Mozzarella Cheese Substitutes
Top Picks for Dairy-Free and Low-Fat Alternatives
Mozzarella cheese (What wine goes well with cheese?), celebrated for its mild flavor and superb meltability, is a staple in dishes like pizza, lasagna, and caprese salad. However, whether it's due to dietary restrictions, availability, or a desire to experiment with new flavors and textures, cooks may find themselves in need of a substitute. The quest for an alternative need not be daunting; a variety of cheeses can step in to fill mozzarella's role in a dish while offering unique tastes and properties.
When looking for mozzarella cheese substitutes, it's important to consider the context in which the cheese is used. For recipes that require a cheese with a similar melting quality and subtle taste, White Cheddar, Provolone, and Gouda are excellent options. They can deliver the familiar stringy, stretchy quality desired in melted cheese applications. Meanwhile, for a more pronounced flavor, cheeses like Swiss or Jarlsberg can be used, and for those who prefer a cheese with a crumbly texture for salads or cold dishes, Feta or Ricotta can be ideal choices.
It's key to remember that each substitute brings its own characteristics to the table, and while they may not precisely mimic mozzarella, they can often provide a delightful twist on the original. By selecting a cheese that can match the melt, stretch, and flavor profile suitable for their specific culinary needs, chefs and home cooks alike can successfully replace mozzarella in their favorite recipes without compromising on taste or texture.
Understanding Mozzarella Cheese
This section takes a detailed look at the characteristics and culinary roles of mozzarella cheese, with a focus on its unique flavor and texture.
Characteristics of Mozzarella
Mozzarella cheese, commonly produced from cow's milk or buffalo milk, is renowned for its distinct qualities.
Flavor: The taste of mozzarella is mildly tangy and milky, with a subtle sweetness that can be more pronounced in fresh mozzarella. The flavor is more intense when made from buffalo milk.
Texture: There are two primary types of mozzarella:
Fresh Mozzarella: Soft, moist, and spongy, intended for immediate consumption.
Low-Moisture Mozzarella: Firmer and denser, with a longer shelf life, making it suitable for grating.
Color: A classic mozzarella has a bright white hue, but it may vary slightly depending on the milk source.
Roles in Dishes
Mozzarella cheese plays versatile roles in the culinary world, particularly in Italian cuisine.
Melting Characteristics: Its excellent melting quality allows for a stretchy texture that is highly desired in hot dishes such as pizza and lasagna.
Fresh Use: In its fresh form, mozzarella is a staple in salads like Caprese, where its soft texture contrasts with the crispness of vegetables.
Cultural Significance: Mozzarella holds a place of honor in many traditional Italian recipes, often serving as a key ingredient that enhances the overall dish without overpowering other flavors.
Each type of mozzarella serves its purpose, seamlessly integrating into a multitude of recipes where either a delicate freshness or a satisfying melt is required.
Dairy-Based Mozzarella Substitutes
For those seeking alternatives to mozzarella, a range of dairy-based options offers similar textures and flavors. These cheeses can be used in recipes calling for mozzarella and are likely available at your local grocer.
Cow's Milk Alternatives
There are a variety of cow's milk cheeses that can stand in for mozzarella. Provolone cheese and cheddar cheese, especially a mild white cheddar cheese, can work in sandwiches and on pizzas. Monterey Jack cheese is another versatile substitute, known for its meltability and mild flavor.
Sheep and Goat Milk Cheeses
Feta cheese, traditionally made from sheep's milk, provides a tangy flavor but does not melt as well as mozzarella. However, it's an excellent choice for cold dishes. Pecorino Romano, another sheep’s milk cheese, is harder and saltier but grates well for topping pasta dishes (What wine goes well with pasta dishes?).
Italian Cheese Varieties
Ricotta is a soft cheese that offers a creamy texture similar to mozzarella when used in lasagnas and stuffings. Other Italian cheeses such as fontina cheese and caciocavallo can also be melted into dishes for a smooth and stretchy texture, making them good mozzarella substitutes.
Other European Cheeses
Looking towards Europe, Dutch gouda cheese and edam cheese have similar mild but rich flavors and are excellent when melted. Jarlsberg cheese, known for its nutty taste, is a good option too. Havarti, a Danish cheese, while creamier, can also be used as a substitute due to its good melting properties.
Mozzarella Substitutes in Popular Dishes
When preparing Italian cuisine and other favorite recipes, choosing the right cheese alternative can maintain the integrity of the dish while introducing unique flavors and textures.
Cheese Alternatives for Pizza
Provolone: Offers a stringy, stretchy quality perfect for pizza.
Stracchino: Known for its soft texture, it also delivers a creamy taste on pizza toppings.
Cheese Options for Pasta
Pasta dishes often rely on the meltability and mild flavor of mozzarella. They can benefit from these substitutions:
Scamorza: A semi-soft cheese with a mild, slightly tangy flavor suitable for pasta recipes.
White Cheddar (Young): It melts well and provides an appealing cheese pull in lasagna and other baked pasta dishes.
Substitutions in Salads
Caprese salad, which traditionally features mozzarella, can be reinvented with:
Crescenza: This cheese can mimic mozzarella's creamy texture in fresh salad applications.
Cheeses for Baked Dishes
Baked dishes such as chicken parmesan require a melty cheese topping. Here are some choices:
Scamorza: Provides a similar melt to mozzarella, suitable for chicken parmesan.
Provolone: It melts well and offers a more pronounced taste than mozzarella in various baked dishes.
Vegan and Dairy-Free Alternatives
The consumer seeking to replace mozzarella cheese has a variety of vegan and dairy-free options available. These alternatives are designed to mimic the flavor and texture of mozzarella without the use of animal products.
Plant-Based Cheese Substitutes
Violife offers a plant-based mozzarella that gets recognized for its pleasant taste, although it doesn't completely imitate the mozzarella flavor profile. It has a gooey texture that is sought after by those looking for a cheese that melts well.
Field Roast Chao Slices – Tomato Cayenne: These slices bring a spicy kick that can complement dishes needing a flavor boost, while also providing that coveted cheese-like consistency.
Here's a recommended list of readily available dairy-free cheese substitutes:
Cashew-Based Cheeses: They are creamy and can be spread over pizzas or incorporated into recipes calling for mozzarella.
Tapioca-Based Cheeses: Often included for their stretchy quality, which is desirable in dishes like pizza and quesadillas.
Homemade Non-Dairy Options
For those who prefer homemade solutions:
Culturing non-dairy ingredients such as cashews or almonds with probiotics can create a sharp flavor reminiscent of aged cheese. This base can then be thickened with tapioca flour or carrageenan for a stretchiness similar to mozzarella.
A dairy-free pesto can serve as a flavor-packed, aromatic alternative on pizzas or in sandwiches in place of mozzarella.
Hummus, while not cheese-like in consistency, acts as a rich and creamy substitute that offers a new dimension to traditional recipes.
Mozzarella Substitute Considerations
When seeking an alternative to mozzarella, one should consider the cheese's unique attributes, especially its mild, sweet flavor and exceptional meltability, to choose a substitute that best serves their culinary needs.
Flavor Profiles and Pairings
White Cheddar: A sharper taste, but when younger, it can have a milder flavor that makes it a versatile stand-in for mozzarella.
Provolone: Offers a similar mild taste but with a slightly tangy edge, suitable for dishes where a hint of piquancy is welcome.
Gouda: Young Gouda presents a mild sweetness, aligning it closely with mozzarella's flavor profile, especially in melted dishes.
Cheese substitutes can remarkably alter the outcome of dishes. It's crucial to match the substitute's flavor intensity and primary taste notes with the original recipe's requirements to maintain harmony in the flavor pairing.
Cooking Behaviors and Meltability
Fontina: Well-known for its superb meltability, making it an ideal substitute in cooked dishes needing a creamy texture.
Oaxaca: Shares mozzarella's impressive stringiness and melts smoothly, thus perfect for recipes like quesadillas or pizzas.
Mild Cheddar and Gouda: While they melt well, the oiliness can differ, so one may need to adjust the amount used or be prepared for a slightly different texture in the final dish.
When replicating mozzarella's meltability, selecting a cheese that behaves similarly under heat is key. The chosen substitute should melt evenly without becoming too runny or oily, ensuring that the dish retains its desired consistency and mouthfeel.
Regional Mozzarella Variants
Different regions around the globe offer their own unique take on mozzarella, each variant bringing distinct textures and flavors that can substitute for the traditional Italian mozzarella in various dishes.
Italian Regional Cheeses
Italy, the birthplace of mozzarella, boasts several regional cheeses with comparable characteristics. Mozzarella di Bufala, heralding from the regions of Campania, Lazio, Puglia, and Molise, offers a creamier and richer taste due to its buffalo milk origin. This cheese has a Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) status, ensuring its quality and authenticity. The northern region presents Asiago, a cow's milk cheese with a flavor profile that ranges from mild to sharp depending on its ageing.
Stracchino and Bel Paese are two other Italian delights that mirror mozzarella's creamy nature. Stracchino, a very soft cheese, is typically enjoyed fresh, similar to how one would enjoy fresh mozzarella. Burrata from Puglia is a fresh cheese that has an outer shell of solid mozzarella encasing a center filled with soft, stringy curd and cream, offering both the familiar mozzarella taste and a uniquely luscious texture.
Mexican Mozzarella Alternatives
Mexican cuisine has cheese varieties that mirror mozzarella's melting qualities and mild flavor. Originating from Mexico, Oaxaca cheese is a semi-soft, white cheese similar in texture to mozzarella and known for its excellent melting properties, making it a favorite for quesadillas and other melted cheese dishes.
Cotija cheese, named after the town of Cotija in Mexico, is often used in a crumbled form and possesses a stronger, saltier taste. This makes it a suitable substitute for mozzarella in dishes requiring a bold cheese topping. Monterey Jack, although of American origin, is often found in Mexican cuisine and offers a buttery, slightly tart taste and superb melting ability akin to mozzarella.
American Cheese Varieties
The United States has developed several cheeses that can stand in for mozzarella in a pinch. Monterey Jack, renowned for its mild taste and meltability, is commonly used in American dishes like pizzas and cheeseburgers. It has a moisture content and texture that is similar to mozzarella, making it an easy substitute.
Other American cheeses, such as Colby and Cheddar, can also replace mozzarella, especially in cooked dishes where their melting characteristics are desired. These cheeses bring a sharper and more pronounced flavor to the dish, which offers a different dimension compared to the traditionally mild mozzarella.
Creative Culinary Ideas
When seeking a twist in traditional recipes, chefs often experiment with cheese substitutes to transform the flavor and texture of dishes. Utilizing alternative cheeses in salads, pizzas, and pasta can offer a refreshing take on beloved classics.
Innovative Salad Additions
Burrata: A fresh Italian cheese, burrata is a luscious addition to salads. It pairs exquisitely with olives and ripe tomatoes, drizzled with a balsamic reduction.
Feta: Crumble feta cheese over greens for a Mediterranean flair. The tangy taste of feta is complemented by sea salt flakes and capers, (What wine goes well with capers?) adding depth to the salad.
Unique Pizza Toppings
Provolone: This semi-hard cheese melts beautifully, making it an excellent mozzarella alternative for pizzas. Top it with salted roast almonds or Brazil nuts for a nutty crunch.
Gouda: For those who enjoy a richer taste, gouda's sweet, buttery notes work well with caramelized onions and thinly sliced pears on a pizza.
Experimental Pasta Mix-ins
Ricotta: For pasta fillings or sauces, ricotta provides a creamy texture. It mixes well with spinach or roasted vegetables in stuffed shells or lasagna.
Fontina: A melt-in-your-mouth cheese that can elevate macaroni dishes, fontina can be combined with mushrooms and thyme for an earthy, aromatic pasta experience.
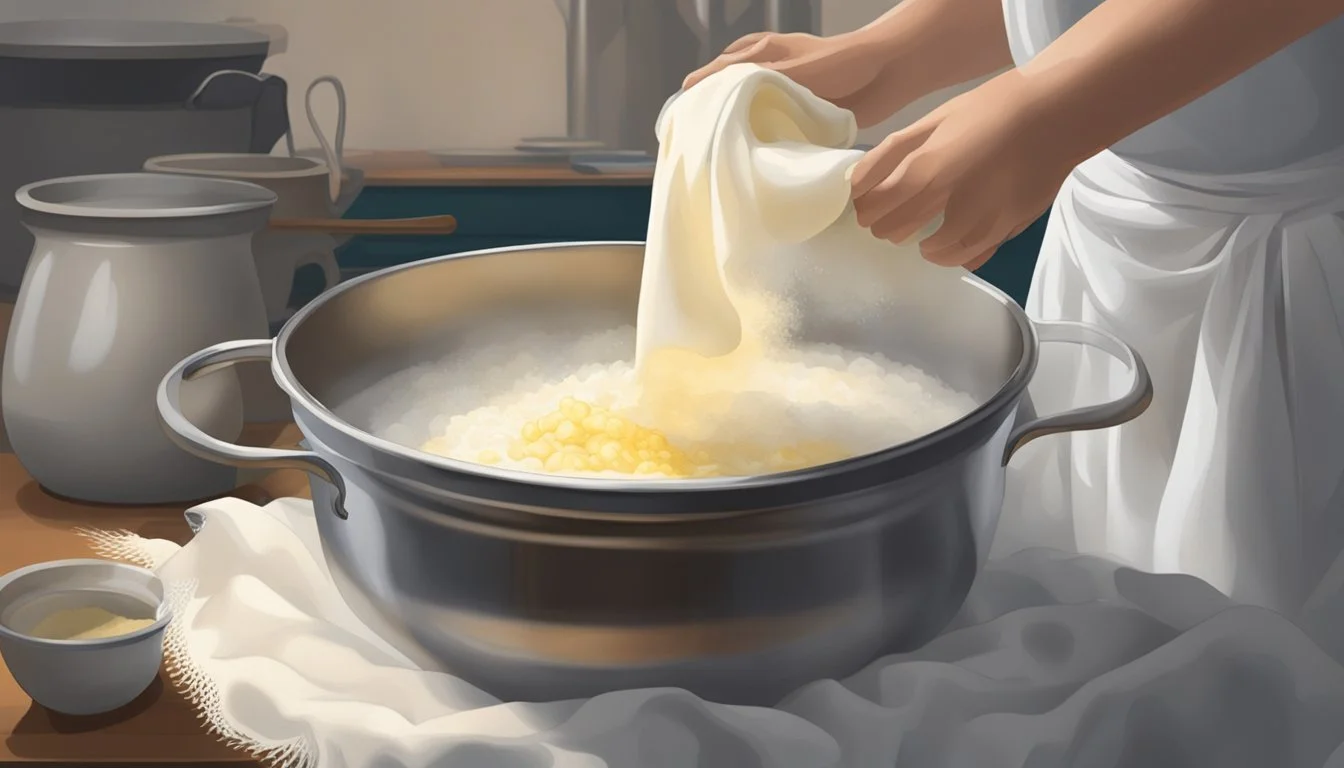
Making Mozzarella Substitutes at Home
When looking to replicate the texture and taste of mozzarella cheese at home, one has options ranging from dairy-free products to nut-based alternatives. Below are ways to create satisfying mozzarella substitutes that can add similar creaminess and melt to various dishes.
DIY Dairy-Free Cheeses
Dairy-free cheeses often utilize tofu for its versatility and neutral flavor profile. To make a tofu-based mozzarella substitute, one needs to blend firm tofu with ingredients like lemon juice, nutritional yeast, and salt to create a mixture that mimics the mild taste and texture of traditional mozzarella. A sample recipe would be:
Ingredients:
1 block of firm tofu
2 tablespoons nutritional yeast
1 tablespoon lemon juice
Salt to taste
Instructions:
Press the tofu to remove excess water and cut into cubes.
Combine tofu, nutritional yeast, lemon juice, and salt in a food processor.
Blend until smooth and store in the refrigerator to firm up before using.
Crafting Cheese Alternatives from Nuts
Cashews are a popular base for homemade vegan cheeses due to their creamy texture when soaked and blended. To create a cashew-based mozzarella substitute, one should soak the cashews overnight, then blend with water or unsweetened plant-based milk, lemon juice, nutritional yeast, salt, and garlic powder until a smooth consistency is achieved. For additional firmness, the mixture can be refrigerated for a few hours. Here’s a simplified recipe format:
Ingredients:
1 cup cashews, soaked overnight
1/4 cup water or unsweetened plant-based milk
2 tablespoons lemon juice
2 tablespoons nutritional yeast
Salt and garlic powder, to taste
Instructions:
Drain and rinse the soaked cashews.
Blend cashews with the rest of the ingredients until completely smooth.
Refrigerate for a few hours to achieve a firmer texture before using.
Brazil nuts can also serve as a robust substitute, though they have a stronger flavor and may not provide the same level of creaminess. One can experiment with the ratio of these nuts to achieve the desired taste and texture.
Health and Nutritional Perspectives
Choosing a mozzarella substitute can impact one’s caloric intake and cater to specific dietary needs such as lactose intolerance, milk allergies, and plant-based diets.
Caloric and Fat Content Comparison
Substitutes for mozzarella cheese can vary widely in their caloric and fat content. For instance, dairy-free alternatives, such as those made from nuts like cashews, typically offer a lower calorie count as compared to traditional mozzarella. Mozzarella made from cow’s milk tends to have a higher fat content, which contributes to its creamy texture and flavor.
Comparison Table (per ounce):
Substitute Type Calories Total Fat (g) Traditional Mozzarella ~85 6-7 Vegan Mozzarella ~60-80 4-6 Cashew-Based ~70-90 5-7
Allergen and Dietary Restrictions
Individuals with dietary restrictions, such as veganism or lactose intolerance, often seek out non-dairy alternatives to mozzarella. Not only are these alternatives dairy-free and suitable for vegans, but they also cater to those with milk allergies. Non-dairy substitutes commonly utilize ingredients like nuts, soy, and root vegetables, offering a creamy texture without using animal products.
List of Common Non-Dairy Bases:
Cashews
Almonds
Soy
Coconut Oil
Root Vegetables (e.g., Potatoes, Carrots)
It is significant to scrutinize labels for additional allergens, as some vegan cheeses might contain soy or nuts, which are also common allergens.