangy flavor and probiotic profiles as beet kvass, as both are lacto-fermented. However, sauerkraut juice may contain different bacterial strains depending on the cabbage and the specific conditions of fermentation.
Beet kvass typically has a more intense and earthier flavor compared to the vegetal and sharp taste of sauerkraut juice. Additionally, while both beverages support digestive health, beet kvass also supplies the body with the unique benefits derived from the phytonutrients in beets, which are not found in cabbage-based sauerkraut juice.
The Future of Beet Kvass
Beet kvass is poised for growth in the fermented beverage market, influenced by both new trends and scientific findings related to its health properties.
Emerging Trends in Fermented Beverages
The market has seen a surge in interest for fermented beverages, and beet kvass is no exception. As consumers increasingly seek gut-friendly probiotics, beet kvass is gaining popularity for its rich probiotic content. Additionally, the rise of home fermentation kits and DIY culture contributes to its accessibility and experimentation with flavors. Artisanal and boutique production of beet kvass are becoming more common, emphasizing local, organic ingredients and sustainable practices.
Consumer Preferences: There is a shift toward natural and wellness-centric drinks.
Innovation in Flavors: Producers are incorporating a variety of flavors into beet kvass to appeal to a broader audience.
Sustainability: Eco-friendly packaging and sourcing of beets from local farmers are gaining traction.
Scientific Research and Health Discoveries
Recent studies underline the potential benefits of beet kvass for digestive health and nutrient absorption. Research points to its role in promoting a healthy gut microbiome due to its fermentation process. Scientists are also exploring the antioxidant properties of beet kvass derived from its beet base, which can aid in reducing oxidative stress.
Gut Health: Investigations reveal beet kvass's probiotic nature supports intestinal health.
Nutritional Value: Beet kvass is a source of bioavailable nutrients, making it a subject of interest for nutritional science.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, readers will find clear answers to common inquiries and can distinguish between the truths and misconceptions surrounding Beet Stem Kvass.
Addressing Common Curiosities
What exactly is Beet Stem Kvass?
Beet Stem Kvass is a fermented beverage created from the stems of beets. It's rich in probiotics and known for its potential health benefits, including aiding digestion.
Can Beet Stem Kvass improve heart health?
Yes, Beet Stem Kvass may contribute to heart health. It contains nitrates that the body converts into nitric oxide, which can help dilate blood vessels and lower blood pressure.
Does Beet Stem Kvass act as a blood tonic?
Beet Stem Kvass is often referred to as a blood tonic due to its potential to improve iron levels and cleanse the blood, although one should consult with healthcare professionals regarding its efficacy.
Myths vs Facts
Myth: Beet Stem Kvass contains high levels of carbohydrates.
Fact: Beet Stem Kvass is a low-calorie drink, and the fermentation process reduces the carbohydrate content, making it suitable for those monitoring their carbohydrate intake.
Myth: Drinking Beet Stem Kvass can cure cancer.
Fact: While it is rich in antioxidants that combat free radicals and may reduce the risk of some diseases, there is no scientific evidence to support the claim that Beet Stem Kvass can cure cancer.
By understanding these key points, individuals can better appreciate the healthful qualities of Beet Stem Kvass and enjoy it as part of a balanced diet.
Conclusion
Beet kvass stands out as a fermented drink enriched with probiotics, known for its potential health benefits. This traditional Eastern European beverage offers a tangy, earthy flavor and can be an excellent addition to one's diet for its digestive health attributes.
Probiotic-Rich: The fermentation process of beet kvass naturally generates a broad spectrum of beneficial bacteria, which can contribute to a balanced gut microbiome.
Nutritionally Dense: Beet kvass is not only rich in probiotics but also a source of essential nutrients, including electrolytes like potassium. The presence of these elements supports hydration and overall well-being.
Preparation Simplicity: Crafting beet kvass requires minimal ingredients and is a straightforward process:
Beets: Chopped into cubes, not grated, to avoid excessive sugar release and potential alcohol fermentation
Water: Ideally filtered, covering the beets in a clean jar
Salt: Unrefined for mineral content, aiding in the fermentation process without the use of whey
Customizable Flavors: One may introduce additional flavors such as ginger, lemon or spices, which not only complements the taste but can potentially offer more healing properties.
In essence, incorporating beet kvass into daily routines may be worthwhile for those seeking natural ways to support their health. Regular consumption is believed to aid in digestion, promote liver detoxification, and may enhance immune function. Beet kvass exemplifies a functional beverage with a historical context, relevant today for its probiotic content and revered in wellness circles for its associated healing qualities.