How Much Rice Vinegar Per Day Is Too Much?
Understanding Safe Consumption Limits
Vinegar has been a staple in culinary practices for centuries, valued for its ability to preserve, flavor, and tenderize food. Rice vinegar, in particular, is a mild type with a slightly sweet flavor, making it especially popular in Asian cuisines. With its unique properties, it's not only a cooking ingredient but also considered by many to have health benefits. These reported benefits include providing a source of antioxidants and potentially helping in the management of blood pressure due to its low sodium content.
Despite its benefits, moderation is key, as with any dietary component. Consuming an appropriate amount of rice vinegar is crucial to maximize its potential health benefits without experiencing adverse effects. Overconsumption of vinegar, in general, could lead to negative outcomes, such as lowered potassium levels, which underscores the importance of consuming vinegar, including rice vinegar, in sensible amounts.
Health experts and nutritional guidelines do not typically specify a recommended daily allowance for vinegar intake. However, incorporating small amounts, such as a few teaspoons, into the diet through dressings, marinades, or simply as a flavor enhancer in cooking, can be a safe practice for most individuals. It's essential to consider individual health circumstances and dietary needs, and seek professional advice if uncertain about the appropriate quantity of vinegar to consume.
Understanding Rice Vinegar
Rice vinegar is an acidic condiment produced from fermented rice with a subtle sweetness and mild flavor. It is commonly found in Asian cuisine, influencing the taste and acidity of the food it is used in.
Types of Rice Vinegar
There are several types of rice vinegar, including:
White rice vinegar: This is the most common type, with a clean and simple flavor.
Black rice vinegar: Characterized by a deeper color and smoky taste.
Red rice vinegar: It offers a distinctive red hue and a zesty, tarter flavor compared to its counterparts.
Each type serves a different culinary purpose and contributes varying acidity levels to a meal.
Nutritional Profile
Rice vinegar's nutritional values per tablespoon are minimal:
Calories: Approximately 3
Fat: 0 grams
Carbohydrates (Including Fiber and Sugar): Less than 1 gram each
Acidity: Around 4.7% on average, which is lower than white vinegar (typically around 6%).
Additionally, rice vinegar contains small amounts of minerals like potassium, magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus.
Rice Vinegar Uses in Culinary Practices
Culinary practices with rice vinegar include, but are not limited to:
Sushi rice preparation: Enhances flavor with its acidic profile.
Salad dressings: Provides a light, tangy base.
Marinades: Tenderizes and adds zest to meats and vegetables.
Dipping sauces: Often combined with soy sauce and other ingredients to give a contrasting sweet and sour flavor to dishes.
Rice vinegar is used in a modest amount within recipes to balance and complement the main ingredients of the meal.
Health Implications of Rice Vinegar
Rice vinegar, a product made through the fermentation of rice, is commonly used as a condiment and health supplement. While it provides various potential health benefits, it is important to consider its effects on different health aspects such as diabetes control, weight management, and digestive health, along with potential risks and side effects.
Rice Vinegar and Diabetes
Rice vinegar may influence blood sugar levels, making it pertinent for individuals managing diabetes. Consuming vinegar can potentially help reduce insulin spikes after a meal, thereby aiding in blood sugar regulation. In fact, studies suggest that vinegar may improve insulin sensitivity, which is beneficial for those who are insulin resistant, a condition commonly associated with type 2 diabetes.
Blood sugar management: Vinegar might moderate glucose and insulin response post-meal.
Diabetes support: Regular but moderate intake of vinegar might assist those managing diabetes.
Weight Management and Satiety
The calorie count in rice vinegar is minimal, making it a low-calorie addition to meals which may assist in weight loss. Vinegar's potential to increase feelings of satiety could result in a lower overall caloric intake. Furthermore, its acidic nature might slow down gastric emptying, aiding in prolonged satiety.
Calorie control: Rice vinegar contains very few calories per serving.
Enhanced satiety: It may contribute to a feeling of fullness, supporting weight management efforts.
Digestive Health Benefits
Regular consumption of rice vinegar in moderation may offer benefits for digestive health. Its acidic composition can stimulate the digestion process. However, it is important to note that excessive acidity might not be suitable for everyone and could lead to digestive discomfort for those with sensitive stomachs.
Digestive stimulation: Vinegar can activate digestive enzymes for better food breakdown.
Moderation is key: To avoid gastric irritation, rice vinegar should be consumed in small amounts.
Risks and Side Effects
While rice vinegar is generally safe when used in food, excessive consumption can pose risks such as acid reflux and erosion of tooth enamel. People with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or kidney disease should be cautious as the high acid content can exacerbate their conditions. Overuse may also affect bone density, potentially increasing the risk of osteoporosis.
Acid-related conditions: Acid reflux and enamel erosion can result from high vinegar intake.
Potential health risks: Those with existing kidney disease or bone health concerns should be cautious.
Daily Intake of Rice Vinegar
Rice vinegar is a popular ingredient in various cuisines, appreciated for its ability to enhance flavors and offer health benefits. However, understanding the proper daily intake is crucial to harness these benefits without adverse effects.
Recommended Amounts
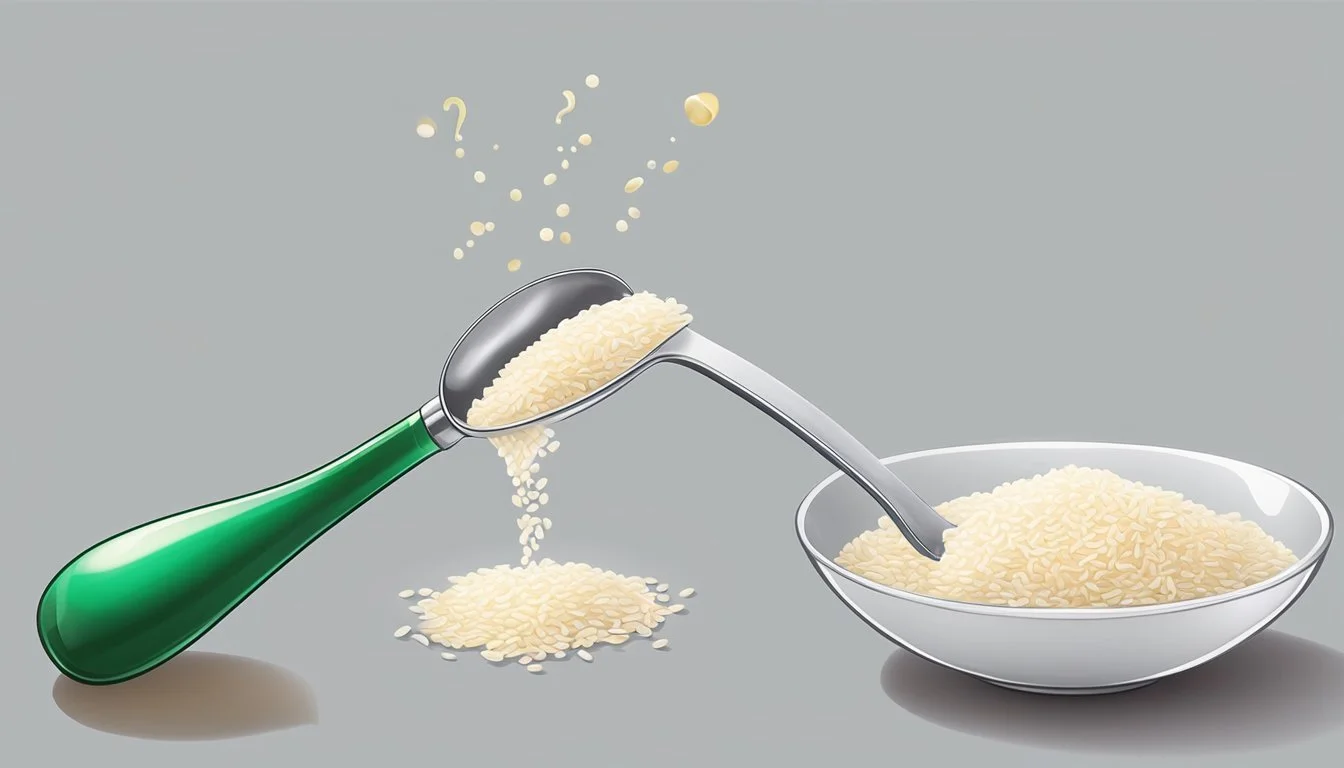
Consuming rice vinegar in moderation is key to enjoying its potential health advantages which can include aiding in blood sugar control. Nutrition experts commonly recommend:
Adults: 1-2 tablespoons (15-30 ml) per day
It is essential to note that this amount includes vinegar from all sources, not just rice vinegar.
Excess Consumption: Signs and Symptoms
Exceeding the recommended daily intake of rice vinegar can lead to several health issues due to its acetic acid content. Signs of overconsumption may include:
Gastrointestinal Distress: Acidic foods can irritate the stomach lining, leading to discomfort.
Mineral Imbalances: High levels of acetic acid from vinegar can leach minerals from bones and affect blood levels of important electrolytes.
Special Considerations for Various Health Conditions
Individuals with certain health conditions should exercise caution:
Diabetes: The acetic acid in vinegar can affect blood sugar levels, but while moderate consumption can help with blood sugar control, those on diabetes medication should consult their healthcare provider to avoid hypoglycemia.
Osteoporosis: Excessive vinegar intake might contribute to lower potassium levels and reduced bone mineral density.
In conclusion, rice vinegar can be a beneficial dietary addition when used in appropriate amounts and with consideration of individual health conditions.
Culinary Uses of Rice Vinegar
Rice vinegar is a versatile ingredient known for its mild acidity and slight sweetness, which enhances a myriad of dishes from sushi to salad dressings, and amplifies the overall flavor profile of a meal.
Rice Vinegar in Sushi Preparation
When crafting sushi rice, a sushi chef typically incorporates rice vinegar to achieve the classic tangy flavor that balances the richness of the fish. The vinegar ratio is crucial: a typical sushi rice recipe might include a blend of rice vinegar, sugar, and salt that is gently folded into the cooled rice, ensuring the grains remain intact. The use of rice vinegar is essential as it imparts a distinctive sour-sweet taste that is integral to authentic sushi.
Rice Vinegar in Salad Dressings and Marinades
The application of rice vinegar in salad dressings and marinades speaks to its capacity to add a refreshing and tangy touch to dishes:
Salad Dressings: In dressings, rice vinegar pairs well with various greens, and its acidity can be balanced with oil and sweetness according to one's personal taste.
Marinades: For marinades, rice vinegar acts as a tenderizing agent while injecting a subtle, vinegary profile. This makes it ideal for both meat and vegetable marinades, where the acidity of the vinegar base can be adjusted to suit individual flavor preferences.
Enhancing Flavors in Cooking
In general cooking, a chef might use rice vinegar to bring life to a dish. A small amount of vinegar can be stirred into a soup or sauce to add complexity, or it could be integrated during the last minute of stir-frying to uplift the dish with a burst of brightness. The key is moderation to ensure that the vinegar enhances rather than overpowers the dish. Rice vinegar should be added gradually and tasted frequently, respecting the balance of flavors and the personal preference of those who will be enjoying the meal.
Comparison with Other Vinegars
In evaluating rice vinegar's role in daily consumption, it's critical to understand how it differs from other popular types of vinegar in terms of acidity and flavoring.
Rice Vinegar vs. White Vinegar
Rice vinegar is milder and slightly sweeter than white vinegar. With an average acidity of 4.7%, rice vinegar offers a more delicate flavor compared to white vinegar's acidity level of around 6%. While both are used in cooking and cleaning, rice vinegar is often favored for its less pungent taste in culinary applications.
How Balsamic and Apple Cider Vinegar Differ
Balsamic vinegar is known for its rich, complex sweetness and is often used in reductions and dressings. It has a much lower acidity, typically around 4%, but the flavor is bold and concentrated. Contrastingly, apple cider vinegar is fruity and mildly acidic, usually sitting between 5% to 6% acidity. This vinegar is often touted for potential health benefits and adds a slightly tart apple flavor to dishes.
Choosing the Right Vinegar for Your Dish
When selecting a vinegar, one must consider the desired flavor profile:
Rice Vinegar: Ideal for Asian cuisines, marinades, and delicate sauces due to its subtle sourness and hint of sweetness.
White Vinegar: Best for pickling and household cleaning, given its higher acidity and robust sourness.
Balsamic Vinegar: Suited for salad dressings and glazes where its sweetness can be showcased.
Apple Cider Vinegar: Preferred for healthful remedies and recipes where a subtle apple flavor is beneficial.
Each type of vinegar brings a distinct taste and level of sourness to the table, so choosing the right one can elevate the dish's flavors precisely.
Nutrition and Diet Considerations
Integrating rice vinegar into a daily diet should be approached with an understanding of its nutritional impact and how it can affect blood sugar and insulin levels.
Integrating Rice Vinegar in a Balanced Diet
Rice vinegar is low in calories, providing approximately 3 calories per tablespoon. It contains negligible amounts of fat and protein; therefore, it can fit into a weight loss plan when used as a substitute for higher-calorie dressings. It also offers a tangy taste which may enhance satiety when consumed as part of a meal.
In addition to being a flavor enhancer, rice vinegar contains potassium, magnesium, calcium, and phosphorus. Its antioxidant properties, mainly derived from phenolic compounds, can contribute positively to an individual's overall antioxidant intake.
Example of rice vinegar in a meal:
Salad Dressing: Combine rice vinegar with olive oil and herbs for a healthy vinaigrette.
Marinade: Use rice vinegar as a base for marinades to add flavor without significant calories.
Impact on Blood Sugar and Insulin Levels
Vinegar, including rice vinegar, has been shown to have an effect on controlling blood sugar spikes after a meal, particularly ones with high glycemic index such as white rice or other starchy foods. Consuming a small amount of rice vinegar, around 1-2 teaspoons, with meals may slow the digestion of carbohydrates and subsequently reduce insulin spikes.
For those managing conditions like diabetes, incorporating rice vinegar could be beneficial. However, it's essential to maintain a balance and not rely on vinegar alone to control blood sugar. A combination of vinegar intake with a diet low in high glycemic foods can help maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
Blood sugar control strategy:
High glycemic meal: Add rice vinegar to potentially lower the glycemic load.
Daily intake: Incorporate moderate amounts of rice vinegar, such as 1-2 teaspoons per meal, to aid in overall blood sugar management.
Historical and Cultural Significance
Rice vinegar, an integral condiment in various cuisines, has a storied history that intertwines with the cultural identity of regions like Japan. It's prized for delicate flavors and food preservation qualities.
Rice Vinegar in Japanese Cuisine
In Japan, rice vinegar is more than just an ingredient; it is a pivotal element of their culinary tradition. Since ancient times, it has been used to enhance dishes with its subtle tartness. Sushi owes its flavor profile to rice vinegar, which is used to season the rice, complementing the fresh taste of the fish. Additionally, it plays a crucial role in tea ceremonies, used to cleanse and purify utensils, reflecting its importance in Japanese culture.
Global Use and Variations
Globally, rice vinegar's use extends beyond Asia. In the Mediterranean and Europe, various forms of vinegar, including those made from rice, have been integral in culinary practices for centuries. Notably, vinegar, similar to rice vinegar, is commonly used in Europe to preserve vegetables and as a flavor enhancement in sourdough breads. Variations of rice vinegar can be found enhancing the taste of dishes worldwide, testament to its versatility and culinary significance.
FAQs About Rice Vinegar Consumption
What is the safe amount of rice vinegar to consume daily? The safe consumption level of rice vinegar has not been officially established. However, due to its acidity, it is wise to limit intake to small amounts such as those used in culinary practices.
Does rice vinegar provide any health benefits? Rice vinegar contains acetic acid, which may offer health benefits such as blood sugar control and potential weight loss. However, these effects are not unique to rice vinegar and can be found in other vinegars like balsamic vinegar.
Can rice vinegar affect insulin levels for people with diabetes? Rice vinegar can improve insulin sensitivity. A study by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Disease found that vinegar may help stabilize blood sugar levels post-meal in individuals with insulin resistance.
Is rice vinegar used in Japan for sushi preparation? Yes, in Japan, rice vinegar is traditionally used to season sushi rice. Typically, 1 to 2 tablespoons of rice vinegar are added per cup of cooked rice, enhancing the sushi's sweetness and acidity without overpowering it.
Are there any concerns with rice vinegar's acidity? Excessive consumption can lead to digestive discomfort due to its acidity. It's advisable to dilute it with water or other liquids if consumed in larger amounts.
Can rice vinegar be used in diet for weight loss? Incorporating small amounts of vinegar in one's diet may support weight loss efforts, but it should not be relied upon as a sole method for weight reduction.
How does rice vinegar compare to other vinegars in terms of flavor? Rice vinegar is milder and slightly sweet compared to other vinegars. Its subtlety makes it suitable for pickles, salads, and enhancing the flavor of dishes without adding excess saltiness.
Future Trends and Research
Research into rice vinegar's impact on health continues to attract attention. Clinical studies are increasingly focusing on the benefits of rice vinegar in managing blood sugar levels and aiding weight loss. One aspect under investigation is the extent to which daily consumption of rice vinegar can influence insulin sensitivity in individuals with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
Diabetes management: Scientists are examining how rice vinegar's acetic acid content may help regulate blood glucose levels. Ongoing studies, such as those commissioned by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, aim to understand its potential role as part of a dietary strategy for diabetes control.
Weight loss: Research is probing the ways in which rice vinegar may contribute to weight management. Future studies are anticipated to clarify the mechanisms behind this effect.
Table 1: Research Areas on Rice Vinegar Benefits
Research Area Description Insulin Response Examining rice vinegar’s effect on lowering insulin resistance. Diabetes Potential integration with pharmaceutical medications for diabetes. Kidney Disease Understanding benefits for kidney functions in dialysis patients. Cancer Prevention Preliminary assessments of anticancer properties in cell studies.
Future investigations will likely explore the safety and efficacy of rice vinegar as compared to other vinegars, and its interaction with pharmaceutical medications. Researchers are particularly interested in identifying the optimal daily intake that balances benefits with potential risks, especially for individuals managing chronic conditions such as kidney disease.
The research aims not just to confirm the health benefits but also to recommend practices that can be easily incorporated into daily life. These investigations will help to establish guidelines that ensure the safe consumption of rice vinegar for health improvement and disease prevention.