USDA Hardiness Zones in Minnesota
Navigating the Planting Map
Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is crucial for gardeners and growers in Minnesota. The map, which is the standard guide to determining which plants are likely to thrive in a particular location, is organized into zones that are defined by the average annual extreme minimum winter temperature. This invaluable tool assists in making educated decisions about which perennial plants can endure the local climate.
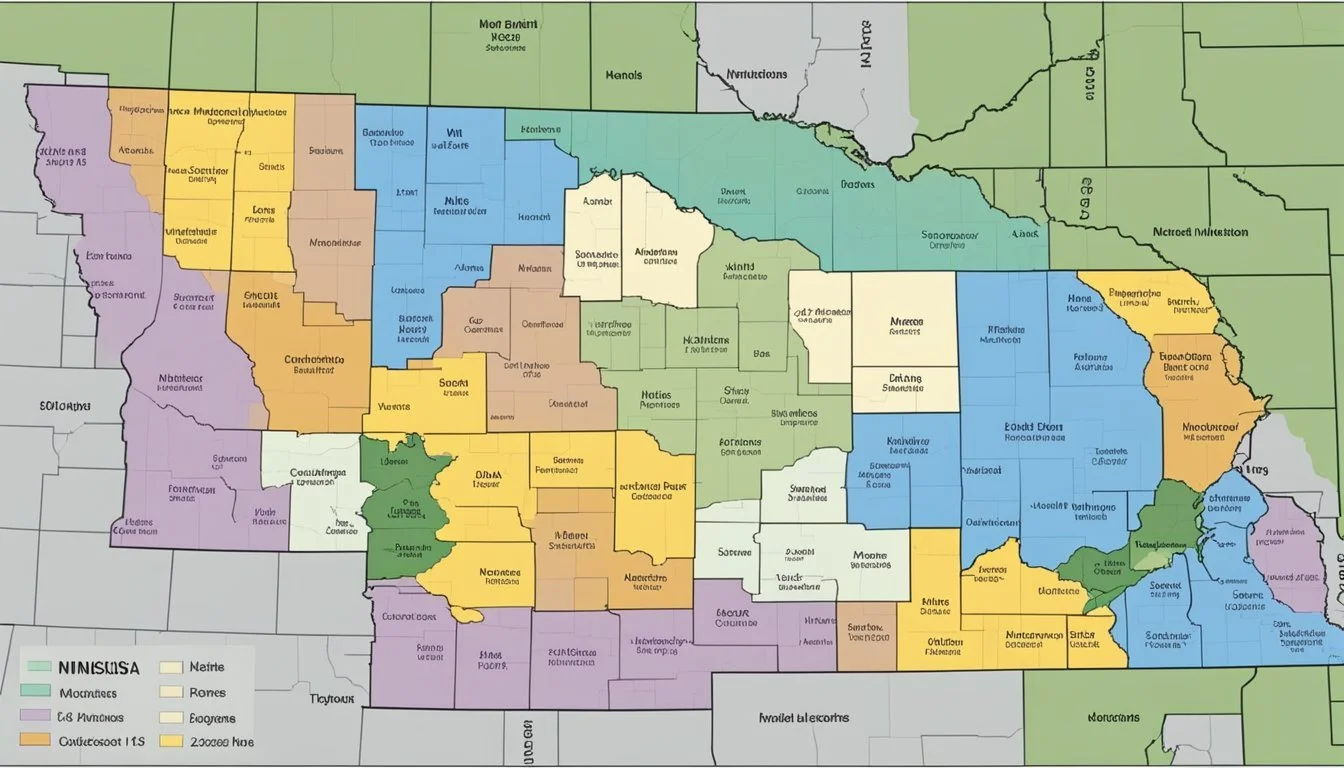
In Minnesota, the USDA Hardiness Zones vary significantly across the state due to its wide range of climatic conditions. The zones in Minnesota range from 2b in the north, with extreme minimum temperatures reaching as low as -45°F, to 4b in the southern regions where temperatures only drop to around -20°F. These zones are subject to change, as observed in the new 2023 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, with alterations reflecting the latest climate data.
The Minnesota Interactive USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map provides a detailed look at the zones within the state, offering localized insight for gardeners. This level of specificity is important for plant survival and successful growth, as even small climatic variations can have a significant impact on perennial plant development and sustainability in the diverse Minnesotan landscape.
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map serves as a pivotal guide for gardeners and agriculturists, delineating regions based on their climatic conditions to inform plant cultivation.
Defining Hardiness Zones
A hardiness zone is a geographically defined area where a specific category of plant life is capable of growing, as defined by climatic conditions, especially the plant's ability to withstand minimum temperatures. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map divides North America into 13 primary zones, with each zone representing a 10-degree Fahrenheit difference in the average annual extreme minimum temperature.
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, updated by the United States Department of Agriculture and Oregon State University's PRISM Climate Group, is based on the most recent 30-year averages of climatic conditions. This authoritative map reveals the temperature extremes of given regions, guiding gardeners in the United States on the most suitable plants for their locales.
Interpreting Zone Classifications
Each hardiness zone is further divided into ‘a’ and ‘b’ half zones, representing 5-degree Fahrenheit differences. For instance, USDA zone 4 is split into zones 4a and 4b, where zone 4a represents colder areas with lower extreme winter temperatures than 4b. Understanding these classifications aids in selecting plants that are most likely to thrive in a given area's winter conditions.
The Role of Climate Change
The update from the 2012 map to the more current versions has marked a noticeable shift in zones, evidencing warmer temperatures in many regions. This is indicative of how climate change plays a significant role in altering the hardiness zones over time. Regions that historically experienced colder climates are now classified into warmer zones, necessitating a reevaluation of planting strategies to adapt to changing climate conditions.
Minnesota's Climate and Hardiness Zones
Minnesota's diverse climate necessitates a keen understanding of its hardiness zones, which are crucial for successful plant cultivation. Gardeners and agriculturists rely on these zones to navigate the intricacies of local climate conditions.
Overview of Minnesota's Climate
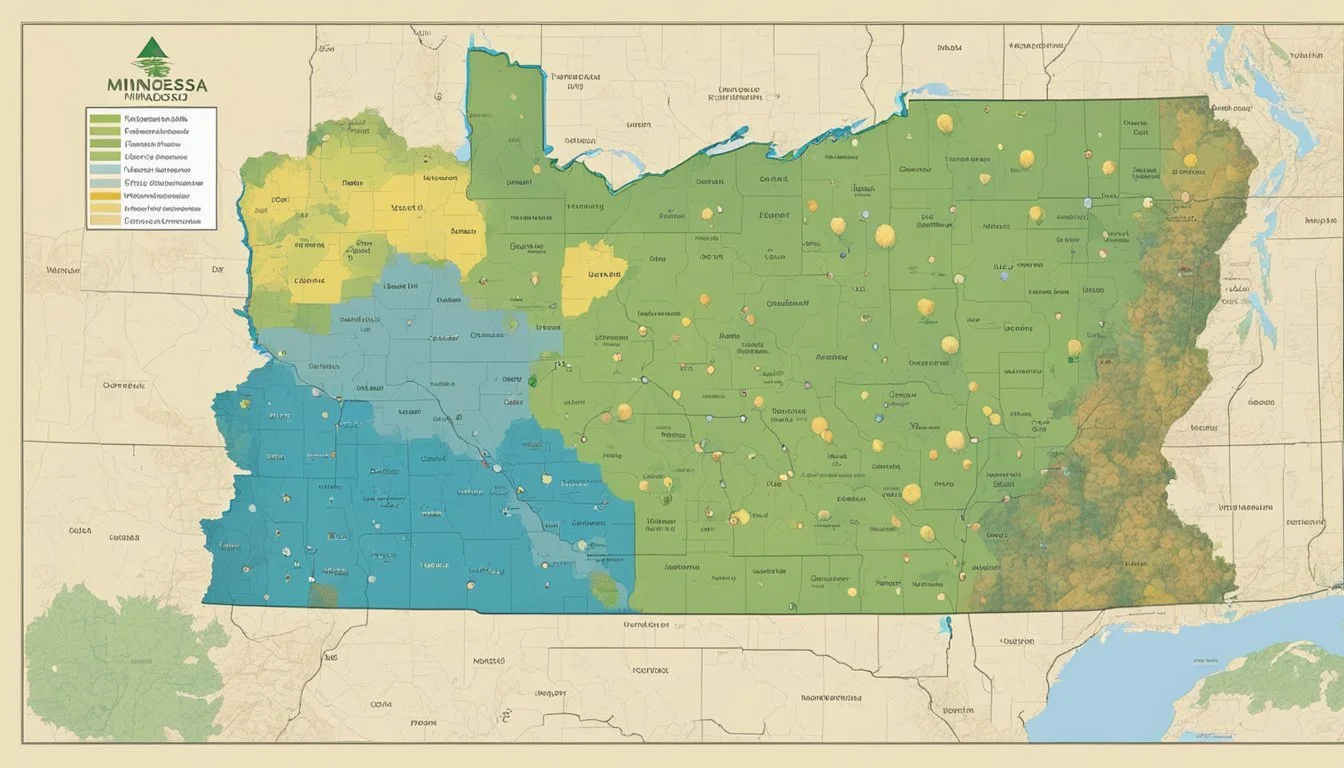
Minnesota experiences a continental climate characterized by a wide temperature range with cold, snowy winters and warm, humid summers. The Twin Cities often face extreme minimum winter temperatures, a critical factor for determining the appropriate plant hardiness zones. The PRISM Climate Group provides detailed climate data that influences mapping these zones, taking into account the state's varying climatic conditions, including average annual extreme minimum temperatures.
Mapping Minnesota's Zones
The USDA has assigned specific hardiness zones to Minnesota, reflecting the regional capacity to support perennial plant life during winter months. Southern Minnesota, encompassing the Twin Cities, has transitioned to warmer hardiness zones in recent years, indicating milder winter temperatures. Cities like Grand Rapids, Ivanhoe, and Russell all fall within distinct zones marked by their unique winter climate profiles.
Minnesota's hardiness zones range from zone 3, with extreme minimum temperatures reaching -40 degrees F, to zone 5, where lows hover around -20 degrees F. Wind patterns and average winter temperatures are critical components used to determine these zones, underscoring the state's climatic diversity.
Gardening in Minnesota's Zones
Gardening in Minnesota requires awareness of the local USDA Hardiness Zones, which dictate the optimal planting times and suitable plants for the region. Gardeners and growers must consider these zones to ensure the vitality and survival of their perennial plants, trees, and shrubs.
Selecting Plants for Your Garden
Understanding the USDA Hardiness Zone Map is essential for Minnesota gardeners when choosing plants for their garden. Zones in Minnesota range from 3a in the northern regions to 5a in the southern areas, a fact highlighted on the UMN Extension site. Plant selections should be based on plants' cold-hardiness and their ability to thrive in Minnesota's zone-specific climate conditions. Local nurseries provide plant options best suited to each zone, ensuring higher chances of plant survival.
Microclimates and Your Garden
A microclimate can significantly affect the growth of plants within any of Minnesota's garden zones. Factors such as soil type, light availability, humidity, and proximity to bodies of water can create warmer or cooler areas, impacting plant survival. Gardeners should observe their local microclimates closely, potentially even consulting data from nearby weather stations, to make informed planting decisions.
Adjusting for Urban Environments
Urban areas within cities like Minneapolis can experience unique gardening challenges due to heat islands created by concrete and buildings. These urban heat islands often result in higher temperatures and altered microclimates, demanding adjustments in gardening practices. Gardeners might need to select heat-tolerant varieties and pay close attention to soil moisture and light conditions to maximize plant survival in urban environments.
Maximizing Plant Survival
In Minnesota's variable climate, ensuring a plant's longevity involves careful consideration of the garden's unique conditions. Using mulches can help maintain soil moisture and temperature, while choosing the correct location, such as a sheltered spot for wind-sensitive plants, contributes to better growth. Regular monitoring and adjusting to changes in light, weather, and soil conditions are key practices to help gardeners and growers extend the life of their plants in Minnesota's diverse gardening zones.
Additional Considerations for Hardiness Zones
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones requires more than just recognizing the zone number of a location. This section delves into the various factors that also play a crucial role, including soil characteristics and recent changes to these zones, as well as how weather variability affects plant selection.
Soil and Hardiness Zones
Soil types significantly affect plant survival and performance within various hardiness zones. For instance, clay soils, which retain moisture, may protect plant roots from extreme cold, whereas sandy soils, which drain quickly, can leave roots more vulnerable. It is imperative for gardeners to assess not just their USDA zone but also their local soil type when selecting plants for their gardens.
USDA Zone Updates and Revisions
The USDA updates to the Plant Hardiness Zone Map reflect more than climate trends; they incorporate better data from more sophisticated GIS tools and more comprehensive weather station reports. The 2012 map was revised to include 30-year averages of extreme minimum temperatures, highlighting the need for gardeners to stay informed of these periodic revisions.
Weather Variability and Plant Selection
When choosing plants, consider not only the hardiness zone but also local weather variability including patterns of snow and rain. These elements can have profound effects on plant health and viability. Regions with a propensity for sudden temperature dips or heavy precipitation may require plant selections that can withstand such extremes beyond their designated zone's guidelines.
Hardiness Zones Beyond Minnesota
The concept of hardiness zones extends to the entirety of the United States, including Alaska, Hawaii, and even Puerto Rico. Each state has unique conditions that are captured within their zone designations, with Hawaii and Puerto Rico having added zones 12 and 13 to account for their tropical climates.
Resources and Tools for Gardeners
Modern gardeners have access to a range of resources and tools. An interactive map with a search box feature allows users to enter their ZIP code and find their precise hardiness zone. It is a highly useful feature for both casual and professional gardeners. This, combined with USDA PHZM resources and information provided by plant companies, equips gardeners to make informed decisions about what to plant and where.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones is crucial for gardeners in planning and planting. The zones take into account the coldest temperatures in the region to help determine which plants are most likely to thrive.
What are the best plants to grow in USDA Hardiness Zone 4b?
In USDA Hardiness Zone 4b, gardeners have success with cold-tolerant plants. Some options include peonies, daylilies, and hostas, all of which can withstand the zone's minimum average temperatures of -25 to -20 degrees F.
How can I find my specific planting zone using my zip code?
To find your specific planting zone using your zip code, you can visit the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map website where a zip code search feature can provide the exact zone for your location.
Where can I find a current map of Minnesota's planting zones?
A current map of Minnesota's planting zones is available at the UMN Extension website, displaying the latest zones and changes made by the USDA.
In which USDA Hardiness Zone is the city of Minneapolis located?
The city of Minneapolis is located in USDA Hardiness Zone 4b, suggesting that plants selected for this area should be able to endure winter lows of -25 to -20 degrees F.
How do the USDA Hardiness Zones vary across Minnesota?
USDA Hardiness Zones in Minnesota range from 3a in the northerly regions to 5a in the southern parts of the state, reflecting the variance in extreme minimum temperatures across different geographic areas.
How can I access an updated Minnesota climate zone map?
An updated Minnesota climate zone map can be accessed by visiting the Minnesota State Horticultural Society or the official USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map websites. These resources offer detailed and updated information on the climate zones across Minnesota.