USDA Hardiness Zones in Louisiana
A Guide to Planting Success
Understanding the USDA Hardiness Zones is essential for gardeners and agriculturalists in Louisiana. These zones are a standard for assessing the most suitable types of perennial plants that can thrive in specific locations. The zones are determined by the average annual extreme minimum winter temperatures, segmenting the region into areas that share similar growing climates. This categorization allows for more informed decisions when selecting plants that have the best chance for success in a given area.
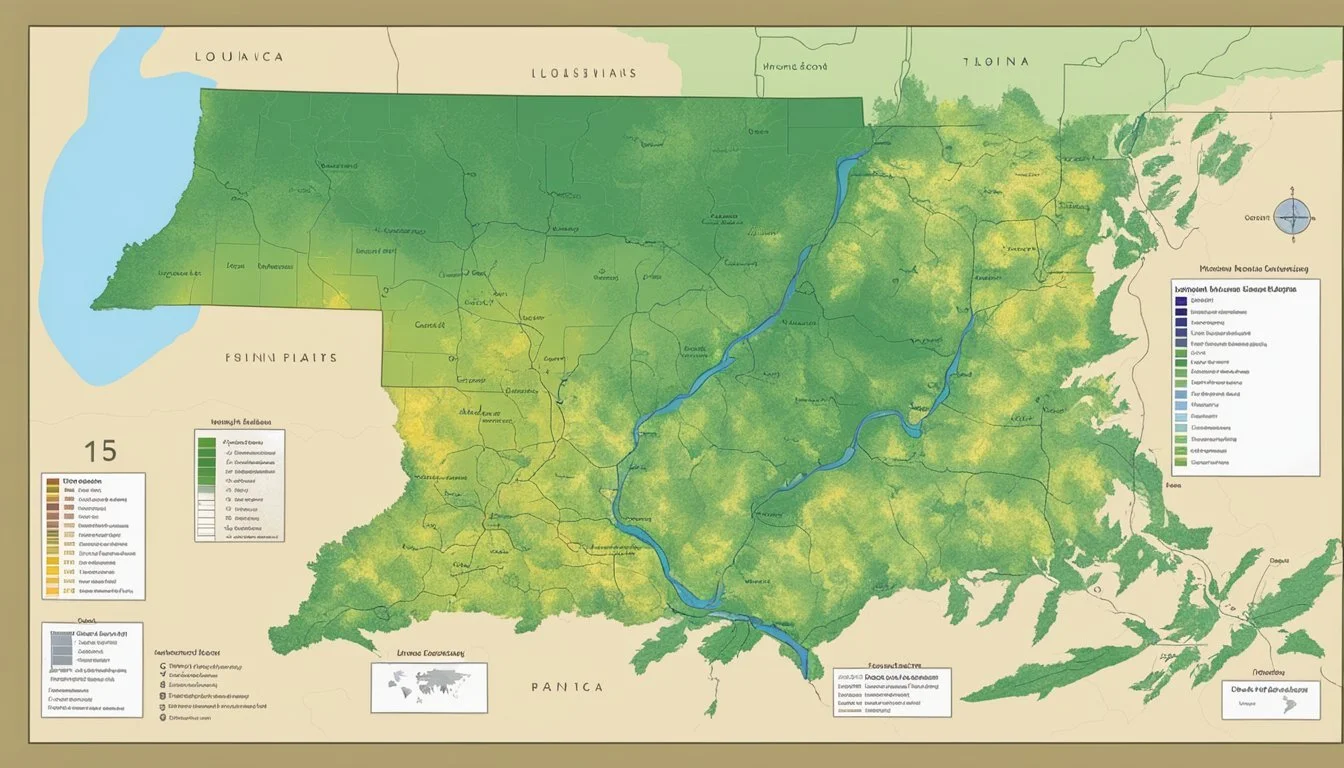
In Louisiana, the climate can vary significantly from the northern reaches to the coastal south, affecting the hardiness zones throughout the state. This geographical diversity requires a nuanced approach to planting and cultivating. By referring to the Louisiana Interactive USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, residents can determine which plants are most likely to endure and prosper in their particular locale.
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones
The USDA Hardiness Zone Map is an essential tool for gardeners and growers to identify which plants are most suited to their locale based on climatic conditions, specifically the average annual extreme minimum winter temperatures.
Hardiness Zones Explained
USDA Hardiness Zones are geographic areas defined to encompass a certain range of climatic conditions relevant to plant growth and survival. The standard by which these zones are measured is the average annual extreme minimum winter temperature. The zones range from 1a (the coldest) to 13b (the warmest), each zone being a 10-degree Fahrenheit band which is then subdivided into "a" (warmer) and "b" (colder) subzones, reflecting 5-degree Fahrenheit differences within each zone.
Significance of USDA Hardiness Zones
Understanding USDA Hardiness Zones is crucial for successful gardening and agriculture. These zones guide growers in selecting plants that will survive their region's lowest temperatures. For instance, in Louisiana, hardiness zones can range from 6a to 10b, indicating a variance in the annual minimum winter temperatures that a plant must be able to withstand to thrive. By using the USDA Zone Map, growers ensure their plant selections are well-adapted to local weather extremes, significantly impacting the vitality and productivity of their gardens and crops.
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map serves as an essential tool for gardeners and growers to determine the most suitable plants for their geographical location. It utilizes temperature zones based on average annual extreme minimum temperatures.
Development of the Plant Hardiness Zone Map
The development of the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map was spearheaded by the U.S. Department of Agriculture. It provides a valuable resource for understanding regional climate variances. These variances are encapsulated in 10-degree F zones and finer half zones, ensuring a detailed framework for plant sustainability assessment.
How to Read the USDA Hardiness Zone Map
To read the USDA Hardiness Zone Map effectively, one must identify their location on the map and observe the corresponding color-coded zone. Each zone reflects a range of temperatures, with full zones indicating a 10-degree Fahrenheit difference and half zones depicting a 5-degree Fahrenheit discrepancy. These temperature zones are crucial for making informed decisions on plant selection.
Hardiness Zones in Louisiana
Louisiana's diverse climate necessitates a detailed understanding of its USDA Hardiness Zones to ensure successful gardening and agricultural practices across the state.
Overview of Louisiana's Climate
Louisiana experiences a humid subtropical climate, characterized by hot summers and mild winters. It's imperative for gardeners to be aware of the specific climate conditions associated with their regions in order to select plants that will flourish.
Identifying Louisiana's Hardiness Zones
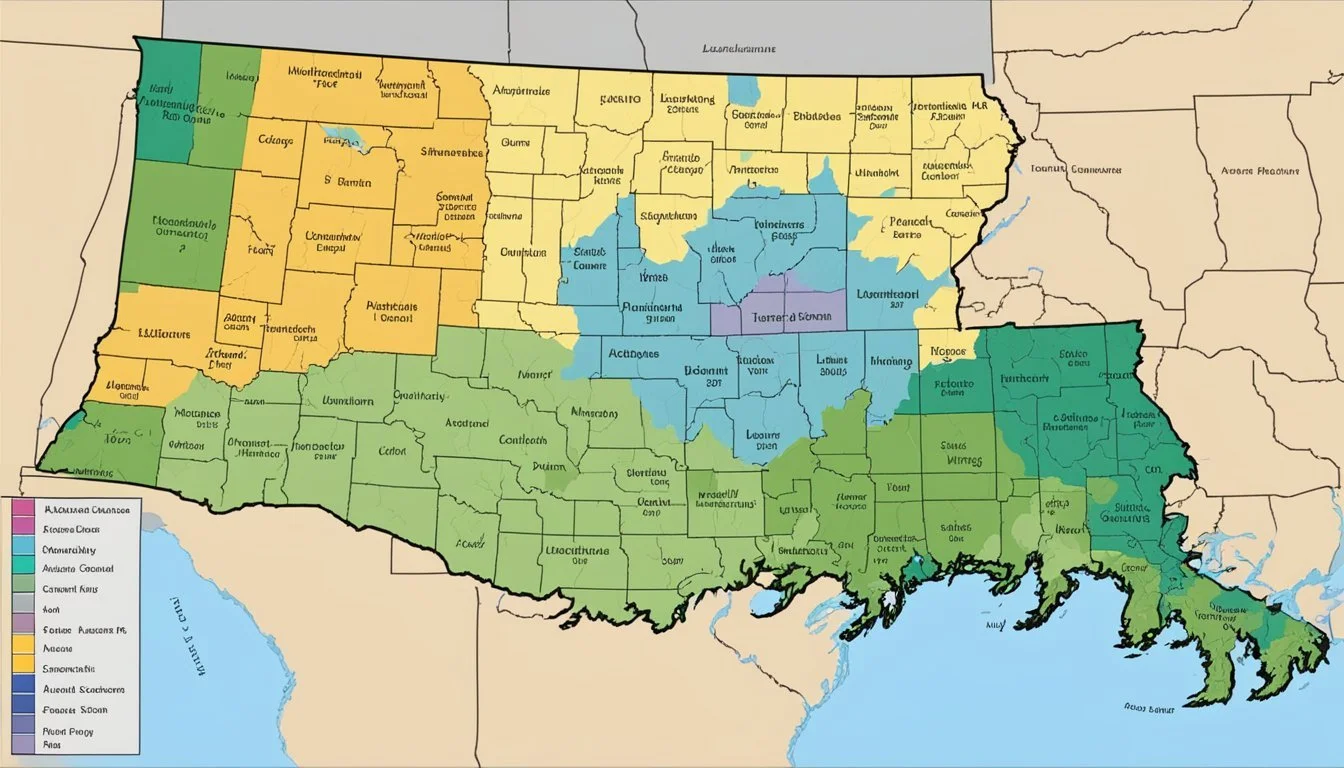
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a vital tool for gardeners and agriculturalists. In Louisiana, zones range from 8b, with temperature ranges of 15°F to 20°F, to 9a, which experiences minimum temperatures of 20°F to 25°F. Recognizing the hardiness zone for a particular location like Baton Rouge or Ama helps in making informed planting decisions.
Distribution of Zones Across Louisiana
Across Louisiana, the hardiness zones vary. Northern cities like Ball tend to fall within zone 8b, while southern regions, including Cade and Delta, are typically classified within zone 9a. The majority of cities in Louisiana, including the state's capital, Baton Rouge, need to select plants that are compatible with these temperature ranges to ensure plant health and growth.
Planting and Gardening in Louisiana
Louisiana's diverse climate presents unique opportunities and challenges for gardeners and growers. Adapting gardening practices to the local climate, particularly the state's varying USDA Hardiness Zones, is essential for the success of perennial plants and managing cold hardiness.
Selecting Appropriate Plants for Louisiana
Selecting plants that are suitable for Louisiana's climate is critical. The state features a range of USDA Hardiness Zones from 8b to 9a, indicating the types of plants likely to thrive in each area. Gardeners should consider the average annual extreme minimum winter temperature when choosing plants, focusing on those that match the cold hardiness required for their local zone.
Examples of Suitable Perennial Plants:
Zone 8b: Gardenias, Camellias
Zone 9a: Crepe Myrtles, Hibiscus
Seasonal Planting Guidelines in Louisiana
Planting at the right time is just as important as selecting the right plant. In Louisiana, seasonal planting windows can vary depending on the hardiness zone. Gardeners should consult the USDA reevaluated planting zones map to determine the best planting times for their area.
Spring Planting:
After the last frost dates, typically from late February to April.
Fall Planting:
Preferable for cool-season crops, usually starts in late September to October.
Managing Extreme Weather Conditions in Louisiana
Louisiana is no stranger to extreme weather, including high winds and abrupt temperature shifts. Gardeners and growers must take steps to protect their plants from these conditions.
Wind Protection:
Utilize windbreaks like fences or shrubbery to shield sensitive plants.
Cold Protection:
Use mulches, row covers, and cloches to insulate plants against sudden drops in temperature.
By following these practices, those who garden in Louisiana can enhance the survival rates and health of their plants throughout the year.
Technological Tools and Resources for Gardeners
Gardeners have access to an array of technological tools that enhance their planting strategies. By utilizing interactive, GIS-based maps and leveraging advanced technology, they can make informed decisions tailored to their regional climate conditions.
Using Interactive Maps for Gardening Assistance
Interactive GIS-based maps, such as the 2023 USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, provide gardeners with precise, zip code-specific information regarding plant hardiness zones. A broadband internet connection is often recommended to take full advantage of these interactive resources. Gardeners can easily find out which plants are most likely to thrive in their local area and plan their gardens accordingly.
Benefits of Interactive Maps for Gardeners:
Accuracy: Tailored gardening information down to the zip code level.
Usability: Easy to navigate and understand, even for those new to gardening technology.
Leveraging Technology for Accurate Planting
Technology plays a pivotal role in modern gardening practices. From national databases that catalog plant species' viability to apps that remind gardeners of planting schedules, the integration of technology into gardening ensures both novice and seasoned gardeners can approach their planting with greater precision.
Technological Advancements in Gardening:
National Databases: Provide comprehensive insights into various plant species and their growth patterns.
Gardening Apps: These send reminders for planting times and care, making the gardening process more manageable.
By employing these technological resources, gardeners can bolster their likelihood of cultivating a thriving garden that's in harmony with their regional climate conditions.
Advanced Topics in USDA Hardiness Zones
The intricacies of USDA Hardiness Zones involve rigorous research, detailed weather data analysis, and accounting for the dynamic nature of climate change. These advanced topics facilitate an informed understanding of how plant cultivation is adapted to evolving climatic conditions.
Research by the Agricultural Research Service
The Agricultural Research Service (ARS) conducts extensive research to refine the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. Their latest update to the map reflects meticulous research that takes into account regional climate variations. For instance, the inclusion of Zone 13 addresses the unique climate conditions of areas like Puerto Rico.
Analyzing Weather Data for Hardiness Zone Updates
Hardiness zones are periodically updated based on comprehensive weather data. ARS utilizes this data to adjust zone numbers, ensuring that the information aligns with current climate trends. It’s a complex process involving temperature records, frost dates, and climate anomalies that may affect survival and growth of perennial plants.
Impact of Climate Change on Hardiness Zones
Climate change has a significant impact on hardiness zones, often leading to shifts in zone demarcations. Researchers note a tendency for zones to migrate northward, indicating warmer conditions across various regions. Such changes might alter planting strategies and encourage the introduction of new plant species better suited to the changing conditions.
Regional Considerations for Growers
In Louisiana, growers must navigate a varied landscape of climates and microenvironments. The state encompasses multiple planting zones, and understanding the specific conditions of each region is crucial for successful cultivation.
Adapting to Microclimate Variations
Microclimates can significantly affect the growth of plants within the same overall zone. For instance, urban heat islands tend to have higher temperatures, which might push a location into a warmer zone. In coastal areas, humidity and salt may influence what can be grown successfully. Gardeners would do well to assess their specific location by observing environmental cues such as frost pockets or heat reflections from buildings, which may demand local adaptations in plant choices and care.
Hardiness Zones and Urban Gardening
Urban gardeners in Louisiana's cities must account for the USDA hardiness zones specific to their urban locality. In cities like New Orleans, much of the southeast has shifted into warmer zones such as 9a or 9b, according to Axios New Orleans. This subtle gradation means selection of plants should be tailored to these conditions, with an emphasis on heat-tolerant varieties. The rise of community gardens and private plantings in such zones underscores the need for local knowledge and resource sharing to maximize urban green spaces.
Frequently Asked Questions
In this section, they address common inquiries regarding the USDA Hardiness Zones specific to Louisiana. Here, one can gain insight into identifying appropriate plants for cultivation, locating up-to-date zone maps, and understanding the impact these zones have on gardening within the state.
How can I determine the USDA Hardiness Zone for my specific location in Louisiana?
To determine the USDA Hardiness Zone for a specific location in Louisiana, one can reference the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map. This map provides detailed information about the various climate zones based on the average annual extreme minimum winter temperature.
Which plants are suitable for cultivation in zones 8 and 9 within Louisiana?
In Louisiana's zones 8 and 9, plants that can tolerate warmer temperatures and mild winters are suitable. One may consider evergreens, some species of palm, and a variety of flowering shrubs that are adapted to these hardiness zones.
Where can I find an updated planting zone map for the state of Louisiana?
An updated planting zone map for Louisiana can be found on websites like Plantmaps, which often include interactive tools to assist gardeners in making informed decisions about planting.
What are the hardiness zones for various cities across Louisiana, such as Baton Rouge or New Orleans?
Cities across Louisiana fall into different hardiness zones; for example, Baton Rouge is in zone 9a, while New Orleans is also in zone 9a. These zones reflect the average minimum temperatures, which guide plant selection for each location.
How do the USDA Hardiness Zones in Louisiana influence planting and gardening activities throughout the year?
The USDA Hardiness Zones in Louisiana significantly influence planting schedules and gardening activities by dictating the species of plants that can survive and thrive throughout the year and when particular plants should be sown and harvested.
Are there any resources for finding the hardiness zone by zip code for locations in Louisiana?
Yes, resources are available to find the hardiness zone by zip code in Louisiana. The USDA provides a searchable map where one can enter a zip code to discover the corresponding hardiness zone, ensuring accurate information for gardeners and agriculturists.