USDA Hardiness Zones in Virginia
A Guide to Gardening and Planting
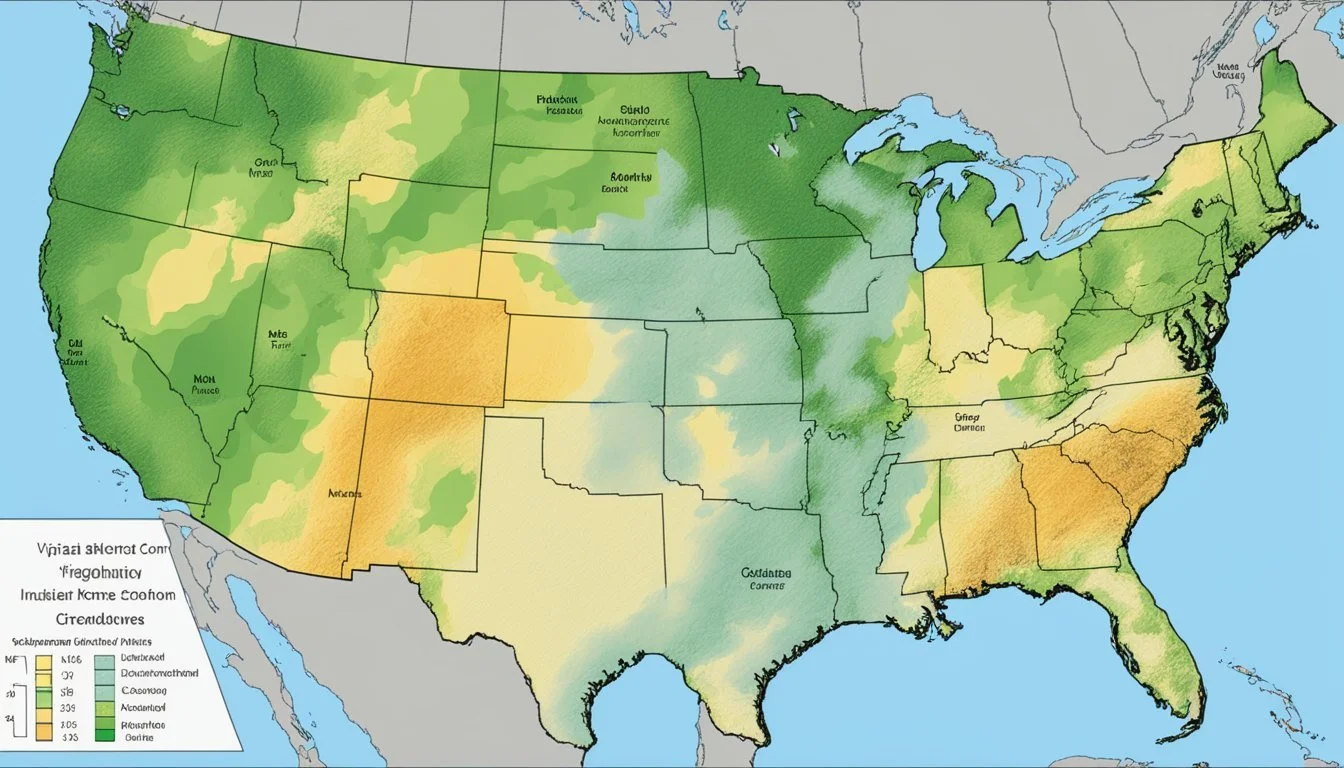
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is the primary reference tool for gardeners and agricultural professionals, delineating regions where various perennial plants are most likely to thrive. Crafted by the United States Department of Agriculture, this map categorizes areas based on their average annual extreme minimum temperatures. In Virginia, the map reveals a diversity of climates, capturing the unique agricultural growing conditions across the state.
Virginia's range of hardiness zones include areas classified from 5b, where winter temperatures can descend to -15°F, through to 8b on the eastern shore, which experiences milder winters. This range of zones signifies the vast differences in climate and, consequently, planting and growing possibilities within the state. Understanding these zones is crucial for successful gardening and farming, enabling the selection of appropriate plants that match each area's environmental conditions.
The USDA has updated the Plant Hardiness Zone Map to reflect more detailed and accurate climatic data. Updated for the first time since 2012, this tool continues to be a vital guide in making informed decisions about plant selection, offering clearer insights into what can be expected in terms of plant survival and growth throughout the various regions of Virginia.
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones
United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Hardiness Zones serve as a crucial guide for gardeners and growers to identify the most suitable plants for a location. These zones pinpoint areas based on their average annual extreme minimum temperatures, thus aiding in plant selection and cultivation strategies.
Definition of Plant Hardiness Zones
Plant Hardiness Zones are classifications used to signify the ability of plants to withstand the climate of an area, especially the cold temperatures. The USDA Hardiness Zone Map divides North America into zones based on 10-degree Fahrenheit increments, with each zone further split into "a" and "b" segments for a 5-degree resolution.
History and Development
The concept of hardiness zones originated in the 2012 edition of the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map and has undergone refinement over time. This tool has incorporated GIS (Geographic Information Systems) technology to offer increased accuracy. The map utilizes extensive climate data from numerous weather stations and is considered the national standard for evaluating plant survivability across different regions.
Interpreting the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
To effectively utilize the Hardiness Zone Map, one must understand that the map displays zones illustrating average annual extreme minimum temperatures. For example, a plant hardiness zone labeled as "5a" indicates the region may reach low temperatures of -20°F to -15°F. Map downloads are available for individuals or organizations that require high-resolution maps for detailed planning and analysis.
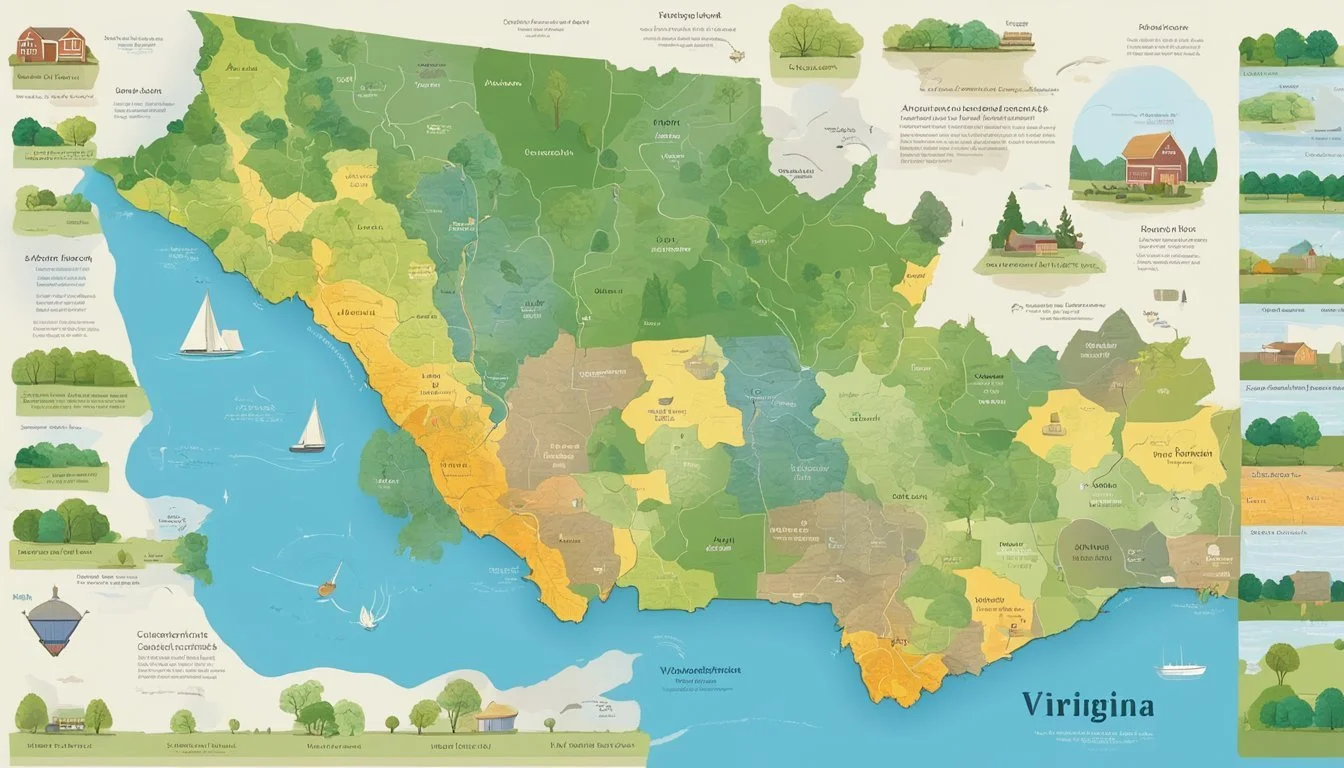
Virginia's Climatic Conditions
Virginia exhibits diverse climatic conditions that are significantly influenced by the Atlantic Ocean and regional topographical factors. These elements are vital in understanding the winter temperatures across the state.
Influence of Atlantic and Regional Factors
Proximity to the Atlantic Ocean and geographic nuances distinctly affect Virginia's climate. The Atlantic contributes to a level of humidity that can moderate winter temperatures along the coast. In contrast, the Appalachian Mountains and the Piedmont region play roles in altering wind patterns and precipitation distribution. Such regional factors can influence temperature variations that lead to the establishment of different hardiness zones within the state.
Assessing Winter Temperatures in Virginia
Evaluating winter temperatures in Virginia is crucial for agricultural success and plant survival. The average annual extreme minimum winter temperature is a benchmark used to classify the USDA Plant Hardiness Zones, which dictate the types of plants likely to thrive in a locale. For instance, Virginia's hardiness zones can range from 5b, where the extreme minimum temperatures dip between -15°F to -10°F, to 8a, with minimums from 10°F to 15°F. These temperatures indicate the resilience required by plant species during the coldest part of winter in Virginia.
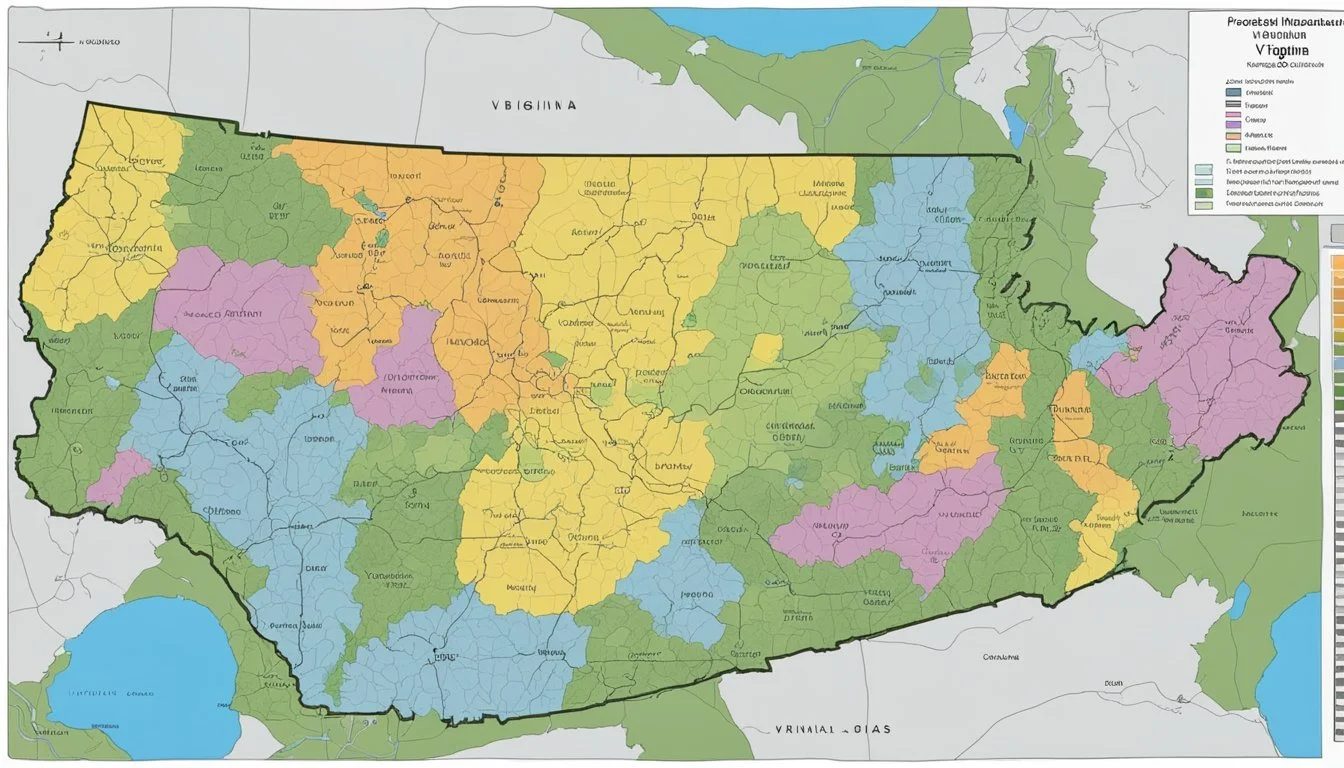
Hardiness Zones in Virginia
Virginia encompasses a diverse range of USDA Hardiness Zones, which are crucial for plant survival and growth. Understanding these zones helps gardeners and growers make informed decisions about planting and landscape designs.
Zone Distribution and Variation
Virginia's Hardiness Zones range from 5b in the northern tip to 8a and 8b on the Atlantic shore. The zones are defined by 10-degree F zones and finer 5-degree F half zones. This variation occurs due to Virginia's wide range of geographical features, from the Appalachian mountains to the Atlantic coastal areas, influencing the climate and thus the categorization of hardiness zones.
Importance for Gardeners and Growers
For individuals interested in cultivating a garden or working on their landscape, the knowledge of these zones is essential. Each zone guides gardeners and growers on what plants are more likely to thrive in their location. This information is crucial for the successful establishment and maintenance of gardens and plants suited to Virginia's climate variations.
Hardiness Zones by Virginia Cities
Below is a brief list illustrating the hardiness zones for selected cities across Virginia:
Abingdon: Zone 6b
Alexandria: Zone 7a
Arlington: Zone 7a
Blacksburg: Zone 6a
Charlottesville: Zone 7a
Richmond: Zone 7b
Roanoke: Zone 7a
Virginia Beach: Zone 8a
This list is not exhaustive; however, it reflects the range of climates found across the state, impacting what can be grown in different cities. Gardeners and growers should refer to the 2023 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map for detailed information suitable to their specific areas.
Gardening and Landscaping in Virginia
Virginia's diverse climate offers gardeners and landscapers a wide range of environments for growing various plants. The state's USDA Hardiness Zones are vital for making informed choices about what to plant for the best chance of success.
Selecting Plants for Virginia Gardens
When choosing plants for Virginia gardens, it's important to consider the USDA Hardiness Zone of the specific area. Virginia's zones range from 5b to 8b, indicating the typical range of winter low temperatures each region can expect. Perennial plants, shrubs, and both annual and perennial flowers have distinct preferences for their ideal hardiness zone.
A gardener in Northern Virginia with typical Zone 6b conditions would select plants capable of withstanding winter lows down to -5°F. Conversely, in the warmer Zone 8a conditions of the eastern shore, gardeners have a wider array of plants from which to choose, as their selections can withstand only slight freezing.
It is also critical to consider the specific soil type and elevation, as these can affect the microclimates within a single garden. Some areas might experience more winter sun exposure, affecting how certain plants might thrive over others.
Zone 5b
Winter Lows: -15°F to -10°F
Suggested Plants: Hardy perennials, cold-tolerant shrubs
Zone 6a
Winter Lows: -10°F to -5°F
Suggested Plants: Broad range of perennials and many shrubs
Zone 6b
Winter Lows: -5°F to 0°F
Suggested Plants: More tender perennials and ornamental trees
Zone 7a
Winter Lows: 0°F to 5°F
Suggested Plants: Including heat-loving plants and some tropicals
Zone 8a
Winter Lows: 5°F to 10°F
Suggested Plants: Wide variety of plants including semi-tropicals
Gardening Tips for Different Hardiness Zones
Gardeners should tailor their gardening practices to the zone they are in. This means adjusting not just for plant hardiness, but also for timing of tasks such as mulching, planting, and watering.
Zone 5b: Mulch heavily to protect plants during harsh winters, and delay planting tender plants until late spring to avoid frost damage.
Zone 6a and 6b: Take advantage of a longer growing season, but remain vigilant for late spring frosts. Plants can usually be started earlier and extended into the fall.
Zone 7a: Focus on soil moisture management as winters are milder but summers can be hot and dry. This zone allows for a wide choice of plants, but the timing of care is crucial.
Zone 8a: Support plants during hotter summers with consistent watering and consider shade cloth to protect from intense sun.
By understanding the nuances of their hardiness zone, Virginia gardeners and landscapers can create beautiful and sustainable landscapes that harness the full potential of their local environment.
Advanced Considerations
When planning for gardening and agricultural endeavors in Virginia, one must account for factors beyond the general USDA Hardiness Zones. Advanced considerations take into account the specificity of local climate conditions, technological tools for assessment, and how changes in climate can shift these zones over time.
Microclimates and Local Variations
Microclimates play a pivotal role in garden planning. Local variations in elevation, soil type, and surrounding structures can cause significant deviations from broader zone designations. For instance, an urban garden may experience a heat island effect, artificially raising temperatures and humidity levels.
Impact of Climate Change on Hardiness Zones
The impact of climate change on USDA Hardiness Zones is evidenced by the updates to the maps, reflecting shifts in average minimum temperatures. These zones are changing over time, with many regions, including parts of Virginia, transitioning to warmer classifications, as seen in the recently updated USDA Hardiness Zone Map.
Using GIS and Detailed Maps for Planning
Advancements in Geographical Information Systems (GIS) facilitate the incorporation of high-resolution data layers such as soil type, elevation, and climate into garden planning. Map downloads and GIS tools provide a granular view of one's specific location, even down to the ZIP code, empowering gardeners and farmers to make informed decisions.
Tips for Consulting the Hardiness Zone Map
When consulting the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, consider the map's detail and any updates. Remember that the map offers a snapshot of average conditions — one's actual garden location may differ. Observe your local microclimate, including soil type and humidity, to better select plants suited to your area. Checking the map for the ZIP code can offer a starting point, but always investigate the specific conditions of your site.
Resources and Further Reading
For those looking to dive deeply into the specifics of plant hardiness zones particularly within Virginia, a wealth of resources and information is readily available. Gardeners and growers seeking comprehensive guides and educational tools can benefit greatly from the described resources.
Hardiness Zone Map Download Options
The 2023 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is an invaluable tool for anyone involved in horticulture or agriculture. It provides detailed information about the various zone classifications across the United States, enabling users to select appropriate perennial plants for their regions. A range of map downloads is available, including high-resolution images and interactive GIS data for precision gardening and regional assessment.
Interactive Map: An online resource for real-time exploration of hardiness zones.
Printable Maps: PDF or image files for personal and educational use.
Educational Materials and Workshops
Extension services and agricultural agencies provide comprehensive educational materials and workshops aimed at equipping individuals with the knowledge to make informed planting decisions. These workshops often cover topics such as plant selection, climate adaptation, and gardening techniques tailored to Virginia's Hardiness Zones.
Workshops: Local and state schedules for events and seminars.
Online Courses: Webinars and self-paced courses for remote learning.
By leveraging these resources, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of plant hardiness zones, enhancing their ability to successfully cultivate plants in their local environment.
Frequently Asked Questions
These frequently asked questions aim to address important aspects of USDA Hardiness Zones specific to the state of Virginia, providing vital information for gardeners and agriculturists.
What are the different USDA Hardiness Zones found within the state of Virginia?
Virginia encompasses USDA Hardiness Zones that range from 5b in the northern regions to 8a and 8b in the eastern coastal areas. The zones indicate the climate variances and are crucial for selecting appropriate plants for cultivation.
How can I determine the specific planting zone for my zip code in Virginia?
To find the specific planting zone for a Virginia zip code, utilize the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, which provides an interactive tool to search zones by ZIP code.
Where can I find a detailed climate zone map for Virginia?
A detailed climate zone map for Virginia is accessible at Virginia Interactive USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, offering a visual representation of the state's various hardiness zones.
How do the hardiness zones vary between Northern Virginia and the rest of the state?
Northern Virginia generally falls in cooler zones such as 5b and 6a, while further south, the state exhibits warmer zones, moving through 6b, 7a, and into 7b to 8b in the southeastern regions, reflecting the warmer temperatures and milder winters.
Can you provide a list of plants suitable for cultivation in Zone 8a within Virginia?
Suitable plants for cultivation in Virginia's Zone 8a include crepe myrtle, windmill palm, and camellias, as these species thrive in this zone's mild winter temperatures.
In which USDA Hardiness Zone is Fairfax, Virginia categorized?
Fairfax, Virginia, is categorized predominantly within USDA Hardiness Zone 7a, though microclimates within the area may slightly shift the zone designation.