Front Range Off Grid Living
Embracing Sustainable Independence
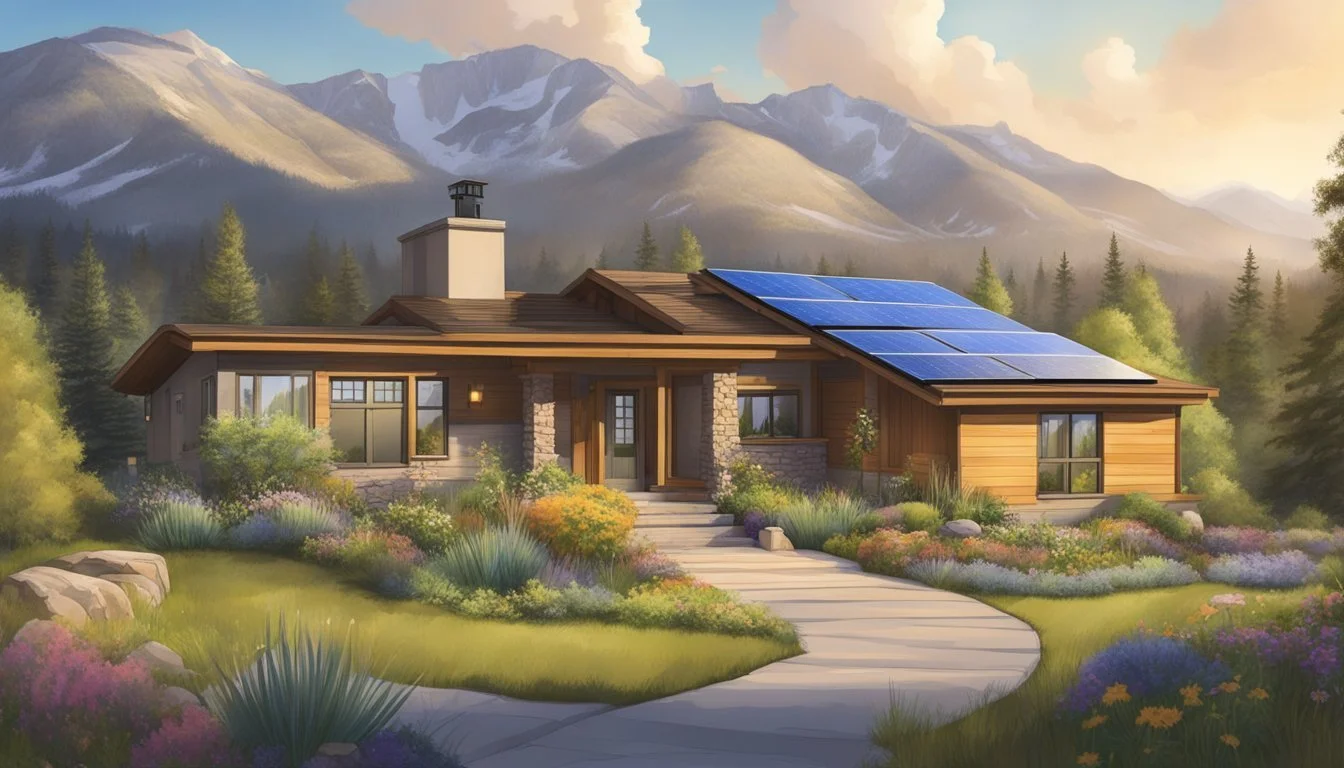
Front Range Off Grid Living offers a unique and sustainable lifestyle for those looking to reduce their reliance on traditional utilities. Nestled in the scenic settings, this mode of living emphasizes self-sufficiency and environmental responsibility. Opting for propane gas ranges can significantly enhance the off-grid experience due to their energy efficiency and dependable performance, even without electricity.
Living off the grid in the Front Range area means harnessing natural resources such as solar power for energy needs and implementing waste management systems to convert waste into useful byproducts like fertilizer and biogas. These strategies not only support a sustainable lifestyle but also ensure that daily needs are met without compromising on comfort and functionality.
Adopting an off-grid lifestyle in the Front Range entails careful planning and a willingness to adapt to new methods of living. From selecting the right location to choosing the appropriate appliances, every decision plays a critical role in ensuring a successful transition to independence. This guide will provide practical advice and insights to help you embark on your off-grid journey with confidence.
Understanding Off-Grid Living
Off-grid living involves a lifestyle choice that embraces self-sufficiency, sustainability, and independence by relying on alternative resources for daily needs. This includes utilizing sources like solar power, rainwater collection, and composting toilets to reduce one's carbon footprint and connect more deeply with nature.
Defining Off-Grid Living
Off-grid living is a method of residing that eliminates reliance on public utilities such as electricity, water, gas, and sewage. Instead, individuals use alternative measures to manage these essential services. For example, solar panels for electricity, rain barrels for water, and composting toilets for waste management.
This lifestyle often requires a substantial initial investment but promises long-term benefits like reduced utility costs and minimized environmental impact. The goal is to live in a way that is both self-sufficient and sustainable, providing a healthier and more independent way of life.
Benefits and Challenges
Benefits include a notable reduction in the carbon footprint and overall environmental impact. Off-grid living promotes energy efficiency and sustainability, encouraging a deeper connection with nature.
Living off-grid can bring financial freedom by eliminating recurrent utility bills, fostering a self-sufficient and independent lifestyle. People often experience improved mental and physical health by living closer to nature away from urban stress.
Challenges mainly revolve around the initial investment required for infrastructure like solar panels or water systems. Another significant aspect is isolation, as off-grid homes are typically located in remote areas. The risk includes potential unforeseen emergencies where modern conveniences and services are not readily accessible.
Evaluating Off-Grid Readiness
Before transitioning to off-grid living, evaluating readiness is crucial. Consideration should be given to financial investment, technical skills, and adaptability to a life involving less convenience. For many, it’s essential to conduct thorough research and possibly undergo training in renewable energy, sustainable agriculture, or other relevant areas.
A readiness evaluation might involve assessing your current lifestyle and determining how to adapt it to off-grid principles. This includes evaluating land for suitable resources like consistent sunlight for solar energy or a reliable water source. Understanding potential risks and planning for them can mitigate some of the common challenges associated with this way of life.
Critical Considerations for Off-Grid Living
To successfully transition to an off-grid lifestyle, you must consider crucial factors such as location, legal regulations, resource assessment, and financial planning. Each element plays a significant role in ensuring a sustainable and hassle-free experience.
Choosing the Right Location
Selecting the right location is foundational for off-grid living. Consider accessibility, ensuring the property is reachable year-round. Climate influences energy requirements and food production capabilities. Land fertility is critical for gardening and farming. Proximity to a supportive community can offer social connections and shared resources, enhancing self-sufficiency. Evaluate the property critically for its natural resources like water sources, woods for fuel, and sunlight for solar energy.
Understanding Zoning Laws and Building Codes
Zoning laws and building codes can significantly affect off-grid living plans. These regulations vary widely by region and dictate what structures can be built, where they can be placed, and their intended uses. Confirm whether the selected land is zoned for residential use and if off-grid technologies like composting toilets and solar panels comply with local codes. Engage with local authorities to ensure full compliance and avoid potential legal issues.
Assessing Natural and Local Resources
Resource availability is a crucial consideration. Investigate the water sources on the property, including wells, rivers, or rainwater collection. Evaluate the solar exposure for potential solar energy generation and wind flows for wind turbines. Local wildlife and plant life could also impact gardening efforts and food security. Forested areas can supply wood for building and heating. Adequate resources ensure a more self-sufficient and sustainable lifestyle.
Financial Planning and Living Expenses
Even though off-grid living can reduce certain expenses, it requires significant initial investments. Costs for land acquisition, building materials, and renewable energy systems can be high initially. Plan for ongoing maintenance costs for systems like solar batteries and water filters. Create a comprehensive budget that includes emergency funds. Evaluate potential living expenses such as food, transportation, and any money needed for unexpected repairs or upgrades to your systems. Sustainable financial planning is essential for long-term off-grid living success.
Setting Up Your Off-Grid Property
Creating a successful off-grid property involves careful planning and implementing systems for sustainable living. Key areas include home design, land development, water and waste management, and food production.
Designing Your Off-Grid Home
Choosing the right structure for your off-grid home is essential. Options include tiny homes, RVs, and yurts. Each has unique benefits:
Tiny Homes: Efficient in space and energy use.
RVs: Provide mobility and built-in utilities.
Yurts: Offer durability and simplicity.
Prioritize insulation and passive solar design to minimize energy needs. Solar panels and wind turbines can be integrated for power.
Land Preparation and Development
Select land with access to natural resources like water and sunlight. Clear and level the land for construction.
Fencing is crucial for security and keeping animals out. Develop pathways and designated areas for different activities such as gardening, housing, and livestock.
Water and Waste Management Solutions
Effective water management is vital. Use rain barrels and wells for water collection. Install filtration systems for clean drinking water.
For waste management, consider composting toilets and septic systems. These options are sustainable and reduce environmental impact.
Food Production and Storage
Grow your own food to ensure sustainability. Plan for vegetable gardens, fruit trees, and livestock like chickens or goats.
Use greenhouses to extend the growing season and protect plants from extreme weather. Implement preservation methods such as canning, drying, and freezing for long-term storage.
Create a root cellar or use an RV's built-in storage to keep produce fresh. These strategies ensure a steady food supply throughout the year.
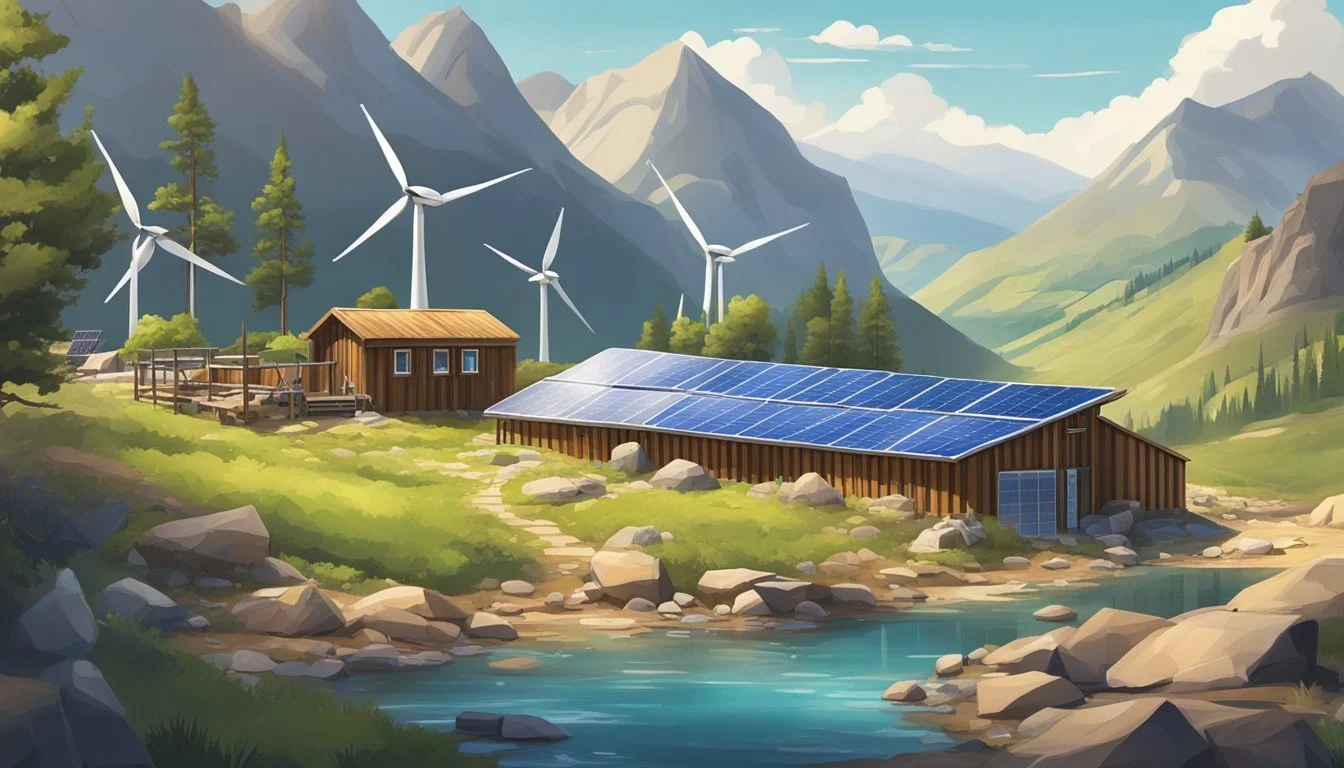
Energy and Power Solutions
Front Range off-grid living requires reliable and sustainable energy solutions to ensure continuous power supply. Key methods include harnessing renewable energy sources, with particular emphasis on solar and wind energy, and effective energy storage and management systems.
Harnessing Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydroelectric, and biomass are ideal for off-grid living. These sources provide a consistent and eco-friendly supply of electricity.
Residents often combine multiple sources to enhance reliability. For instance, solar panels and wind turbines can be used together to compensate for periods of low sunlight or wind.
Hydroelectric power, generated from flowing or falling water, offers another sustainable option where water sources are available.
Solar Energy Systems
Solar energy systems are a popular choice for Front Range off-grid living due to their reliability and efficiency.
Solar panels capture sunlight and convert it into electricity through photovoltaic cells. These panels are installed on rooftops or open land spaces to maximize sun exposure.
A key advantage is the reduction in energy consumption from the grid, leading to lower electricity costs. Additionally, solar energy is highly scalable, allowing residents to expand their system as needed.
Wind Energy and Other Alternatives
Wind energy plays a crucial role in providing a stable electricity supply, especially in areas with sufficient wind speeds.
Wind turbines are installed at high points to capture wind and convert it into electrical power. They are particularly effective during winter months when wind patterns are stronger.
Other renewable options like biomass involve converting organic materials into energy. This can supplement solar and wind energy, providing a more diverse and dependable energy mix.
Energy Storage and Management
Effective energy storage and management systems are essential for ensuring a continuous power supply in off-grid settings.
Batteries store excess energy generated from solar panels or wind turbines, making it available for use during periods of low production. Popular battery types include lithium-ion and lead-acid due to their efficiency and capacity.
Smart energy management systems optimize energy consumption, ensuring that electricity use is efficient and sustainable. This entails monitoring energy usage patterns and automating processes to improve overall energy efficiency.
Self-Sufficiency in Food and Water
Achieving self-sufficiency in food and water is fundamental for a sustainable off-grid lifestyle. It involves securing reliable water sources, purification methods, and growing or raising food.
Sustainable Water Supply and Purification
Reliable water sources are critical. Rainwater harvesting systems, which capture and store rain, are essential. Wells can also provide consistent supply if groundwater is accessible.
Water filtration and purification are necessary to ensure safety. Methods like sand filters, activated carbon filters, and UV purifiers eliminate contaminants. Proper storage in clean, covered tanks prevents contamination.
Natural water sources like lakes or streams can be used, but always require filtration and purification. Implementing these systems not only secures clean water but also reduces dependency on external suppliers.
Gardening and Livestock for Food Self-Reliance
Gardening is key to a dependable food supply. Raised beds and greenhouses extend growing seasons and protect from pests. Crops like grains, vegetables, and fruits should be chosen based on climate and soil conditions.
Livestock farming complements gardening by providing protein and other nutrients. Chickens for eggs, goats for milk, and rabbits for meat are viable options.
Animal manure is valuable as fertilizer, closing the nutrient cycle in gardening. Balancing crop and livestock production ensures a continuous food supply, leading to a resilient, off-grid lifestyle.
Tools and Infrastructure for Off-Grid Life
Living off-grid successfully involves a range of essential tools and robust infrastructural setups. These tools are necessary for daily maintenance, construction, and ensuring sustainability and self-reliance.
Maintenance Tools and Equipment
Reliable maintenance tools are vital for an off-grid lifestyle. An all-purpose folding knife is indispensable for various tasks, from cutting rope to food preparation. Axes are crucial for chopping wood, an essential fuel source. For everyday repairs, duct tape or Gorilla Tape is extremely useful due to its durability and versatility.
Basic hand tools such as hammers, wrenches, and screwdrivers are necessary for repairs and DIY projects. Shovels, rakes, and pitchforks are essential for gardening and managing your landscape. Power tools, powered by renewable energy sources like solar panels, can also significantly ease construction and repair tasks.
Building Robust Off-Grid Infrastructure
Infrastructure forms the backbone of off-grid living. A reliable solar power system provides electricity, reducing dependency on external power sources. Water harvesting systems, like rainwater collectors, ensure a steady water supply. Composting toilets offer an eco-friendly solution for waste management.
Gardening tools like trowels and spades support sustainable food production. For preserving food, root cellars provide a natural refrigeration option. Effective plumbing tools help maintain your water systems, ensuring efficient water flow and sanitation.
Overall, building a comprehensive and reliable infrastructure is key to achieving self-sufficiency.
Lifestyle Considerations
Embracing an off-grid lifestyle in the Front Range requires careful planning to maintain comfort and safety without public utilities. Essential aspects include daily living arrangements and ensuring health, safety, and connectivity.
Daily Living without Public Utilities
Living off-grid necessitates alternative solutions for cooking, heating, and powering appliances. Propane stoves and wood-burning stoves offer reliable options for cooking and heating. Electric ranges can also be used if sufficient solar power or other renewable energy sources are available.
Water is another essential aspect, with rainwater collection systems and wells being common solutions. Composting toilets and gray water systems help manage waste efficiently.
Off-grid appliances designed for low energy consumption are crucial. These appliances often minimize power use, making them ideal for solar-powered homes.
Daily living without traditional utilities requires thoughtful planning regarding energy usage and appliance size.
Health, Safety, and Connectivity
Maintaining health and safety involves having systems for waste management, water purification, and emergency medical supplies. Biogas systems can convert waste into fuel, enhancing sustainability.
Connectivity plays a vital role in modern off-grid living. Satellite Internet and cell signal boosters help ensure reliable communication. Security systems, such as motion-sensor lights and surveillance cameras, can be included to protect the property.
Being prepared for emergencies with well-stocked first aid kits and knowledge of basic medical procedures is crucial. Additionally, robust insulation and heating solutions ensure the home remains safe and livable during extreme weather conditions.
Economic and Ecological Impact
Front Range off-grid living provides both financial benefits and substantial environmental advantages. It focuses on reducing energy costs and mitigating carbon emissions through sustainable living practices.
Cost-Effectiveness and Savings
Living off the grid in the Front Range can result in significant cost savings. By generating their own power through solar panels or wind turbines, residents reduce reliance on traditional utility services.
Initial setup costs might seem high, but the reduction in monthly utility bills can lead to long-term financial benefits. For many, avoiding natural gas and fossil fuels translates to financial autonomy over time.
Additionally, off-grid homes often use rainwater harvesting and composting toilets, lowering water expenses. These cost-effective measures maximize resource efficiency and save money.
Reducing Carbon Footprint and Environmental Conservation
Off-grid living in the Front Range notably reduces the carbon footprint by minimizing dependence on fossil fuels. Utilizing renewable energy sources such as solar and wind enables sustainable living.
Residents often adopt eco-friendly practices like growing organic food, which reduces transportation-related emissions. The reduction of waste through composting and recycling further minimizes their environmental impact.
By preserving local ecosystems and reducing pollution, off-grid communities contribute to broader environmental conservation efforts. These sustainable practices foster a healthier environment for future generations.
Preparation and Transition
Transitioning to an off-grid lifestyle in the Front Range requires meticulous planning and preparation. Key elements include creating a comprehensive checklist and making a seamless shift to off-grid living, focusing on resilience and self-reliance.
Creating a Comprehensive Checklist
Creating a checklist is essential to ensure nothing is overlooked. Begin with energy sources like solar power, wind turbines, and backup generators. Assess the local climate and availability of natural resources to make informed decisions.
Next, address water sources. Plan for wells, rainwater collection systems, and water purification methods. Evaluate sewage and waste management including composting toilets and gray water systems to ensure sustainability.
Housing and shelter is another critical aspect. Determine if you will build a new structure or retrofit an existing one. Ensure it is well-insulated and energy-efficient.
Food production involves planning gardens, greenhouses, and livestock if feasible. Stockpile non-perishables and preserve seasonal produce to maintain a year-round food supply.
Finally, consider financial plans. The initial investment can be substantial, so budgeting for setup and ongoing maintenance is essential.
Making the Shift to Off-Grid Living
Making the shift to off-grid living involves both mental and physical adjustments. Begin with a trial period, possibly living semi-off-grid to ease the transition.
Initially, focus on establishing energy systems and ensuring they are reliable. Install and test solar panels, batteries, and backup generators to familiarize yourself with their maintenance.
Next, secure a sustainable water source. Digging a well or setting up a rainwater collection system should be prioritized. Ensure you have the necessary filters and purification setups.
Adapting to seasonal changes is crucial. Prepare for extreme weather by insulating your home and having a backup source of heat, such as wood stoves.
Community connections can provide support and knowledge. Engage with local off-grid communities to share resources and solutions to common challenges.
Lastly, building resilience and self-reliance means being prepared for emergencies. Stock up on medical supplies, learn basic first aid, and develop skills for everyday repairs and maintenance.