USDA Hardiness Zones in Kentucky
Your Guide to Planting Success
Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is essential for gardeners, farmers, and researchers alike. It signifies the most crucial aspect of plant cultivation: where a plant can thrive year-round. This map is delineated into zones based on the average annual extreme minimum winter temperature, with each zone representing a 10-degree Fahrenheit difference. The specific zones are further refined into 5-degree Fahrenheit half zones to provide a more precise guide for plant compatibility.
In Kentucky, this map becomes a vital tool for the state's diverse climates and topographies. Kentucky's gardeners and agricultural professionals refer to these hardiness zones to determine which plants are most suited to their area’s conditions. The state spans several zones, showing a variation in climate profiles from one region to another, influencing what flora can be grown successfully.
The USDA’s updates to the Plant Hardiness Zone Map reflect changes in climatic conditions and offer a more accurate resource for plant hardiness information. This is not just an academic utility but a practical guide with a direct impact on the state's agriculture and gardening success. The map's use underscores the importance of recognizing and adapting to the dynamics of the national climate, ensuring that the plant hardiness zones remain an indispensable part of Kentucky's horticultural practices.
Understanding Hardiness Zones
When discussing the cultivation and survival of perennial plants in Kentucky, it's crucial to understand the concept of USDA Plant Hardiness Zones, which take into account historical climate data, notably extreme minimum temperatures.
Hardiness Zone Fundamentals
Hardiness zones, established by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA), categorize regions based on their climate, specifically the average annual extreme minimum temperature. These zones guide gardeners and farmers in determining the most appropriate plants for their location.
The 2012 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
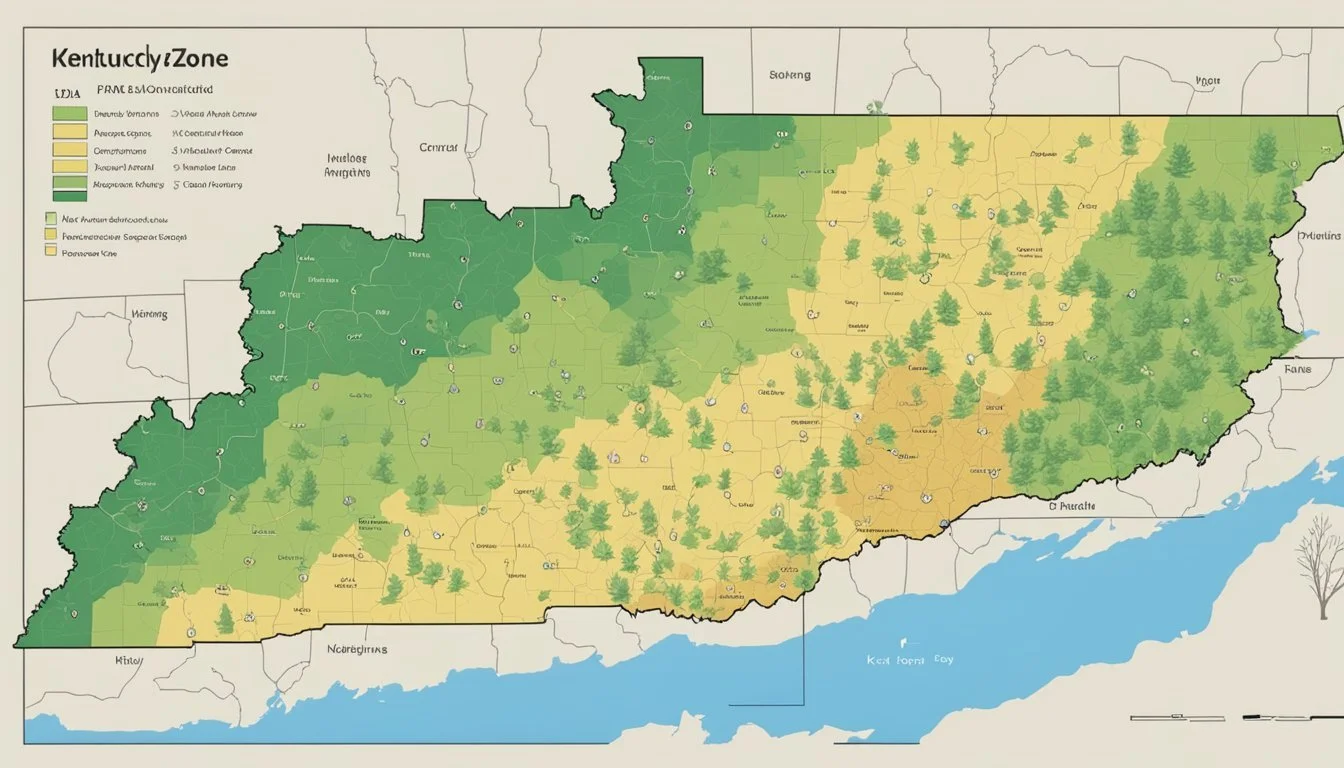
The USDA released an updated Hardiness Zone Map in 2012, which is a detailed outline reflecting modern climate patterns across the United States. Kentucky falls into several hardiness zones, indicating a range of temperature extremes from one area to another within the state.
Interpreting Zone Classifications
Each hardiness zone is clearly delineated, often in 10-degree F increments with 5-degree F half zones to provide more precision. Kentucky's zones, for instance, vary from Zone 6a to Zone 7a, signifying minimum temperature ranges such as -10°F to -5°F and 0°F to 5°F, respectively. Understanding these classifications helps predict plant performance and survival, factoring in local weather variations.
Kentucky's Climate Profile
Kentucky's climate is characterized by moderate to cool winters and warm, humid summers, with distinct variations across different regions. The state's topography and the Ohio River influence its climate, contributing to the diversity in weather patterns and precipitation.
Winter Temperature Averages
Kentucky experiences a range of winter temperatures, with colder conditions in the northern regions near Louisville and milder temperatures toward the south near the Tennessee border. Louisville observes average winter lows of 26°F (-3°C), while more southern areas like Frankfort have slightly higher average lows at 28°F (-2°C). These temperatures are consistent with Kentucky's climate zones, which fall within USDA Hardiness Zones 6a to 6b, indicating average winter lows between -10°F to 0°F.
Weather Patterns and Precipitation
The state's weather patterns are influenced by its position in the southeastern United States, thus subjecting it to both Gulf moisture and dry continental air masses. This intersection results in varied precipitation throughout the year. Kentucky's weather stations record an annual precipitation average ranging from 40 to 50 inches (1,016 to 1,270 mm). Precipitation is fairly evenly distributed throughout the year, though spring and summer typically see slightly higher amounts due to thunderstorm activity.
USDA Zone Map for Kentucky
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a critical resource for gardeners and horticulturalists in Kentucky. It provides detailed information on the various climate zones within the state, informing which plants are most likely to thrive in a particular location.
Exploring the Zone Map
The Kentucky Interactive USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map delineates distinct zones based on average annual extreme minimum temperatures. This intricate breakdown helps gardeners understand the subtle climatic variations across Kentucky and allows them to make informed planting decisions. Each zone is clearly defined, for instance, Aberdeen falls within Zone 6a, indicating an average minimum temperature range of -10°F to -5°F.
Map Accessibility and Search Features
Accessibility to the USDA zone map is enhanced by digital platforms. The 2023 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map website incorporates user-friendly tools such as a search box, where Kentuckians can enter their zip code for a quick lookup of their specific hardiness zone. The map's design facilitates easy navigation, making the search for information both efficient and precise.
Kentucky Zone Variations and Microclimates
Kentucky's topography contributes to the presence of multiple microclimates within the state. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zones of Kentucky offers a nuanced view of how these different regions affect plant hardiness zones. Variations range from Zone 6a in regions like Aberdeen to Zone 6b in Adairville, reflecting Kentucky's diverse climate conditions. This awareness of local microclimates is indispensable for the successful cultivation of a wide array of plants.
Gardening in Kentucky
Gardening in Kentucky requires an understanding of the regional USDA Hardiness Zones and local soil conditions. Accessibility to various plant species suited to this region is crucial for a thriving garden.
Choosing the Right Plants
In Kentucky, gardeners have the advantage of a diverse range of plants that can be grown, from colorful perennials to hearty vegetables. The state spans several USDA Plant Hardiness Zones, primarily Zone 6a to 6b, which influences the type of plants that will succeed. For detailed zone information, one can refer to the Kentucky Interactive USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. It is vital for gardeners to choose plants that are well-adapted to these zones to ensure garden health and productivity.
Soil and Microclimate Considerations
Kentucky's soil ranges from rich loams to heavy clays, impacting moisture retention and drainage. Gardeners must assess their local soil type and consider microclimate factors such as exposure to sun and wind, as well as humidity levels. Amending soil with organic matter can improve soil health and moisture capacity, facilitating better root growth and plant resilience.
Seasonal Planting Strategies
Gardening in Kentucky encompasses a strategic approach to seasonal planting. Vegetables such as tomatoes, peppers, and leafy greens benefit from being planted after the last frost date, taking advantage of the full growing season. Fall is ideal for planting perennials, giving them time to establish before winter. The University of Kentucky provides a comprehensive guide on planting times specific to Kentucky's zones and conditions.
Agricultural Practices in Kentucky
Agriculture in Kentucky is deeply influenced by the region's specific plant hardiness zones, with each zone playing a critical role in the selection of perennial plants for farming. Growers in the Commonwealth must consider both the climatic conditions and the latest findings from the Agricultural Research Service to ensure sustainable and profitable crop production.
Hardiness Considerations for Agriculture
In Kentucky, it is essential for farmers to be aware of the USDA Plant Hardiness Zones when selecting crops. The zones vary across the state from 6a to 7a, which indicates the average annual extreme minimum temperature. Farmers rely on these zones to determine the most suitable perennial plants that can withstand local winter conditions. For instance, certain fruit trees may only be ideal for zones with milder winters, while other plants, like bluegrass, have been traditionally hardy in Kentucky's climate.
Adapting to Changing Climate Conditions
Kentucky's farmers are continuously adapting to changing climate conditions, which include fluctuations in heat and wind patterns. This adaptation often requires consultation of updated zone maps, such as the recently released USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. These maps reflect the latest climate data and are crucial for agricultural planning. Agricultural research provides Kentucky growers with strategies to adjust planting schedules and select crop varieties more resilient to temperature variations.
Improving Crop Resilience
Improving crop resilience is a constant focus for Kentucky's agricultural practitioners. They incorporate findings from the Agricultural Research Service to enhance the robustness of their yields against unexpected weather events. Methods include using crop covers to protect against early frosts, planting windbreaks to reduce wind erosion, and choosing plant varieties bred for stronger disease and pest resistance. Such measures are vital in ensuring that agriculture in Kentucky remains productive and viable, even in the face of climatic challenges.
Hardiness Zone Updates and Data
In an effort to provide accurate guidance for gardeners and researchers, the USDA's Hardiness Zone Map has been updated to reflect recent climatic conditions, offering a detailed view of the zones with bifurcation into half zones based on the average annual extreme minimum temperature.
Evaluating the 2023 Map Updates
The latest release, the 2023 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, presents crucial updates from the previous 2012 version. These updates take into account the changes in climate patterns over the past decade, providing a more current and precise breakdown of temperature-based growing zones across Kentucky. Gardeners and growers should note the alterations in zone classifications that might affect plant survival and selection.
Historical Data: 1991 to 2020 Climate Analysis
A comprehensive analysis of the 1991 to 2020 climate data underpins the adjustments in the latest version of the map. This longitudinal study incorporates over two decades of temperature records, ensuring that the map reflects long-term temperature trends rather than year-to-year fluctuations. This historical perspective is critical for understanding the trajectory of climate change and its impact on plant hardiness zones.
Understanding Half Zones
Half zones, an integral aspect of the Hardiness Zone Map, represent 5-degree Fahrenheit increments within the larger 10-degree zones. For instance:
Zone 6a: -10°F to -5°F
Zone 6b: -5°F to 0°F
Such distinctions in half zones allow for even greater detail and precision when selecting plants for gardening and agricultural purposes, accounting for the subtle differences in climate within a general area.
Plant Survival and Hardiness
Understanding the key elements that influence plant survival is crucial for gardeners in Kentucky. The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map serves as a guide to identifying how well plants will withstand the local climate, particularly winter temperatures.
Mitigating Frost Damage
Frost can cause cellular damage to plants, leading to desiccation and even death. To safeguard plants, they must be acclimated to cold conditions gradually. Protective measures include:
Using mulch to insulate the ground
Erecting windbreaks to reduce frostbite
Applying anti-transpirants to minimize water loss
Strategies for Plant Longevity
For a plant to thrive and endure through variable seasons, it is not just about the right zone but also about understanding the local microclimate. Strategies to enhance plant longevity are anchored in:
Selecting species adapted to Kentucky's Zone 6a to Zone 7b
Recognizing the importance of light, heat, and humidity levels
Studying Regional Plant Survival Rates
Gardeners can evaluate regional plant survival rates by examining Kentucky's hardiness zones. These rates are greatly influenced by:
Winter temperatures, dictating the survival of many perennial species
Snow coverage, which can insulate against severe cold
Wind intensity, which can exacerbate freeze damage
By understanding these dynamics, one gains a deeper insight into the resilience of local flora.
Additional Resources
Gardeners and horticulturists seeking to expand their knowledge and support network can find a variety of valuable resources related to USDA Hardiness Zones in Kentucky. The following sections highlight carefully selected materials, community groups, and services that provide insightful information and assistance tailored to gardening within the specific climate zones of the state.
Educational Material and Research
For those looking to deepen their understanding, the USDA Hardiness Zone Finder offers extensive guidance on selecting appropriate plants for different regions. Educational materials from reputable sources, including peer-reviewed research and detailed zone maps, can be accessed via institutions such as the University of Kentucky's Department of Horticulture, offering insights on plant survival rates across various climate conditions.
Local Gardening Communities
Local gardening communities can provide personalized advice and support. Gardeners in Kentucky might engage with groups through social media platforms or in-person meetings, sharing experiences and knowledge specific to the USDA Hardiness Zones found within the state. They often organize events and plant swaps that can be very useful for both novice and experienced horticultural enthusiasts.
Government and Extension Services
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a fundamental resource provided by government services to assist gardeners in making informed planting decisions. Additionally, the Cooperative Extension Service, guided by university research, delivers educational programs and resources tailored to Kentucky's climate challenges. These services are invaluable for those seeking reliable information on plant hardiness and zone-specific gardening practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones is crucial for successful gardening in Kentucky. This section addresses common queries related to planting zones specific to the state.
How can I determine my specific planting zone using my ZIP code in Kentucky?
Kentuckians can easily identify their planting zones by entering their ZIP code into the USDA Hardiness Zone Finder. This tool provides local zone information essential for selecting appropriate plants.
What are the variations in planting zones across different regions of Kentucky?
Kentucky features a range of climate zones due to its diverse geography. Zones typically progress from cooler Zone 6a in the eastern mountains to warmer Zone 7a in the southwestern regions.
Which USDA hardiness zone does Louisville, KY fall under for gardening purposes?
Louisville, KY is generally classified within USDA Hardiness Zone 6b. This zoning dictates the selection of plants suitable for the area's climate.
Is there a detailed climate zone map available for Kentucky gardeners?
Yes, detailed climate zone maps tailored for Kentucky gardeners can be obtained, illustrating the variations in zones throughout the state.
In which USDA hardiness zone is Lexington, KY categorized for planting and horticulture?
Lexington, KY falls into USDA Hardiness Zone 6b, influencing plant selection and gardening strategies appropriate for its specific climate conditions.
How do Kentucky's varied climates impact the USDA hardiness zones throughout the state?
The varied climates across Kentucky, from the humid eastern mountains to the temperate central plains, establish a mosaic of hardiness zones. This diversity impacts gardening, as plant hardiness can vary even within short distances.