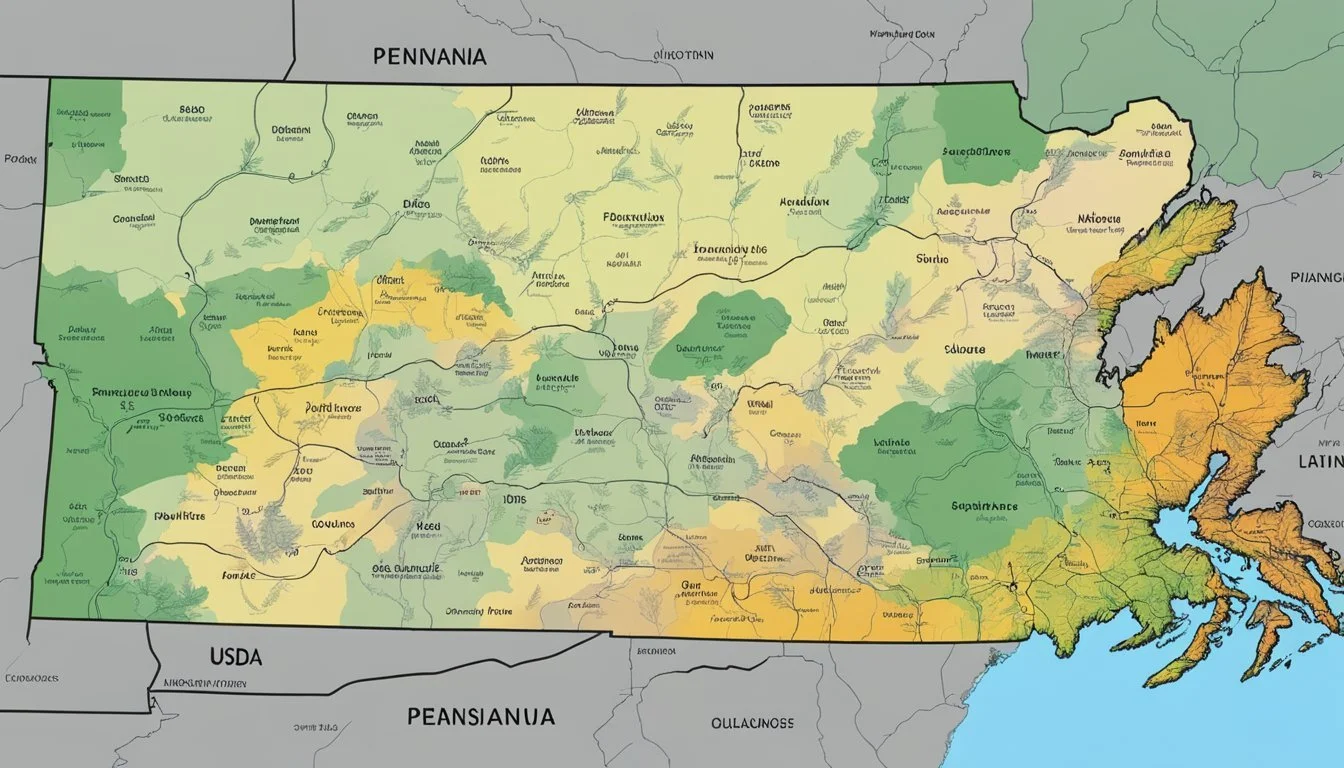
USDA Hardiness Zones in Pennsylvania
Understanding Climate and Planting Guides
Understanding the USDA Hardiness Zones is essential for gardeners and growers in Pennsylvania. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map serves as a valuable guide, indicating which perennial plants are most likely to thrive in specific locations. These zones are defined by the average annual extreme minimum winter temperature and segmented by 10-degree Fahrenheit increments. Pennsylvania encompasses a range of zones from 5a up to a small section of 8a, which suggests a wide variety of plants can be cultivated successfully across the state's diverse climates.
The map's precision allows individuals to make informed decisions about their plant selections, ensuring that the vegetation they choose is suited to withstand local winter conditions. In Pennsylvania, the variation in hardiness zones reflects the state's varied topography and climatic conditions, from the Appalachian Plateau to the Atlantic Coastal Plain. Gardeners can refer to the detailed boundaries of these zones to select plants that have the best chance for year-over-year survival and create landscapes tailored to their region's specific environment.
The 2023 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map itself has been crafted with considerable detail, incorporating modern satellite and meteorological data to offer a more accurate representation of growing climates. This information is particularly useful for the state's agricultural community, which can utilize the zone distinctions to maximize crop resilience and productivity. By aligning planting strategies with the researched zone data, Pennsylvania's growers and gardeners can cultivate their gardens and fields with greater confidence, knowing they are working in concert with the climatic tendencies of their region.
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map directs gardeners and growers in determining the suitability of perennial plants for their locales, which hinges on site-specific extreme minimum temperatures.
The USDA Hardiness Zone System
The USDA Hardiness Zone System is a geographically designated guide developed by the U.S. Department of Agriculture to categorize regions based on their climatic conditions, particularly the average annual extreme minimum temperature. The map divides North America into 13 primary zones, with each zone representing a 10-degree Fahrenheit difference in average annual minimum temperature. Additionally, these zones are further split into 'a' and 'b' segments to represent a 5-degree Fahrenheit difference within the same zone.
Interpreting the Zone Classifications
When interpreting hardiness zones, it's crucial to understand that each zone reflects the region's extreme minimum temperature range. For instance, if a perennial is rated for Zone 5, this indicates it should withstand a minimum temperature of -20 to -10 degrees Fahrenheit. Conversely, Zone 9 plants can typically survive in conditions where the temperature does not fall below 20 to 30 degrees Fahrenheit. Gardeners can utilize the Plant Hardiness Zone Map to make informed decisions about which plants have the best chance of thriving in their specific location.
The Pennsylvania Plant Hardiness Zone Map
The Pennsylvania Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a crucial resource for gardeners and agricultural professionals, detailing the regions in which various plants are most likely to thrive based on climatic conditions.
Overview of Zones in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania is mapped into diverse USDA Hardiness Zones that range from Zone 5a to 7b, with a small section of Zone 8a. This illustrates the minimum winter temperatures experienced across the state: Zone 5a represents areas where the temperature falls between -20°F to -15°F, while Zone 8a indicates regions with milder winter temperatures of 10°F to 15°F.
Regional Variations Across the State
The state of Pennsylvania exhibits considerable regional variations due to its topography and size. Erie, for instance, located in the northwestern part of the state, is classified as Zone 6b, experiencing winter temperatures between -5°F to 0°F. The map's detailed zip code search function allows users to find specific hardiness zones tailored to their exact location.
Using the Map for Gardening and Agriculture
Gardeners and farmers use the map to determine which plants are best suited for their region's hardiness zones. It helps in assessing the average annual extreme minimum winter temperature and allows for informed decisions when selecting crops and ornamentals. The USDA has introduced updates to the map, reflecting changes such as half zone increments, which provide a more nuanced take on microclimates within the state.
Climate Data and Zone Designations
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map employs historical climate data to guide gardeners and agricultural stakeholders in selecting plants suited for their local conditions. These designations serve as critical tools for understanding growing potential and preparing for the impacts of climate change.
Utilizing Historical Climate Data
The Agricultural Research Service (ARS) utilizes climate data from 1991 to 2020 to delineate Plant Hardiness Zones. Zones are marked by 10-degree F increments and refined by 5-degree F half zones to provide a precise framework for plant selection. The PRISM Climate Group, led by Oregon State University, plays a pivotal role in analyzing this temperature data, ensuring that the map reflects the average annual extreme minimum winter temperature.
Impacts of Climate Change on Hardiness Zones
Climate change introduces significant variables in hardiness zone designations. Observations indicate shifts in 10-degree F zones, hinting at tangible manifestations of global climate change. These alterations are crucial for the Agricultural Research Service to consider when issuing updates to the map, reflecting the dynamic nature of low temperature extremes, which are pivotal to plant survival and selection.
Contributions of Weather Stations and GIS Technology
The accuracy of Hardiness Zone Maps relies on the aggregated data from numerous weather stations and the sophisticated processing capabilities of GIS (Geographic Information System) technology. The GIS framework, heavily utilized by ARS researchers, facilitates the distinction of zones and half zones by meticulously analyzing localized low temperature data. This spatial analysis is essential for providing up-to-date information to account for shifts due to global climate change between historical periods such as 1976-2005 and the present-day benchmarks.
Practical Applications for Hardiness Zones
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones is crucial for selecting plants that are suitable for the local climate in Pennsylvania. These zones guide gardeners and agricultural professionals to make informed decisions about planting and crop insurance.
Gardening and Choosing the Right Plants
Pennsylvania gardeners rely on the interactive USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map to determine which plants are most likely to thrive in their specific location. The zones reflect the average annual extreme minimum temperatures, enabling gardeners to:
Select plants: Knowing the zone helps in choosing plants that can survive the winter.
Plan gardens: Residents can design their gardens based on the survival rates of plants in their zone.
Manage risks: Gardeners can anticipate potential issues with exotic weeds and pests that may affect plant resilience.
Agricultural Planning and Crop Insurance
Hardiness zones are vital in agricultural planning and implementing crop insurance standards. The zone map serves the USDA Risk Management Agency and other entities as a tool to:
Inform crop selection: Farmers select crops compatible with their zone's temperature thresholds.
Determine planting dates: Optimal planting windows are established, minimizing risks from late or early frosts.
Establish insurance parameters: Crop insurance terms are based on typical survival and yield rates within these zones.
Nurseries and agriculture researchers utilize hardiness zone information to advise on best practices, anticipate the impact of climate on plants, and study the relationship between plant survival and temperature extremes. These applications contribute to more sustainable gardening and farming practices in Pennsylvania.
Additional Resources and Tools
Gardeners and researchers seeking detailed information on plant hardiness zones can turn to a variety of online resources and tools. These resources provide high-resolution maps, horticultural guidance, and educational support tailored to American gardeners.
Accessing the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map Online
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map serves as the cornerstone for gardeners to identify which plants are most likely to thrive in a specific location. Available online, one can effortlessly search by ZIP code or use the interactive map to zoom into their state for more detail. The online map offers enhanced resolution and seamless navigation, essential for precise horticultural planning and research.
Enhanced Tools for Gardeners and Researchers
For those requiring more sophisticated functionality, interactive tools such as the Pennsylvania Interactive USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map allow users to view changes in zones over time. This tool features a search box for quick access and also provides various overlay options for deeper insights into the state map. Such enhanced tools help gardeners and researchers study climate trends critical to horticulture.
Educational Materials and Support
In addition to maps, the USDA and other government sites offer a range of educational materials including ebooks, videos, and articles that help gardeners understand the complexity of plant hardiness zones. These materials cover a variety of topics, from the basics of plant hardiness zones to advanced horticultural techniques, offering valuable support to American gardeners.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones is vital for gardeners in Pennsylvania, providing information on which plants are most likely to thrive in their specific region.
Which USDA Hardiness Zones are included in the state of Pennsylvania?
Pennsylvania encompasses multiple USDA Hardiness Zones ranging from 5a to 7b Pennsylvania Interactive USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map.
How can I find out my specific planting zone using my ZIP code in Pennsylvania?
Individuals can use the USDA's online tool by entering their ZIP code to determine their specific planting zone 2023 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map.
What are the differences between USDA Hardiness Zones 6a and 6b in Pennsylvania?
Zone 6a experiences minimum temperatures between -10°F to -5°F, whereas Zone 6b withstands slightly warmer extremes, from -5°F to 0°F.
Can you provide a list of plants suitable for Zone 6b in Pennsylvania?
Plant suitability lists for Zone 6b in Pennsylvania are available on gardening websites and include species that can tolerate winter temperatures as low as -5°F.
Where can I access a detailed map of Pennsylvania's USDA Hardiness Zones?
A detailed map of the state's hardiness zones is accessible on various websites, including the USDA's plant hardiness site USDA Hardiness Zone Map And Pennsylvania Planting Zones | Gardening Knowhow.
What are some considerations for gardening in Philadelphia’s USDA Hardiness Zone?
Gardeners in Philadelphia should select plants suitable for Zone 7a and consider the urban heat island effect, which may slightly raise minimum temperature averages.