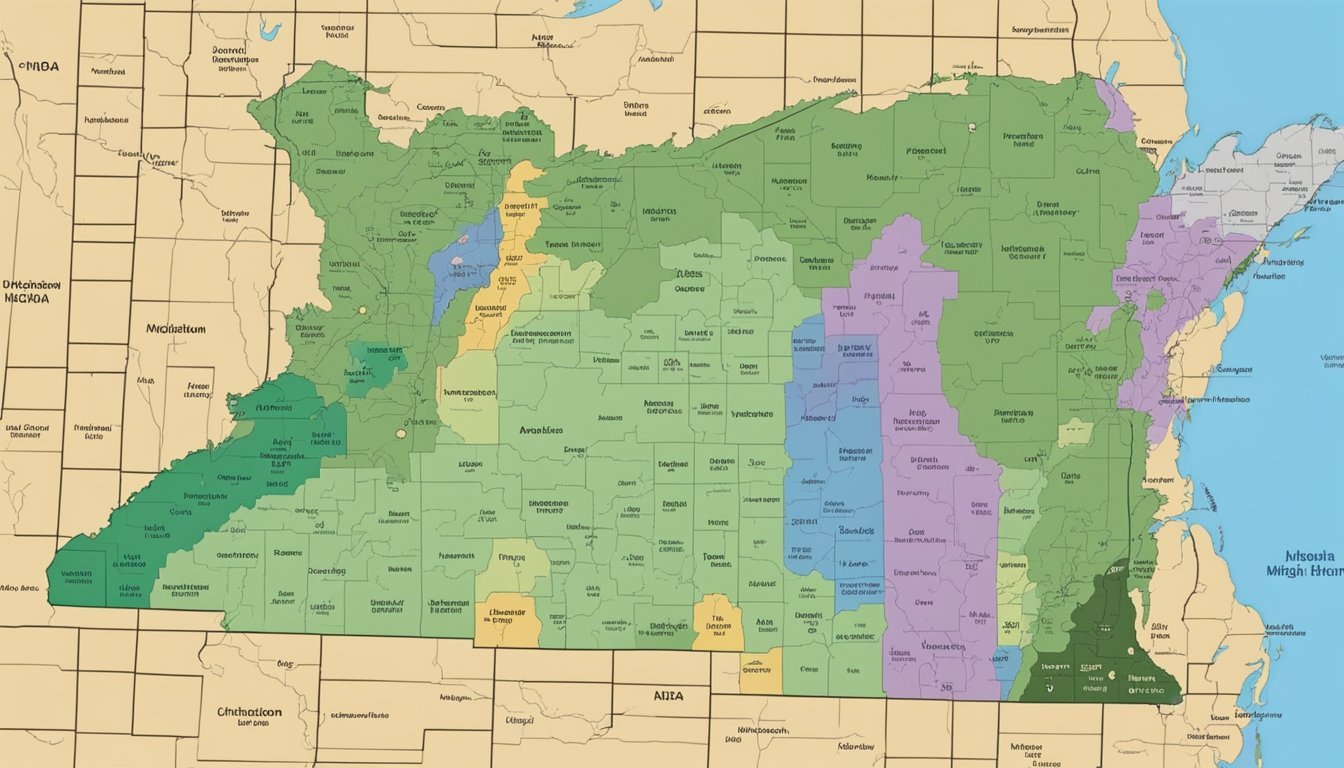
USDA Hardiness Zones in Michigan
A Guide to Successful Gardening
Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is essential for gardeners and agriculturalists in Michigan to determine which plants are most suitable for their region. Michigan spans a variety of hardiness zones due to its diverse climates ranging from the brisk shores of the Great Lakes to its southern borders. This variability means that plants suitable for one area may not survive winter temperatures in another.
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map provides a standard by which plant suitability is gauged. Its zones are delineated by the average annual extreme minimum winter temperature, comprising both 10-degree F zones and 5-degree F half zones. In Michigan, these hardiness zones range from 3a, indicative of colder northern regions, to 6b, which pertains to warmer southern areas.
Accurate knowledge of Michigan's hardiness zones assists in making informed decisions about planting and horticulture. The Michigan Interactive USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is an example of a resource that provides localized information, ensuring that plant enthusiasts can select species with the best chance of thriving in their specific location.
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones
The USDA Hardiness Zone Map is a critical tool for gardeners and agriculturists, indicating which plants are most likely to thrive in specific locations. It categorizes regions based on their average extreme minimum winter temperatures into zones.
The Basics of Hardiness Zones
Hardiness zones, a fundamental concept for gardening and botany, reflect the climatic conditions of an area, especially the cold hardiness a plant must possess to survive the location's winter. In the United States, these zones are defined by 10-degree Fahrenheit increments, representing the average annual extreme minimum temperatures experienced within a geographical area. Each zone is then further divided into 5-degree Fahrenheit half-zones to provide a more precise understanding of local climates.
USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map Overview
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is the authoritative resource gardeners and growers use to determine plant viability in their region. There are 13 zones in total, numbered from 1 through 13. Michigan ranges across multiple zones, suggesting a significant variability in climatic conditions within the state itself. This map, updated in 2023, accounts for the latest climatic data and represents a nuanced breakdown of regions to guide horticultural decisions effectively, relying on comprehensive data from numerous weather stations.
USDA Hardiness Zones in Michigan
Michigan's diverse landscape profoundly influences its planting climate, segmented into distinct USDA Hardiness Zones, ranging from 3a to 6b. These zones provide valuable insights into which plants are most likely to thrive in various locations within the state.
Geographical Diversity in Michigan's Climate
Michigan's topography, consisting of rolling hills, expansive valleys, and its proximity to Lake Michigan, creates microclimates that affect the local hardiness zones. For example, Ada is situated in a zone that can support a slightly different range of plant life than Advance, due to these geographical nuances.
Regional Differences Across Michigan
Hardiness zones in Michigan experience notable variation from region to region. Cities in the southern parts of Michigan tend to fall within zones 5b to 6b, emphasizing a milder climate suitable for a varied plant palette. In contrast, northern areas may be mapped as zone 3a, indicating much cooler temperatures that influence the survival and growth of different plant species.
Effects of Lake Michigan
The presence of Lake Michigan significantly impacts the climatic conditions of nearby areas. It moderates temperatures, thus creating a "lake effect" that shields the adjacent cities from extreme cold. This phenomenon can be observed by the higher hardiness zone ratings found along the lake's coastline, where wind patterns and lake-induced warmth cast a protective blanket over the local flora.
Using the Hardiness Zone Map
The USDA Hardiness Zone Map is an invaluable tool for gardeners and growers, providing a guide to the expected minimum temperatures that directly impact the survival of plants, trees, and shrubs.
Practical Guide for Gardeners
For gardeners, understanding the Hardiness Zone Map is essential for plant selection and long-term gardening success. The map categorizes regions based on the average annual extreme minimum temperatures, ensuring that the gardener selects plants best suited for their local climate. Specifically, Michigan's zones range from 3a to 6b, indicating a minimum temperature range from -40°F to +5°F. This information guides gardeners to choose perennials, trees, and shrubs with the resilience to survive winter conditions.
To use the map effectively, gardeners should:
Identify their specific zone by searching their local area on the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map.
Select plants rated for their zone or colder to ensure survival.
Consider microclimates within their own garden that might allow for the cultivation of plants from adjacent zones.
Applications for Growers and Agricultural Research
Growers rely on the USDA Hardiness Zone Map to cultivate crops suited to the regional climate. Choosing the right zone ensures the plants can withstand the coldest winter days. For example, a grower operating in a zone designated as 5b would avoid planting species susceptible to dying off at -15°F.
Agricultural research utilizes the map to:
Inform decisions about crop and variety selection.
Analyze climate adaptability for new varieties of crops.
Guide experimental setups based on regional temperature norms.
The updated zone map for Michigan assists researchers by providing a more accurate and detailed interpretation of temperature trends to gauge potential shifts in plant hardiness requirements.
Navigating the USDA Website and Map Tools
Efficient navigation through the USDA's online resources is essential for understanding plant hardiness across various locations. The USDA ARS website hosts robust and detailed map tools tailored for gardeners, researchers, and growers.
Accessing the Interactive GIS-Based Map
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a vital tool that leverages Geographic Information System (GIS) technology, enabling users to view detailed zones with great precision. To access this interactive GIS-based map, a broadband internet connection is recommended due to the granular level of data presented. Visitors can simply enter their zip code for localized information or navigate through the map by panning and zooming to their region of interest. This level of interactivity and detail aids users in making informed decisions on plant selection based on climatic suitability.
Understanding Map Updates and Revisions
The USDA actively refines its resources, exemplified by the 2023 map, which revisits and updates the previous editions with the latest climate data. Such revisions ensure that the map reflects current temperature trends and extreme climatic events, providing users with an up-to-date guide for their planting needs. The ARS's commitment to accuracy means that gardeners and growers can trust these revisions as they pursue planting strategies aligned with the evolving USDA guidelines.
Hardiness Zones and Climate Change
With the release of the 2023 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, evidence of climate change's impact on Michigan's planting zones has become more concrete, reflecting shifts in overall average temperatures and weather patterns.
Impact on Planting Zones and Weather Patterns
The USDA's map updates reveal that planting zones are shifting northward as global climate change drives up overall average temperatures. Previously colder regions now support plant life typical of warmer zones. Michigan, as highlighted by the Michigan Gardener, has experienced modifications in its planting zones, which are determined by evaluating 30-year averages of the lowest annual winter temperatures. These adjustments have implications for biodiversity, native ecosystems, and the seasons themselves.
Detroit's Zone: Remains unchanged at 6b, with an extreme minimum winter temperature of minus 5 degrees to zero, yet the zone itself has expanded north according to Freep.com.
Climate Data Utilized: Incorporates over 13,000 weather station records to finalize the zone boundaries.
Adaptation of Agricultural Practices to Climate Change
Farmers and gardeners must now adapt to altered weather patterns due to climate change. The adaptation involves selecting crop varieties suitable for the new temperature regimes and adjusting planting schedules. These practices reduce the risk of crop failure due to unseasonal weather events—a pressing concern as extremes in weather become more common.
Risk Management: Involves more dynamic and flexible planning to accommodate unexpected weather-related challenges.
Crop Selection: Embraces plants that can thrive in warmer, longer growing seasons, which Michigan might now experience.
As detailed by USDA ARS, understanding and integrating these updates into local agricultural practices is crucial for sustaining crop yields in a changing climate. Changes in the USDA's map act as a guidepost for anticipating the needs of the future, aligning with the sentiment of gardeners reported by NPR, recognizing the shifts in planting zones as an affirmation of the palpable changes they have observed in their gardens.
Scientific and Technological Advances
In the realm of plant hardiness and agricultural planning, profound leaps in scientific understanding and mapping technologies have resulted in more precise and useful tools for gardeners, farmers, and researchers alike.
Contribution of Research Institutions
Oregon State University (OSU) and partnerships with entities like PRISM Climate Group have proved to be instrumental in elevating the granularity and accuracy of the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) plant hardiness zone map. These institutions utilize comprehensive research models grounded in robust climate data to substantiate the agricultural guidelines that are fundamental for national agricultural stakeholders.
Advancements in Mapping Techniques
Mapping methods have evolved, thanks to agricultural research and innovation in geographical information systems. The USDA's Agricultural Research Service (ARS) has deployed enhanced mapping techniques that integrate extensive location-specific temperature data. Such advancements have refined the Plant Hardiness Zone Map, revealing subtle climate shifts and enabling more precise zone delineation.
Implications for Policy and Insurance
The recent updates to the USDA Hardiness Zones in Michigan have significant ramifications for policy making and insurance coverage. These changes reflect shifts in climate patterns and will be used to inform decisions impacting the agricultural sector at both the national and regional levels.
Policy Development in Response to Zone Changes
Policy makers are now incorporating the updated USDA plant hardiness zone map into their strategic planning to reflect the changing climate in Michigan. This data layer serves as a crucial tool for informing agricultural policies, as it can lead to adjustments in recommendations for crop planting and resource allocation. Changes in the plant hardiness zones could compel the U.S. Department of Agriculture to modify growing guidelines, which in turn impact national agricultural policies and gardeners' practices.
Crop Insurance and Hardiness Zones
The redefined hardiness zones are instrumental in shaping crop insurance standards. They affect which crops are insured and how risk is assessed. Insurance providers, backed by the U.S. Department of Agriculture, may need to update their policies to accommodate the likelihood of successful crop yields in newly classified areas. If a region becomes warmer and supports more delicate crops, insurers may adjust coverage options and premiums to reflect this new data. Coordination on a regional level is essential to ensure that the agricultural community is well informed and protected under these evolving conditions.
Educational Resources and Support
Educational resources and workshops are readily available to help Michigan gardeners and agricultural professionals understand USDA Hardiness Zones. These resources are designed to facilitate learning and provide hands-on experience with effectively utilizing the zone information for successful planting and gardening.
Availability of Learning Materials
The USDA provides comprehensive learning materials that cater to a range of expertise levels, from amateur gardeners to commercial growers. This includes an interactive Plant Hardiness Zone Map, which offers detailed insight into the various zones within Michigan. Additionally, state-specific ebooks and online guides are accessible, presenting crucial information that aligns with the local climate and planting conditions.
Outreach Programs and Workshops
Outreach programs are essential in disseminating knowledge and practical skills regarding hardiness zones. Educational institutions and state organizations frequently host workshops and seminars that focus on how gardeners can adapt to Michigan's climate zones. These programs often include expert-led sessions, providing the latest strategies for plant selection based on location-specific hardiness data.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones is crucial for gardeners in Michigan as it guides them in selecting plants that can survive the winter in their specific location.
How can I determine my exact gardening zone in Michigan?
A gardener can determine their exact gardening zone in Michigan by consulting the 2023 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, which provides detailed information on 10-degree F zones and 5-degree F half zones.
Where can I find the updated planting zone map for Michigan?
The latest planting zone map for Michigan is accessible online. For an interactive version of the map that delineates the zones throughout the state, one can visit Plantmaps.
What is the range of hardiness zones found within Michigan?
Michigan's climate encompasses a range of USDA Hardiness Zones from 3a to 6b, reflecting the varied winter temperature extremes across the state.
How do the USDA Hardiness Zones vary across Michigan?
The USDA Hardiness Zones in Michigan vary from the colder zones in the Upper Peninsula to the warmer zones found along the southern border. Each zone represents the average annual extreme minimum temperature range for the area.
Which hardiness zone does Ann Arbor, Michigan fall under?
Ann Arbor, Michigan is generally classified in the USDA Hardiness Zone 6a, indicating its winter temperature range and suitable plant selection.
How do I interpret Zone 5 when gardening in Michigan?
Interpreting Zone 5 for gardening in Michigan involves considering the average annual extreme minimum temperatures, which fall between -20°F to -10°F, and selecting plants accordingly that can withstand these conditions.